Information Security Risk
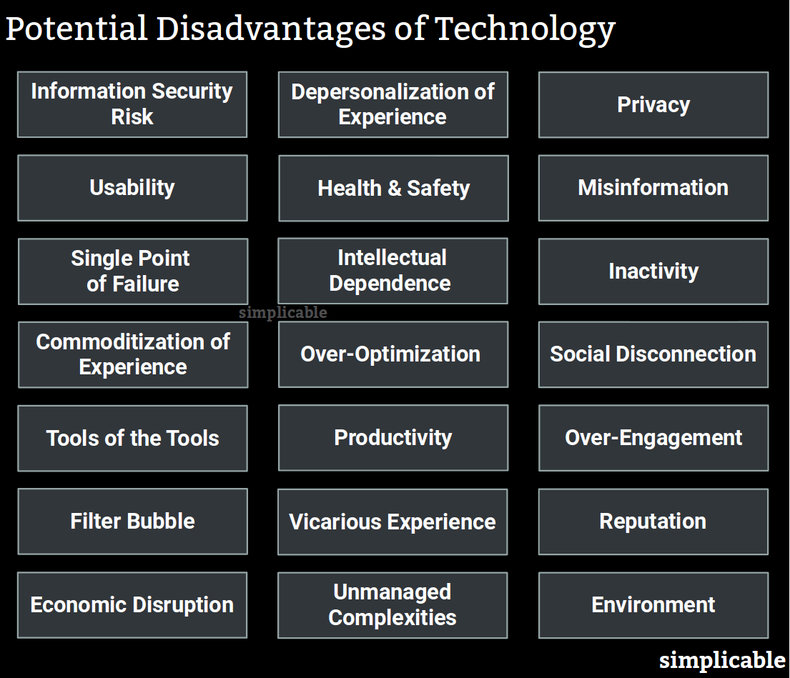
The risk of malicious disruption, misuse and access to systems, applications and data. For example, a school that loses personally identifiable behavioral data about its students to an unknown malicious entity.Depersonalization of Experience
Replacing human experiences such as a one-to-one lesson from a language teacher with digital interactions such as a game that teaches a language.Privacy
In many cases, digital experiences record information about you permanently and transfer this to third parties where it is aggregated with other information about you. For example, a mobile app that requires location services such that the software provider can see where your phone is at all times and maintain a database of this information.Usability
Technologies with poor usability such that they represent an unpleasant experience. For example, a worker who must deal with a slow, unreliable, unstimulating, error prone, inefficient and needlessly annoying tool for 8 hours every day.Health & Safety
Health and safety impacts of technology. For example, a health condition that is related to repetitive user input tasks or extended periods of looking at a screen.Misinformation
Modern technologies such as the internet that have the capacity to instantly share information on a global basis may become a medium for misinformation, propaganda and manipulation by malicious agents.Single Point of Failure
Technology allows a large number of things to be controlled from a single platform. As a hypothetical example, millions of self-driving vehicles that are effectively controlled by a single cloud platform such that any errors or compromise of the service could cause a large number of accidents or attacks at the same time.Intellectual Dependence
A tendency for people to use technology in place of independent thought. For example, a student who simply paraphrases websites when writing an essay as opposed to collecting, organizing and composing their own opinion.Inactivity
A tendency to spend a large number of hours engaged with digital tools such that you don't exercise or more generally experience the physical world.Commoditization of Experience
A tendency to replace human experience with commodities such as products, services, media and digital entities. For example, social status that was historically based on your behavior and position in a community can be commoditized into products, services and digital entities such as followers on a social media platform.Over-Optimization
Optimizing for what you are measuring such that factors you aren't measuring or that can't be measured are neglected. For example, a school that measures many aspects of learning to determine how to best increase scores on standardized tests that reduces time for play that is a right of every child that develops valuable abilities such as creativity and sociability.Social Disconnection
A tendency to become immersed in screens such that social interaction declines. For example, children who find it very easy to focus on screens in a classroom such that the class becomes eerily quiet and non-social.Tools of the Tools
A tendency for people to be controlled by technology as opposed to the other way around. For example, individuals who are obsessed with a particular metric on social media such that it dramatically shapes their behavior.Productivity
The common tendency for entertaining digital technologies such as games, media and ecommerce to disrupt an individual's productive flow. For example, an employee who checks fashion blogs and ecommerce sites several hundred times in an average work day such that they seldom concentrate on work for more than 2-3 minutes at a time.Over-Engagement
People commonly find digital environments such as games and internet addictive such that they find it difficult to disengage or break harmful habits.Filter Bubble
A filter bubble is the use of technology such as social media to discover only information that aligns with your opinions such that you may begin to believe your opinions are more popular, uncontested and indisputable then they are in reality.Vicarious Experience
Replacing experience in your life with the passive experience of consuming media, gossip and news. For example, we tend to think of characters from TV shows or video games much the way the way that we think about people we know. As such, consumption of media may fulfill social needs without actually being particularly social.Reputation
Digital information is easily transmitted and stored such that mistakes or rumors can become a permanent feature of an individual's reputation. For example, a student who makes a mistake in life that is recorded in various social media databases that is then accessible to employers for their entire career.Economic Disruption
Disruption of labor markets whereby an entire profession experiences declining employment levels due to automation. For example, a future without teachers because apps are found to be better at rote learning drills that allow students to pass standardized tests that are valued by a society.Unmanaged Complexities
Societies and organizations may adopt technologies without fully managing or recognizing the complexities that they have introduced. For example, a local government that begins aggressively using information technology to gather information about citizens without properly securing it.Environment
Environmental costs of technology. For example, a digital currency that consumes a great deal of electricity to mine such that it has real impacts on the environment despite being completely intangible. In theory, the Earth's resources could be completely consumed in a pursuit to create abstract, intangible digital entities at great scale that are demanded by consumers.Advantages of Technology
This article is part of a series of articles that examine the advantages, disadvantages, problems and risks associated with technologies. Despite the stark list above, technology has a great number of advantages. It should also be noted that most information technologies aren't inherently bad or good such that any advantages or disadvantages of technologies extend from how you use them.| Overview: Technology Disadvantages | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Losses, inefficiencies and poor outcomes that result from the inappropriate use, management or design of information technology. | |
Related Concepts | ||