Manufacturing
The production of physical products such as mobile devices.Consumer Staples
The production of products that consumers need to buy on a regular basis such as food and cleaning supplies.Consumer Discretionary
Products that consumers choose to buy when they have discretionary income such as sporting equipment.Consumer Durables
Consumer products that have a useful life of more than three years such as furniture, appliances and vehicles.Fashion
The fashion industry has unique properties as it is a basic human need and could be considered a staple. However, it is often a discretionary purchase as people overpay for clothing because it can be viewed as a status symbol. Fashion is often physically durable but people often wear items for less than a year.Business Products
Products specifically designed for businesses. This is a shrinking category of the secondary sector because businesses increasingly use products designed for consumers.Craft
Products that require significant human attention in the production process such as a violin crafted by a luthier.Construction
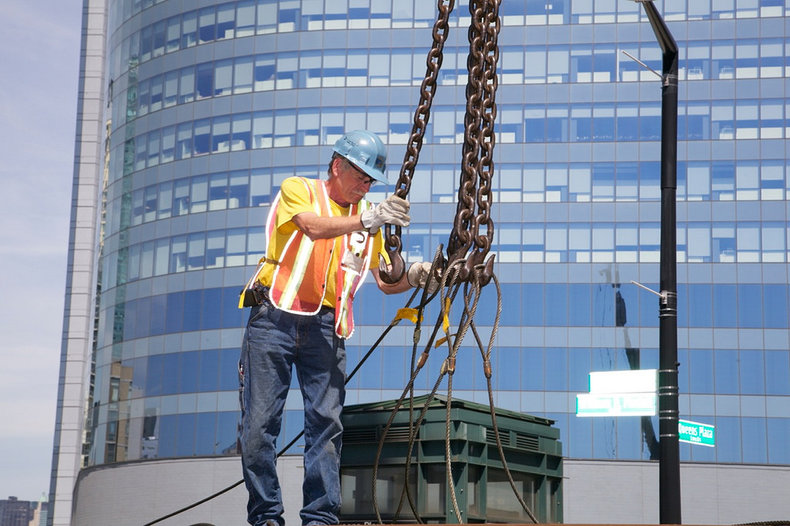
The construction industry a major component of the secondary sector that produces buildings, landscapes and infrastructure.Heavy Industry
Heavy industry is the manufacture and construction of unusually large, complex things such as a port or aircraft.| Overview: Secondary Sector | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Industries based on a finished physical product. | |
Related Concepts | ||