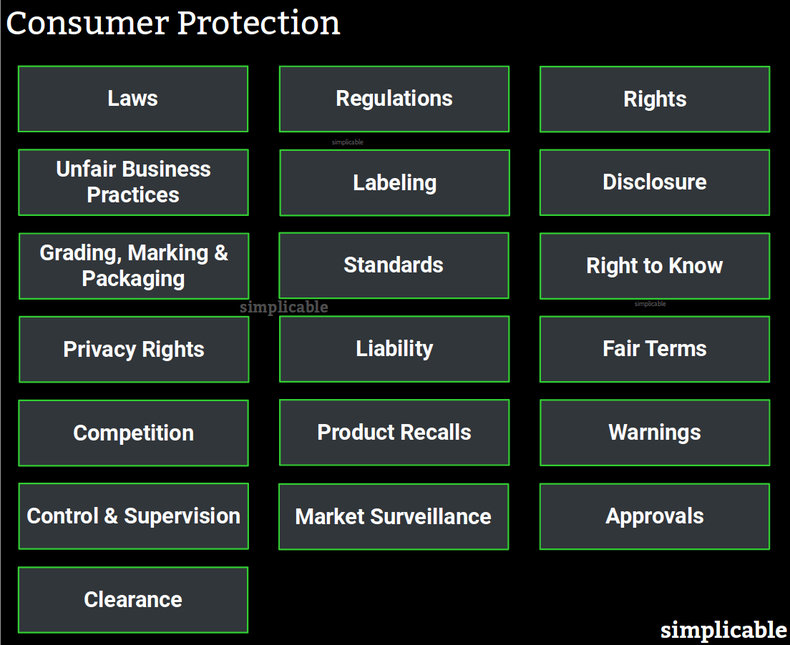
Laws
Laws to protect consumers such as a law that a consumer may cancel a contract for any reason within a limited time period. These may solve a large number of problems, reduce litigation and encourage sellers to present realistic depictions of their goods.Regulations
Regulations are rules set by a government agency in order to implement a given law. For example, a transportation agency that implements a rule that a part that often catches fire can't be used in vehicles to implement an automotive safety law.Rights
Consumer rights are principles of law that are broadly applicable. For example, a right to choose that prevents sellers from automatically ordering things for the customer with their informed consent.Unfair Business Practices
Prohibitions on practices that are deemed unfair such as sale above advertised price.Labeling
Consumers have limited time and ability to research the complexities of product quality, safety and environmental impact. As such, the market benefits from labeling standards that help consumers to make informed decisions. This drives competition to meet consumer needs without restricting commercial rights. For example, a requirement to list trans fats as an ingredient using clear terms as opposed to "vegetable oil" that makes it unclear that the ingredient is a trans fat.Disclosure
Laws and regulations that require producers to notify consumers of certain facts as they become known. For example, a rule that banks must disclose leaks of customer data to all impacted customers within a reasonable time period.Grading, Marking & Packaging
Government programs to certify the quality of products and services. For example, government standards that allow fruit to be labeled as "Grade A" or similar. This may benefit both the consumer and producer as it can be used as a marketing term.Standards
The development of standards such as a standard for organic food. This implies voluntary participation whereby producers can be certified in the standard if they choose.Right to Know
The right to know is the principle that people have a right to know if they are being exposed to hazards such as unhealthy substances in a product. For example, a requirement to inform consumers of lead in glassware.Privacy Rights
Restrictions on data collection, surveillance and other practices that consumers find invasive to their privacy rights. For example, the principle that cameras can't be installed in a changing room or bathroom where there is a expectation of privacy.Liability
A consumer's right to sue for damages related to faulty, misrepresented, unsafe, unhealthy or otherwise damaging products and services. For example, a consumers right to sue an airline for denial of basic human rights in the delivery of their service such as a flight that denies a child water for extended periods of time because they don't have a credit card.Fair Terms
Restrictions on legal "agreements" imposed by producers. For example, a right to repair that prevents producers from mandating that you replace items as opposed to maintaining, upgrading, repurposing or fixing them.Competition
Consumer protection is closely related to competition laws that prevent anti-competitive practices. For example, a price fixing law that prevents telecom companies from coordinating their prices to eliminate competitive pricing.Product Recalls
Regulations and controls that force a producer to recall a dangerous or defective product.Warnings
Communicating warnings to the public about fraudulent, dangerous or defective products, services and commercial practices.Control & Supervision
Monitoring producers to ensure they comply with laws, regulations and voluntary standards. For example, a food safety agency that conducts surprise inspections of restaurants and food production facilities.Market Surveillance
Monitoring the market for emerging threats to the consumer.Approvals
Products that have critical health, safety and environmental implications that have to be approved by a government before they can be sold based on the precautionary principle. For example, a medication that must be approved as safe and effective before it can be marketed.Clearance
Clearance is a quick approval for a product that is effectively the same as products that are already approved.| Overview: Consumer Protection | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A basic government function that ensures that products, services and terms offered to consumers in markets are safe and fair. | |
Related Concepts | ||