|
| |
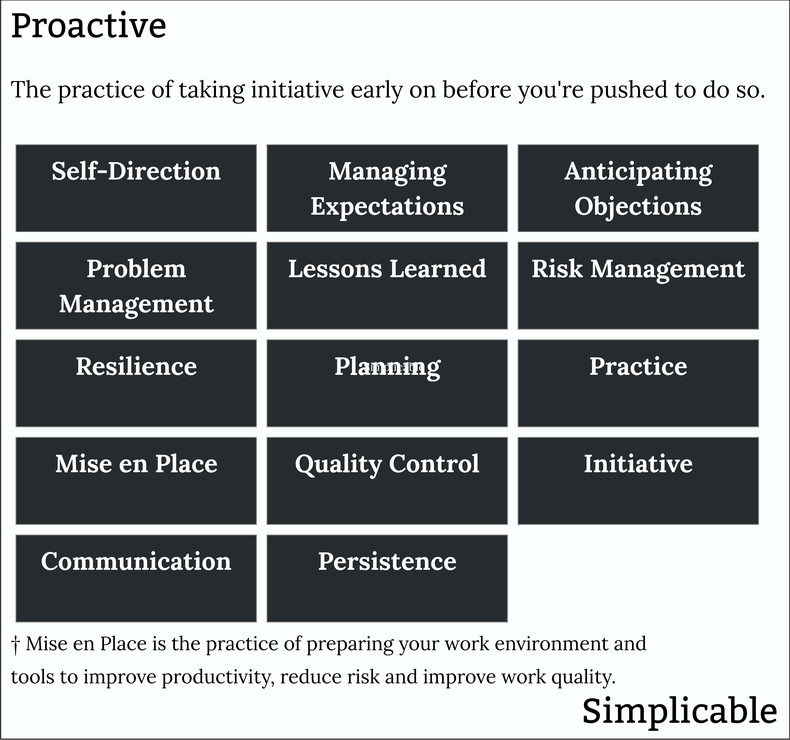
A proactive approach is any self-initiated action that prepares to handle the future. Proactivity is a considered desirable trait in an employee, team or organization that can be contrasted with reactive approaches that wait for the future to happen before taking action. The following are illustrative examples of proactive strategies and behavior.Acting to add value without waiting to be told what to do. For example, a software developer who pushes into important projects as opposed to waiting for work assignments.Setting expectations for what you will and will not do. This avoids future surprises based on the imaginative assumptions placed on you by others. For example, clearly communicating to your boss on a regular basis what you are delivering and what has been placed on a lower priority queue for later.
Thinking through how people will react to your ideas and planning your response. For example, a salesperson who plans for what to say when a customer complains a car is more expensive than a competing model.Identifying and correcting the root cause of a problem as opposed to addressing symptoms. For example, a customer service manager who escalates a design problem to product development teams to fix the root cause of customer complaints. Processes that prevent the same mistakes from being repeated over and over such as a farmer who learns that a particular winter crop gets damaged if it is watered at below 46°F who implements a process of checking the temperature before turning on sprinklers.Identifying potential future failures and taking steps to avoid, transfer or reduce such risks. For example, waterproofing a basement that is prone to flooding.ResilienceResilience is a term for advanced, but often simple, strategies that prevent risks as opposed to managing them. For example, exercising, eating healthy food and carefully cultivating your mind in order to avoid a broad set of health risks.PlanningPlanning ahead such as an ice cream manufacturer that plans to meet summer demand by ramping up production in line with demand forecasts.PracticePracticing for something you need to do in future such as a speaker who rehearses a speech a few times.Mise en place is the practice of preparing your workspace before work. For example, a chef who carefully lays out ingredients and cooking implements before each dinner rush.Inspecting things for problems before they are shipped to the customer such as a coffee company that automatically tests that every bag of coffee is properly sealed before boxing.InitiativeTaking initiative as opposed to waiting for events. For example, a salesperson who calls customers a week after a purchase to make sure they haven't had any problems.Communicating early and often to avoid problems such as a telecom company that immediately informs a customer when their monthly charges are trending higher than usual.PersistenceA proactive approach implies an energetic and persistent set of actions such as a student who is interested in a masters program who tries to schedule an appointment with a professor to ask a few questions. When the professor ignores several requests, the student shows up at the end of one of the professor's lectures and corners them.SummaryThe following are examples of a proactive approach.OverviewTaking initiative to manage things before being pushed to do so by circumstances.Next: Initiative
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
The basics of productivity.
The definition of attention span with examples.
The definition of motivation with examples.
The definition of effort with examples.
The definition of labor intensive with examples.
The definition of busy work with examples.
The definition of bikeshedding with examples.
A list of common productivity goals and measurements with examples.
The common types of efficiency with examples.
A comprehensive guide to time management techniques.
The process of managing commitments to goals, projects and action items.
The definition of persistence with examples.
The common causes of procrastination.
TrendingThe most popular articles on Simplicable in the past day.
Recent posts or updates on Simplicable.
Site Map
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|