Decision Rationale
A decision rationale describes the reasons for a decision. This may be used to sell a decision to stakeholders or may be used as an artifact to explain the decision to the future. For example, a decision to reject a business plan may explain the risks or shortcomings of the plan.The business plan was rejected because the business model created value for customers by creating large risks for us. In the current competitive pricing environment and without any special competitive advantages, it was clear that revenue would not be high enough to compensate for these risks such that the business plan was likely to be unsustainable over time.
Design Rationale
A design rationale documents the reasons for design decisions. This explains why a design was selected from alternatives and how it achieves design goals. For example, the architect for a public school that creates a rationale based on the project's requirements and constraints.The dense urban location of the school and small size of its land relative to its student population calls for a tall structure of 7 floors with a courtyard in the middle that serves as a playground. This is remarkably visually appealing and integrates with the neighborhood as several important historical structures in the area have similar courtyards. As a courtyard, the playground is isolated from the noise and pollution of the street. The roof of the school will be used as a 400 meter running track. This gives students plenty of space to run and play despite the severe constraints of creating a school for 1,400 students on a small parcel of land.
Research Rationale
A research rationale explains the significance and uniqueness of a study. This will often explain other research and how a study fits into the current knowledge of a topic.Machine biases are systematic patterns of machine decisions that humans judge as unfair, biased or irrational. Recent studies in this area have been confined to anecdotal evidence of such occurrences. The mechanisms by which such biases are created are loosely explained as machines that have been influenced by human biases, organizational biases, "bad" data or simply machine error. No study or publication to date has documented the concrete patterns by which such biases may be introduced to algorithms or artificial intelligence. This study documents a list of 44 antipatterns that allow machine biases to be introduced to decision making systems. This is based on interviews with artificial intelligence experts, algorithm designers and software architects together with case studies that determine the root cause of instances of machine bias.
Project Rationale
A project rationale is a pitch for a project. This may be done for a small project that doesn't have a full business case or as a preliminary artifact to pitch a project to stakeholders. A project rationale typically states a problem, a solution and the benefits of the solution as compared to alternatives.Our lobby was recently renovated to comply with accessibility regulations at a cost of $660,000 but our rooms are still problematic for people with disabilities. In order to respect the spirit of the law, guarantee customer satisfaction for all guests and reduce the risk of reputational issues it is proposed to renovate 8 junior suites on the 2nd floor to have special accessibility features for people with disabilities. Contractors have estimated the cost at $122,000. This will allow front desk staff and customer service representatives to offer a complimentary upgrade to anyone who has a special need to rooms that are far more likely to be satisfactory. In the past 5 years, 8% of our negative reviews were based on our limitations in accommodating special needs. It is estimated that we can reduce this by 80% and increase our average customer review score by 1.28% with this minor change. It is estimated that 9.7% of our customers last year had some type of special need.
Lesson Rationale
Rationales are an essential element of a lesson plan that simply explain why a lesson has value to students.This unit is designed to teach students the concept of mechanical advantage, also known as leverage. This is a foundational element of engineering that conveys basic physics such as the concept of force, work and friction. The lesson activity will allow students to build working simple machines that create leverage. This gives students hands on experience in engineering design. It is hoped that this will make the lesson memorable and give students the confidence to design and create mechanical things.
Strategy Rationale
A strategy rational explains why a strategy benefits a firm and why the strategy is better than alternatives. This may be included in a strategic planning document or a strategy pitch.The local procurement strategy will seek to secure direct long term supply contracts with organic farmers in a 300 mile radius of our production facilities for key ingredients for our jam, peanut butter and honey products. This is expected to reduce unit costs by at least 5% and allow us to market goods as domestic and local products that will enhance our premium brand image. This will create some risk as such supply may be irregular and requires more complex logistics as we will deal directly with small suppliers. However, strategy implementation will retain diverse international suppliers as a backup such that risks can be managed without material cost impact.
Summary
The following is a common structure for a rationale that includes background, goals, arguments, sources and alternatives that were considered.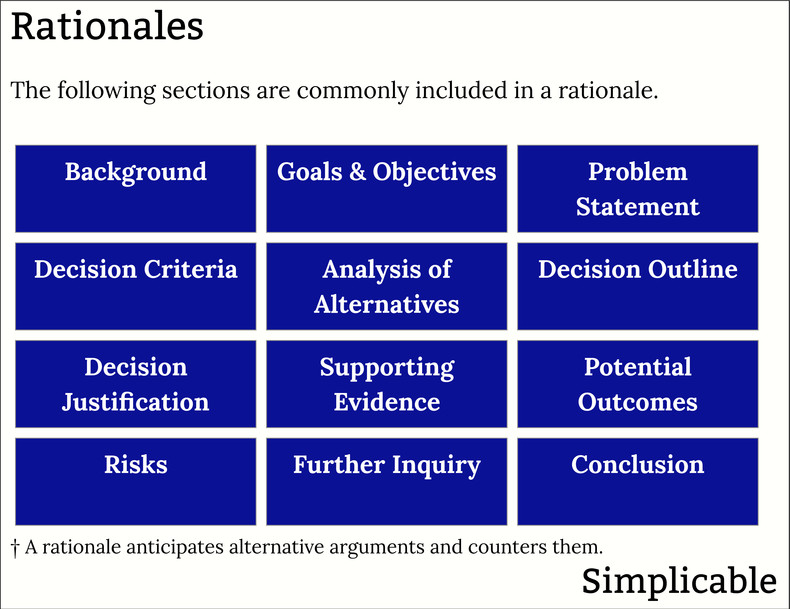
Overview
Rationales can be used to explain and document a decision, strategy, argument, position or policy.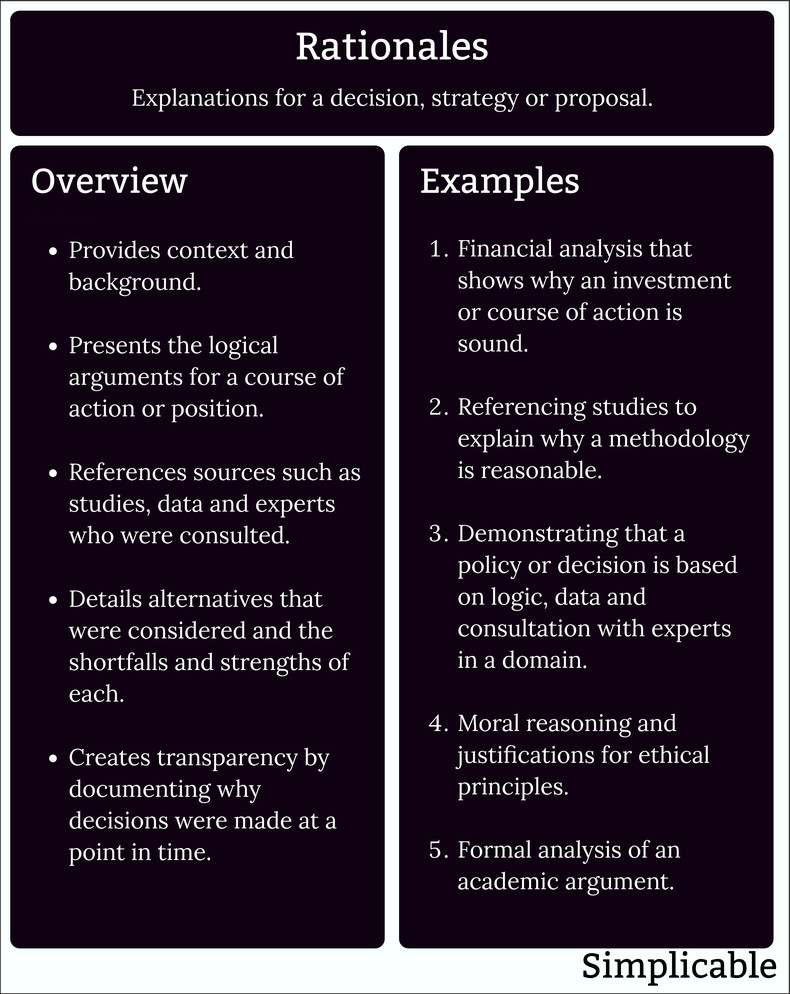
| Overview: Rationale | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Communication that explains why an action, decision, approach or strategy is valuable or reasonable. | |
Related Concepts | ||