Materials
A substance such as a chemical that represents a health and safety risk.Machines
Machines such as a conveyor belt that can easily catch a person's clothing or hand.Structures
Dangerous structures such as a heavy portable soccer net that is stored on a field in an unsecured manner such that children may climb on it not realizing that it can easily fall on them.Nature
Natural conditions such as a beach with a strong current.Weather
Weather conditions such as a strong wind that is a hazard to construction workers.States & Conditions
A state or condition such as a firm with a large debt that represents a risk of bankruptcy.Behavior
A repeated behavior such as gambling that is a source of a financial risk.Design
A design flaw in a jet engine that represents a safety risk.User Interfaces
A user interface that is difficult to use such that it demands a person's attention in a fast moving situation. For example, a car navigation system with a difficult to use touch screen that tends to distract drivers.Communication
Vocabularies and communication procedures that can lead to confusion in a fast moving situation. For example, standard instructions from air traffic control that sound alike such that they can be easily misunderstood.Information
Information that is unclear or misleading such as instructions for securing furniture that represent a safety risk because they are commonly misinterpreted by users.Human Error
Training and talent issues can represent a hazard. For example, a pilot who is too quickly put in charge of equipment that is new to them.Latent Human Error
A design that makes human error likely. For example, trading software with a visually similar price and quantity field such that the two numbers can easily be confused.Procedures
Procedures that are lacking or failure prone. For example, a maintenance procedure for a jet engine that fails to account for tools such that they could have been left in an engine.Processes
Process hazards such as a production process that involves workers performing tasks in close proximity to extremely hot materials.Practices
Practices such as a diet program that encourages customers to adopt an unhealthy or dangerous diet such as drinking large volumes of water.Culture
A culture that encourages risk such as an airline that disciplines a pilot for being too cautious about safety.Threats
A threat is a mode of attack. This is a security term that is also applied to information security. For example, computer viruses are a security hazard.Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses that can be exploited by a threat. For example, software that lacks security patches are a hazard to information security.Political
Political conditions can represent a hazard to a business or individual. For example, a trade war between two nations may represent a supply risk to a business.Ergonomic
Repeated tasks that represent a health and safety hazard. For example, repeatedly lifting heavy objects generally puts a worker at risk of injury.Environments
A physical environment that represents a health and safety hazzard such as a former industrial site that has structures and materials that are likely to injure anyone who is unprepared.Environmental
Waste that enters the environment that harms people, animals and/or ecosystems such as particulate matter emitted by a diesel truck.Summary
The following are common types of hazard: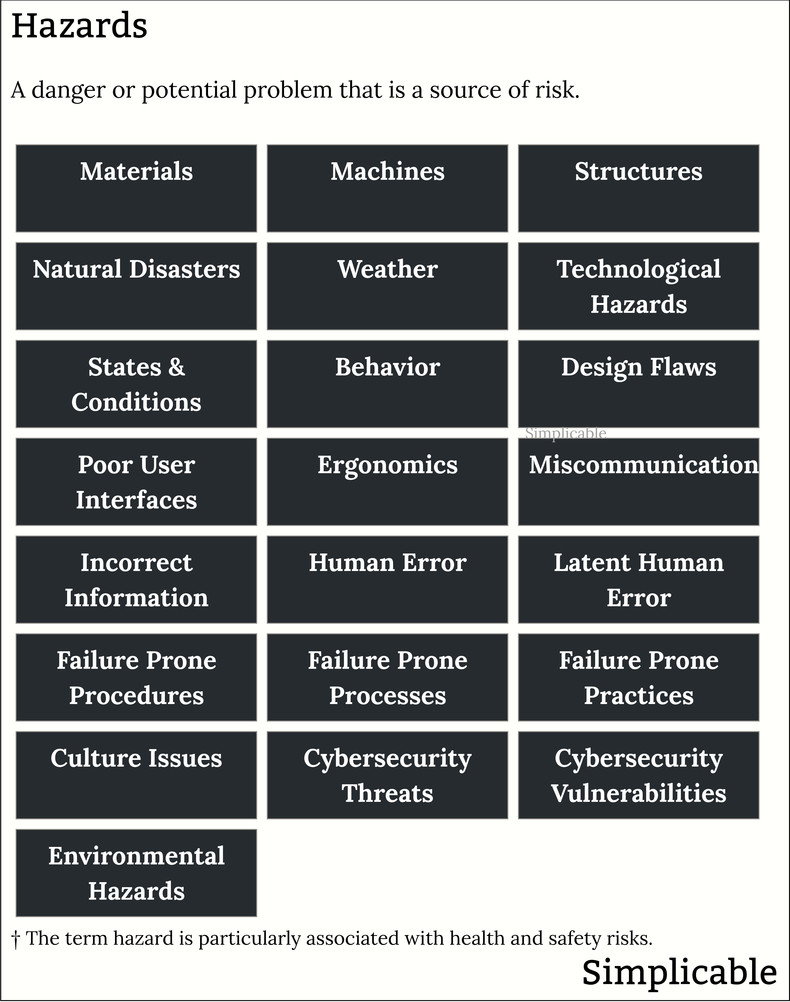
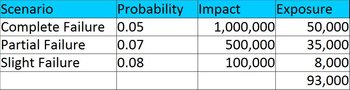
| Overview: Hazard | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A source of risk. | |
Related Concepts | ||