Trade
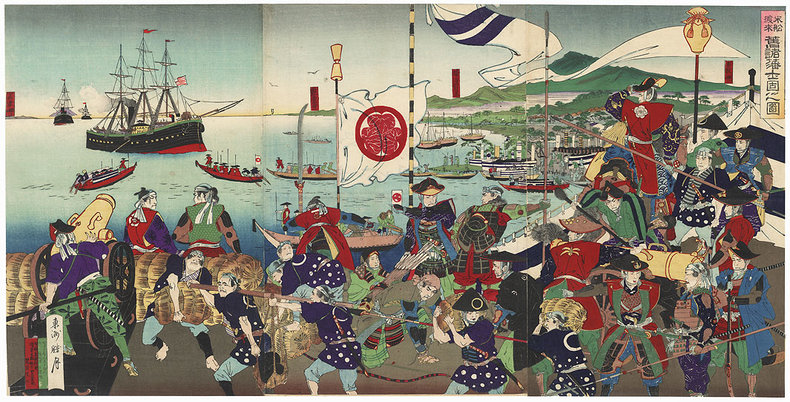
The process of influencing or forcing other nations to open their markets to your products. This can occur even when this represents a grave threat to the culture, way of life and political stability of a nation. For example, between 1853 and 1867 the United States forced Japan to end its isolationist foreign policy with displays of its superior military power. This led to an economic, social and political crisis in Japan that ended a long period of stability known as the Edo-era.Legal
Imposing your laws on other countries with stipulations that foreign nationals or nations that don't cooperate will be penalized. This may include influencing the legislative process in other nations to get them to enact laws that may be unpopular with the locals.Economic
Control of economic systems such as a reserve currency or institutions that settle transactions. These can be leveraged to exert significant control over other nations.Military
Military dominance such that a nation represents a threat of invasion to its neighbors or on a global basis.Technological
Situations where other countries depend on your computer infrastructure, hardware, software and services such that you can threaten to disrupt their society and economy in a dispute.Ideas
A civilization, society or elite that is able to influence the beliefs, ideology, philosophy, values and norms of other civilizations, societies and elites. For example, the French Revolution greatly influenced Europe and the World with ideas such as liberty, tolerance and separate of church and state that defined the modern era.Cultural
The dominant influence of large wealthy countries in cultural arenas such as entertainment, media, music, fashion, arts, food and sport. For example, the global spread of American, Chinese and Japanese cuisine.Globalization
Globalization can be viewed as a process of formal hegemony whereby the global elite and dominant developed countries develop rules that all countries must follow in order to avoid political and economic isolation.Soft Power
Influence over other nations that doesn't depend on a threat of any kind. For example, a nation that can influence others with its education system or media.Notes
Hegemony implies that those you're influencing retain their sovereignty. For example, a colonization is a step beyond hegemony.Hegemony is a persistent feature of history as any civilization or society that has high relative wealth tends to have great influence or control over other nations.| Overview: Hegemony | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The dominant influence of an civilization, nation or elite over other nations. | |
Related Concepts | ||