Revenue
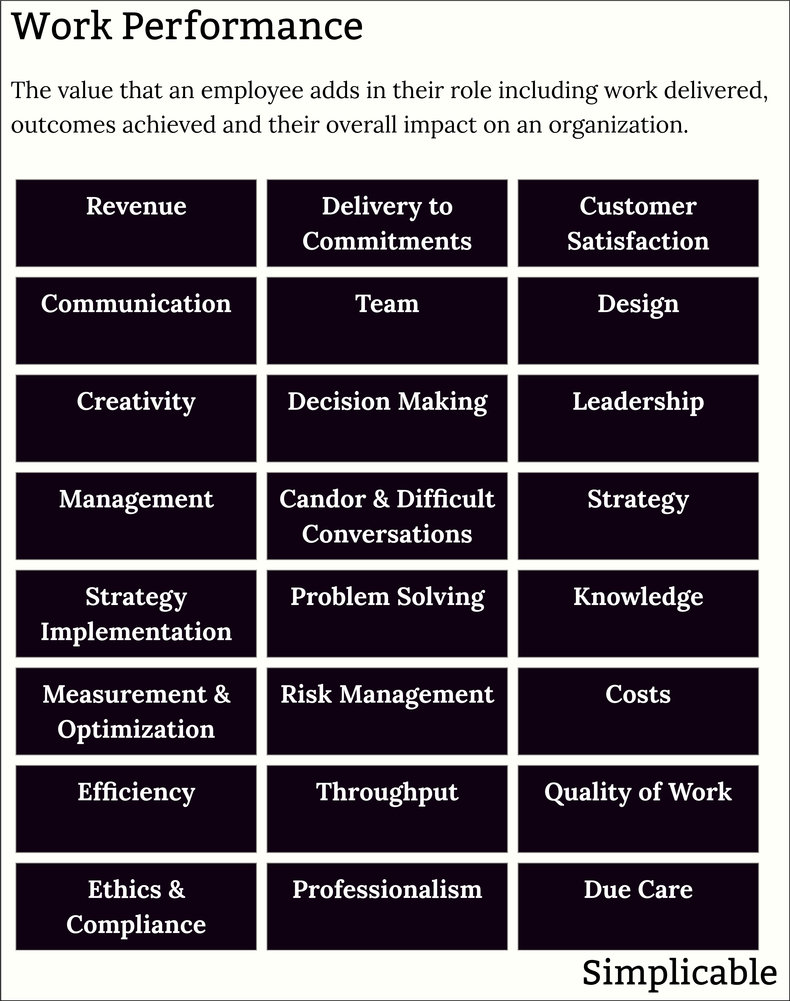
Revenue related performance such as the ability to close sales or develop products that sell.Delivery to Commitments
Delivering things to schedule and budget.Customer Satisfaction
In many cases, pleasing the customer is a key accomplishment. It is often productive to view performance in terms of customer experience. This can include employees who aren't customer facing. For example, a web designer might gather customer feedback for a design as a means of documenting performance.Communication
The effectiveness of verbal and written communication. For example, an engineer who is good at explaining technical things to marketing teams.Team
Contributing to the success of others and the culture of a team. Avoiding counterproductive politics, particularly within your team.Design
Creating useful things. For example, a software architect who designs an elegant structure of components that break a large problem into a number of easy to implement chunks of functionality.Creativity
Being the source of valuable ideas that get implemented.Decision Making
Making clear and timely decisions. Accepting your accountability and responsibility and learning from mistakes.Leadership
The ability to motivate and influence people in a directed way that achieves something.Management
Directing and controlling the resources of an organization.Candor & Difficult Conversations
Being candid but polite to provide feedback including difficult conversations. For example, a manager who lets an employee know right away if their performance is low as opposed to waiting for review time.Strategy
Developing, evaluating, documenting, selling and leading strategies. Ultimately, strategic abilities are assessed according to the success of the strategies themselves.Strategy Implementation
Individuals who embrace and deliver change. The opposite of a common tendency to resist change.Problem Solving
Solving problems in a timely manner. For example, a software engineer who troubleshoots and solves technical issues for customers.Knowledge
Developing knowledge materials and communications that have an impact on the business.Measurement & Optimization
Developing metrics and optimizations. For example, implementing a daily report that shows the defects on a production line by root cause in order to make quality improvements.Risk Management
Identifying potential losses and taking action to manage and reduce risk.Costs
Reducing costs. For example, an IT manager conducts an investigation to discover payments that no longer need to be made to vendors for unused software licenses.Efficiency
Improving efficiency such as reducing the turnaround time of a business process.Throughput
The total amount of work that is delivered by an employee.Quality of Work
The quality of delivered work. This can be assessed in terms of non-functional requirements. For example, the quality of code can be assessed in terms such as reliability.Ethics & Compliance
Ethical behavior and strategy with respect to coworkers, customers, communities and the environment including compliance to laws and regulations.Professionalism
Professionalism such as refraining from inappropriate personal conversations in front of customers.Due Care
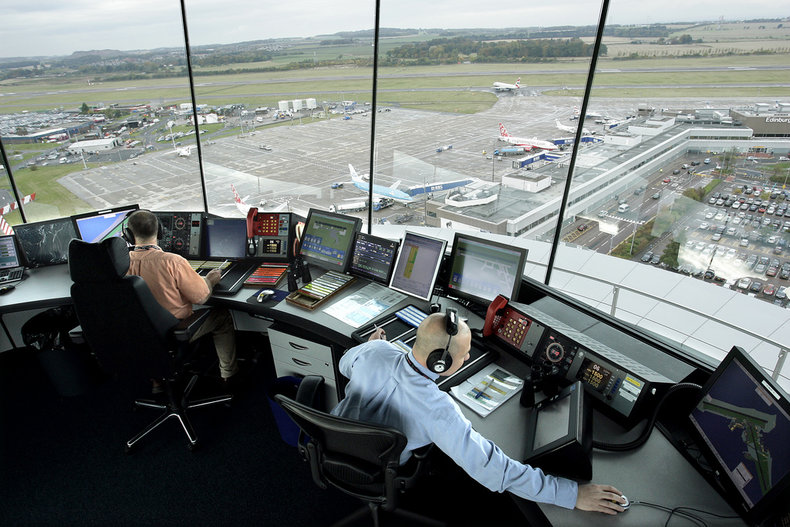
Exercising the diligence that is reasonably expected of your profession and industry. For example, an air traffic controller is expected to be alert with a high degree of situational awareness at all times.| Overview: Work Performance | ||
Type | ||
Definition | How well an individual performs a job, role, task or responsibility. | |
Related Concepts | ||