Mission statement | Vision statement |
Grand strategies | Change management |
Roadmaps | Strategies |
Goals | Performance objectives |
Plans | Policies |
Programs | Projects |
Initiatives | Action plans |
Mission
A mission defines your purpose as an organization. If your mission is to provide the highest quality bicycles on the market then this provides long term strategic direction that calls for prioritizing quality over other goals such as cost savings.Vision
A vision statement paints a picture of the future of a society, city or organization. This is a basic way to provide strategic direction alongside a mission statement. For example, a city with a vision of a high quality of life, zero pollution and expansive green spaces can use this vision to prioritize current planning and spending.Culture
Culture is the set of behaviors, expectations and norms that evolve in a society, city or organization as a result of the shared experiences of its members. Culture is difficult to change but acts as a strong form of strategic direction. For example, a department store that has a deeply ingrained service culture with respect for the customer will easily implement improvements to customer service where other firms fail.Ideology
Ideology is a system of ideas and values that provide social, economic, political and moral direction. Ideologies provide strategic direction to a society such that policies remain consistent and stable over time.Principles
Principles are foundational guidelines or rules that provide direction to future strategy and decision making. For example, a technology company that establishes the information security principle that all data be strongly encrypted in storage and transit. This leaves no excuse for lapses of encryption and provides strategic direction to new projects and initiatives.Values
Values are principles that relate to matters of right and wrong. For example, a technology company that establishes the sustainability principle that energy be procured from the most sustainable source available and used as efficiently as possible.Grand Strategy
Grand strategy is a long term strategy that considers every possible approach and tool at your disposal. In some cases, an organization's current strategy may appear to be irrational but makes sense when you have a view of its grand strategy. For example, an electric car manufacturer that opens up its patents for free use by the competition. This may be viewed as irrational by its shareholders as they view the patents as valuable assets. However, this may speed the adoption of electric vehicles and related infrastructure such as charging stations that ensure the technology wins over competing approaches such as hydrogen vehicles. A grand strategy provides strategic direction over time and represents a long term optimization of strategy over short term considerations.Summary
The following are common ways that management documents and communicates strategic direction.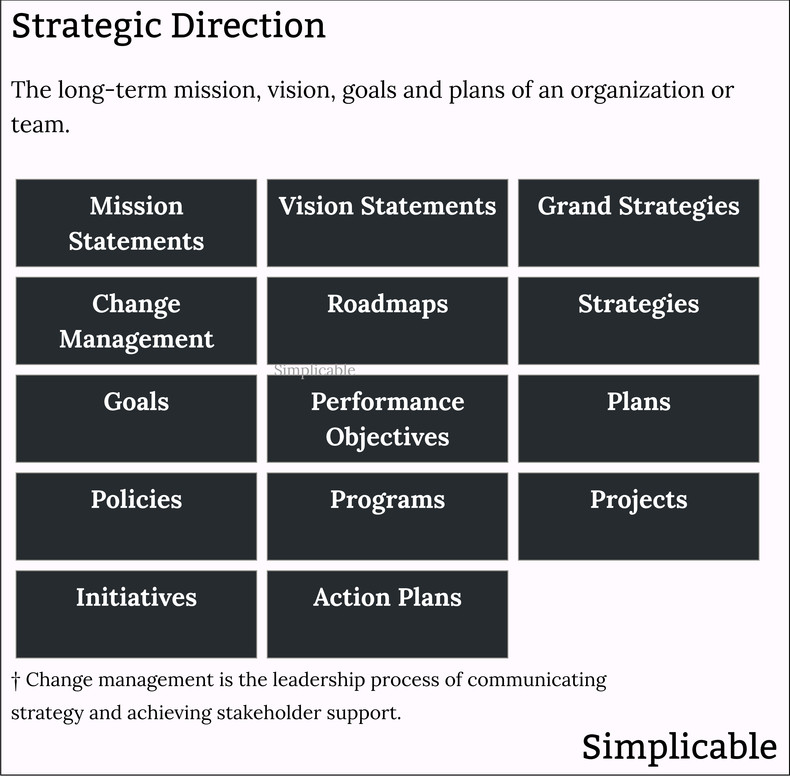
Overview
The common types of strategic direction are retrenchment, expansion, innovation, operational excellence and customer experience.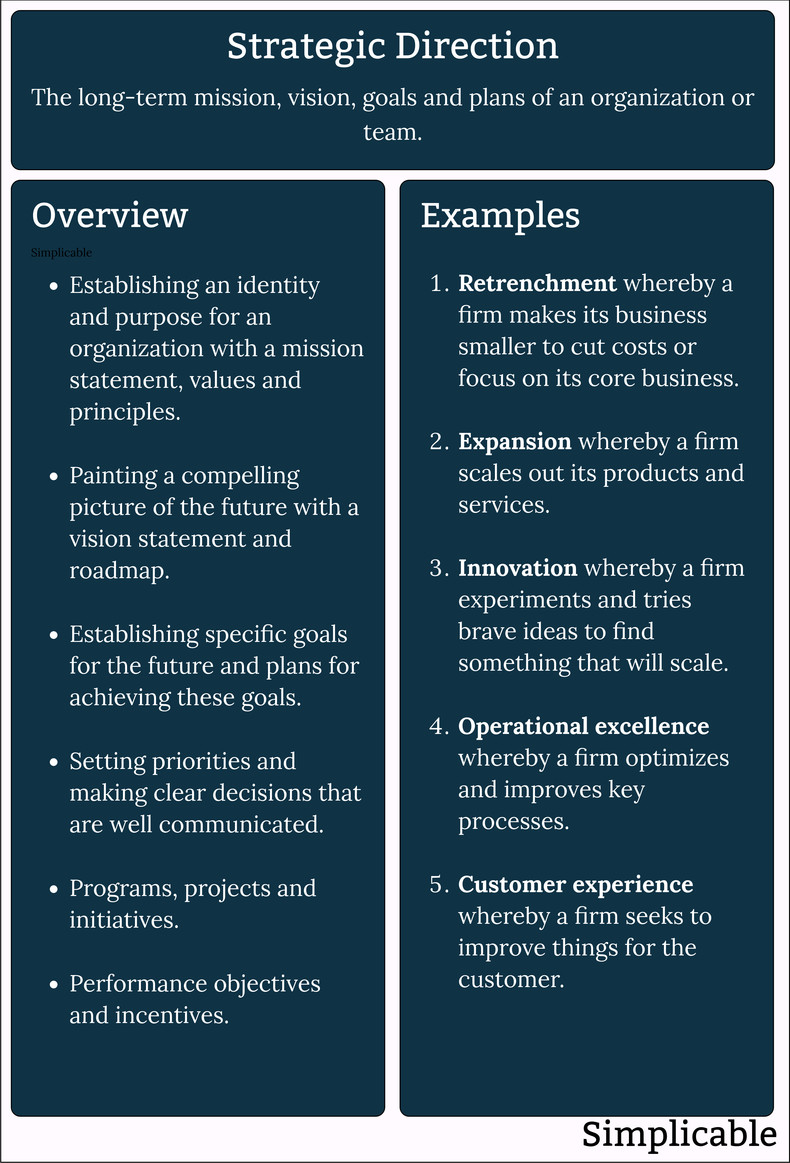
| Definition: Strategic Direction | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A mechanism that provides consistency to strategy over time. | |
Related Concepts | ||