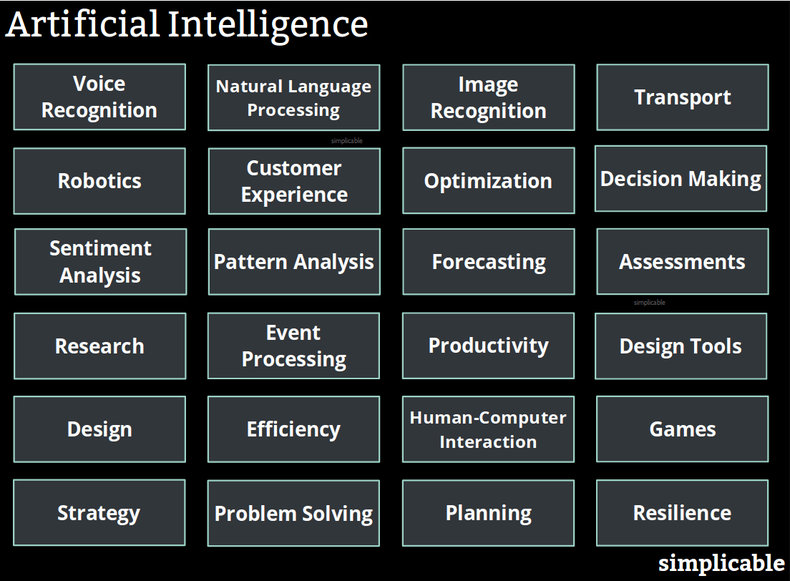
Voice Recognition
Translating voice into a natural language such as English. For example, a digital assistant who understands what you are saying.Natural Language Processing
Determining what a language such as English means. This potentially goes beyond understanding a few keywords to understand the actual meaning of grammar in different languages. For example, being able to respond to a question such as "what was that high school in Paris where the students all had terrible academic performance so they shut it down?"Image Recognition
Image recognition such as the ability to recognize people, objects, places, symbols and emotions from a real time video feed.Transport
Self-navigating vehicles and safety systems for transport.Robotics
Systems that learn to interact with the physical world such as a robot that can accurately sort recycling materials at high speed.Customer Experience
Customer experience such as a media platform that recommends songs based on the properties of music itself as opposed to simple correlations between your viewing history and those of other users.Optimization
Systems that can learn from diverse experiences to optimize things in millions of unique situations. For example, an digital advertising engine that can learn about the needs and interests of a billion consumers at the same time and treat each as an individual.Decision Making
Decision making such as a space probe that can make its own survival decisions in a harsh environment such as an alien planet.Sentiment Analysis
Understanding what people want. For example, a vehicle that pops the trunk when it sees you approaching with heavy bags of groceries.Pattern Analysis
Machine learning is mostly based on statistics and building probability models for different situations. As such, artificial intelligence is excellent at making guesses about what might happen. For example, AI might be used to find patterns in stock trades that can be exploited for gain.Forecasting
Forecasting the future based on a large number of factors such as a weather forecast based on millions of sensor readings.Assessments
Artificial intelligence can be used in ways that people commonly perceive as unfair. For example, deciding you are a high credit risk based on factors unrelated to your financial history such as your friends or hobbies. Societies may decide to govern the use of artificial intelligence to prevent it from harming quality of life by systematizing the human experience according to cold logic. Artificial intelligence opens up a large number of issues of technology ethics as an AI is often autonomous as it learns its own behaviors. This can lead to situations such as machine biases.Research
Artificial intelligence can find complex patterns using techniques that are similar to data dredging. If you look too hard for patterns you often find patterns that are meaningless. For example, an artificial intelligence might discover that people who eat strawberry toast are more likely to have headaches. This may be a meaningless pattern or it may have meaning. As such, artificial intelligence can be used as a starting point for research with the recognition that randomly discovered patterns are often meaningless.Event Processing
Discovering the meaning of a large number of events. For example, a network device fails in a data center causing 22,000 alarms a second from thousands of devices. Artificial intelligence could be used to determine the root cause of the alarms to quickly fix the problem.Productivity
Productivity such as a software tool that quickly adapts to the behavior of the user. For example, a complex graphics design tool that quickly adapts to your work patterns and preferences to be more pleasing and useful.Design Tools
Tools that allow you to design things beyond your knowledge. For example, a game-like environment that allows users who have no knowledge of architecture to architect buildings. Such a game may score your results such that you are continually becoming a better architect as you work. The game may place constraints such that users can only produce designs that are architecturally sound.Design
An artificial intelligence that fully automates a design. For example, AI that creates an algorithm without the aid of a software developer.Efficiency
Getting more output for a unit of input. For example, an artificial intelligence that waters plants in a greenhouse by learning how different types of plants respond to water in different conditions and stages of their lifecycle.Human-Computer Interaction
Software that is able to communicate or socialize with people in a natural way given context such as language and culture. For example, a digital personal assistant with personality.Games
Characters and environments in games that learn and self-improve. For example, a character who learns to tell good jokes.Strategy
Developing plans to achieve goals given constraints and competition. For example, an artificial intelligence that develops a playbook for a sport based on the strengths and weaknesses of an opponent in a given situation.Problem Solving
Problem solving such as a diagnosis tool that can determine why an aircraft engine is vibrating based on learning from millions of flight hours.Planning
Planning such as a tool that develops project estimates based on machine learning from thousands of projects.Resilience
Systems that improve the resilience of a community or organization to stresses. For example, a system that gives some advanced warning of earthquakes including an estimate of impact to each area. This can be used to warn people and automatically secure things such as a kitchen range, gas valve or an elevator.| Overview: Artificial Intelligence Examples | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A class of software that can learn and self-improve. | |
Related Concepts | ||