Worldview
Political polarization occurs along broad divisions in thinking such as conservative vs progressive, libertarian vs authoritarian, rural vs urban, religious vs secular and nationalism vs globalism.Nuance
Political polarization results in a neglect of nuance whereby everything is viewed as a struggle between right and wrong, us and them, right and left. This can be contrasted with the pragmatic view that many things are grey areas that contain degrees of truth and exceptions.Compromise
Political polarization prevents compromise. For example, it doesn't allow for a policy that is formed with a few good conservative ideas and a few good progressive ideas.Two-Party System
A political landscape dominated by two political parties tends to increase polarization. This may be more common in a winner-take all political system such as a presidential system with a single person who is elected to rule an executive branch. Parliamentary systems allow 3rd or 4th tier parties to have influence due to the possibility of forming a coalition government.Partisan Media
Partisan media such as a television channel, newspaper or film production company that heavily promotes a particular worldview. This can be contrasted with objective media that tries to present both sides evenly if an issue is controversial.Filter Bubble
A filter bubble is when an individual has arranged their life so that they don't have to hear views that differ from their own. It is common for technology and media companies to offer tools for constructing filter bubbles. For example, a social media tool where you can follow someone who you agree with and then unfollow them the first time they say something with which you disagree. Physical locations such as a safe space offered by a university or a small town that ostracizes outsiders can also act as a filter bubble.Silent Majority
Silent majority is the idea that people with relatively moderate political views are less outspoken or are less interested in politics. According to this theory, both sides in politics tend to levitate to extremes because moderate individuals are less engaged, insistent and loud.Virtue Signaling
Virtue signaling is an attempt to create self-esteem, social status or revenue by communicating support for issues or shaming others. This can create a tense political environment as people may say anything that will get them attention without regard to objectivity and civility.Social Desirability Bias
Social desirability bias is when people say what they think people want to hear as opposed to speaking their mind. This may prevent the moderate from challenging those who are pushing politics to extremes for fear of criticism.Groupthink
Groupthink is when a social group doesn't tolerate open debate and instead socially punishes anyone who challenges the dominant thinking of the group by labeling them as bad and socially isolating them. Self appointed enforcers within the group seek out non-conforming opinions and behaviors and quickly act to name and shame the offending individual. In this context, people in the group exercise careful self-censorship such that it is unclear how many people actually believe the group's ideology.Civility
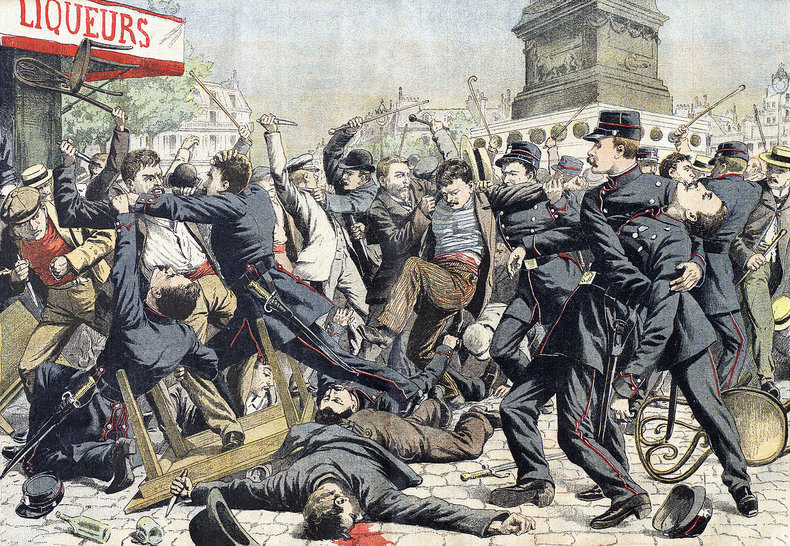
Political polarization is an extremely tense situation where there is temptation to break rules and violate norms in an attempt to "win" against the other side. This results in a breakdown in civility whereby society become unstable due to a lack of shared rules, understanding and respect.Backfire Effect
The backfire effect is a tendency for people to harden their viewpoints when challenged. This is extremely common and tends to occur when challenges are low quality. For example, telling people they are irrational and out of touch with the facts is generally not an effective way to influence people such that it is likely to backfire.Conflation
Conflation is the merging of ideas that need not be merged. This is a common source of political polarization. For example, attempts to tie an environmental problem with lifestyle choices that are likely to be extremely polarizing. Conflation can make an issue that is in everyone's interest to solve suddenly extremely controversial such that a solution is unlikely. It is possible for an elite to use conflation as a divide and conquer strategy that encourages the masses to argue about minor divisive issues to prevent large scale problems from being addressed.Vindictiveness
In an environment of intense political polarization, parties may implement irrational policies simply to offend the other side. This can be remarkably destructive.| Overview: Political Polarization | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A high level of tension between two political ideologies that causes positions, attitudes and policies to diverge to ideological extremes. | |
Related Concepts | ||