Disaster Risk
The insurance industry defines external risk as the risk of disasters that are beyond the control of a policy holder such as earthquakes, wildfires, floods and pandemics.Act of God
Another term for disasters of a non-human cause such as a volcanic eruption.Force Majeure
Force majeure is a major adverse event such as a disaster. This potentially includes human caused disasters such as a war but definitions vary by jurisdiction.Environmental Hazards
The potential for an environmental disaster such as very low air quality that threatens the health and safety of large populations.Infrastructure Risk
The potential for major infrastructure disruptions beyond your control such as an event that causes large scale internet outages.Political Risk
The potential for political disruptions such as a revolution, strike or protest.Economic Risk
Large economic risks such as the potential for a recession or depression. Predictable economic risks such as exchange rate fluctuations aren't considered external as these can be mitigated.Project Risk
Projects often define external risks as anything beyond the capacity of the project to mitigate. For example, a merger or acquisition might derail a project but be well beyond the control of the project.Summary
An external risk is a major risk that is fully beyond your control to prevent. Although you can't prevent external risks you can prepare for them with techniques such as insurance or disaster preparedness.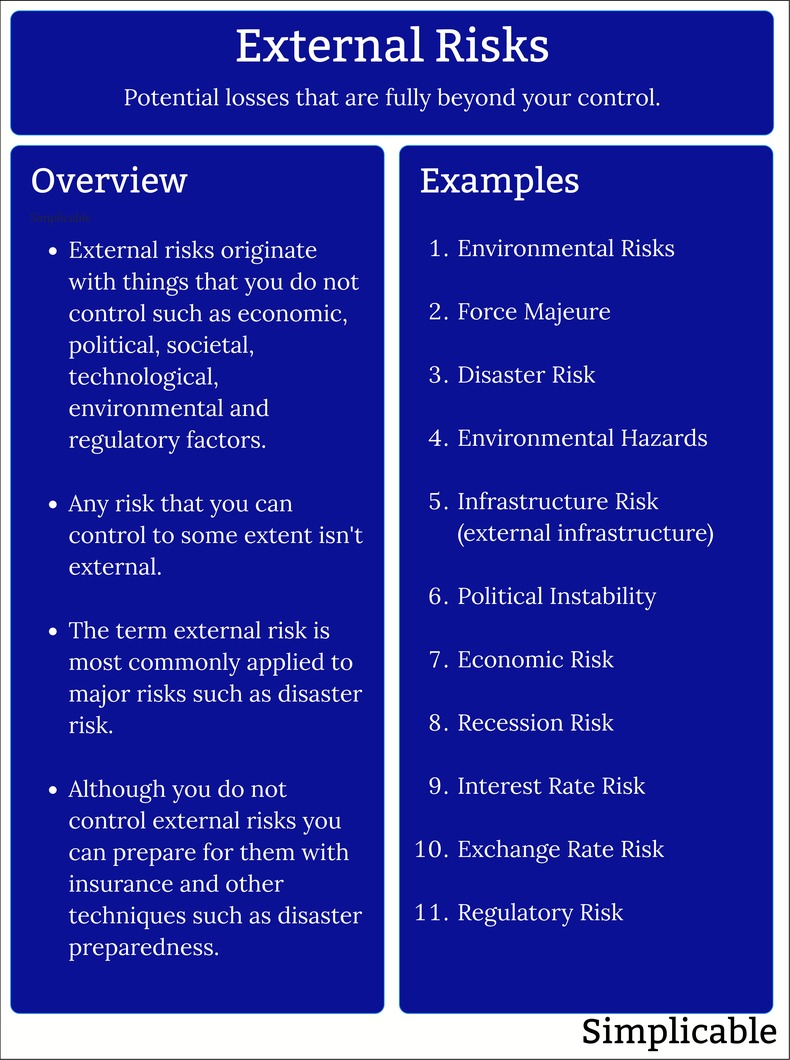
Discussion
The insurance industry and contract law have a narrow definition of external risk that is often synonymous with Act of God.Any risk that can be avoided by you isn't external. For example, a predictable level of weather risk whereby you should reasonably expect it could rain and plan accordingly.| Overview: External Risk | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A risk that is fully beyond your control. | |
Related Concepts | ||