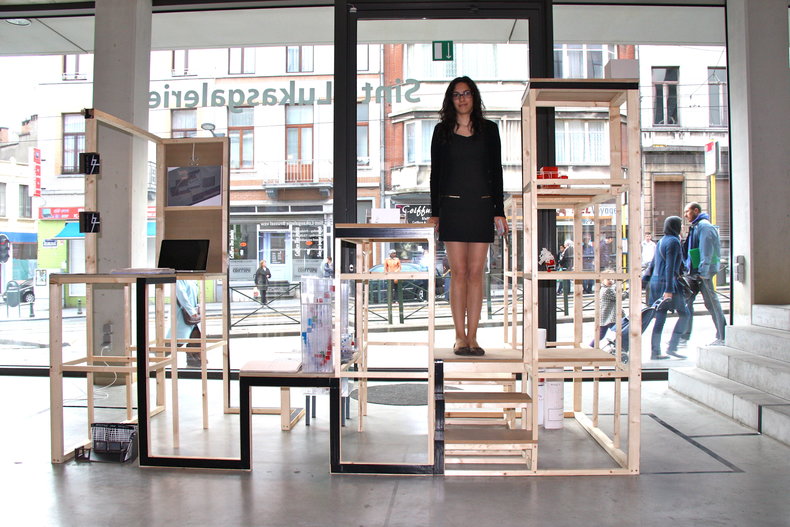
Modular vs Non-modular
Modular designs tend to have benefits for customers and sustainability as they allow for reuse and incremental upgrades as opposed to replacing an entire unit. In many cases, a culture of do-it-yourself customization will evolve around designs that are highly modular.
Designed Obsolescence
Non-module designs may have commercial advantages for the manufacturer as it encourages people to replace units as they can't be easily upgraded. This is known ad designed obsolescence.
Interfaces
Module designs depend on standard interfaces between parts. For example, shelves that can take different components such that they can be reconfigured in countless ways.
Poor Interfaces
Historically, many module designs were unpopular because interfaces were too difficult to use. In theory, personal computers were module as you could upgrade things such as memory. However, the interfaces never worked well and required obscure technical skills. Generally speaking, modular designs fail when parts don't fit together easily.
| Overview: Modular Design | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Designs with independent parts with standard interfaces. | |
Value | Creating a culture of customization.Allowing other firms to contribute to your products.Reuse & sustainabilityIncremental upgrades | |
Related Concepts | ||