
Safety Risk
The risk of an accident or crime that impacts your health or quality of life.Health Risk
The risk of negative health outcomes such as a disease. For example, the health risks associated with living in a location with poor air quality.Property Risk
Risk to your property such as fire, flood or theft risk.Weather Risk
The risk that bad weather will result in losses.Force Majeure
The risk of a large scale negative event such as a disaster or war. This is often not insurable or requires highly specialized insurance.Pure Risk
Pure risk is risk that only has a downside such as fire risk. This can be contrasted to risk taking that is done for a potential gain such as purchasing a risky investment. Generally speaking, pure risk is insurable.Opportunity Costs
An opportunity cost is what you must give up in order to do something with your life. For example, if you spend three years studying economics in university, that is three years that you could have done anything else. Opportunity costs are the fundamental reason that all things are surrounded in risk. If you make a poor choice, you may waste your time, health, youth, energy and resources such as money and influence.Ventures
Taking risks as part of your day to day behavior or your grand plan for your life. For example, meeting new people and being outgoing can be viewed as a form of social risk taking.Financial Risk
Financial risks including investment risk, tax risk, interest rate risk, refinancing risk, recession risk and liquidity risk. For example, the risk that your employer will not pay you and you will be unable to pay your creditors.Information Security Risk
The risk that your technology will be accessed, modified, controlled, disrupted or destroyed by a malicious agent. For example, the risk that someone will access your private information and media on your phone.Career Risk
The risk of a negative outcome in your career due to action or inaction. For example, the risk that your skills will become out of demand in the labor market.Business Risk
The risks to a business owned by an individual or family. For example, the risk that the only restaurant in a small town will face stronger competition.Political Risk
The potential for political events or conditions to result in losses. For example, a student studying in a foreign country who risks an inability to complete their degree due to a sudden change in immigration policy.Purchase Risk
The risk that a purchase will not have the value you anticipate. For example, a student who buys an expensive laptop risks that it will break such that they have to spend more or go without a critical tool.Dread Risk
Risk that people particularly fear such as the risk of an airplane crash. In some cases, people focus on dread risk and ignore other risks that are less emotional.Passive Risk
Passive risk is the risk of doing nothing. Risk is too often associated with action but inaction can be equally risky. For example, inactivity may be a health risk.Secondary Risk
Secondary risks are risks that are created by attempts to reduce risk. The classic example of this is an individual who puts money under their mattress to avoid investment risk only to face inflation risk as the value of the money declines over time.Summary
The following are common types of personal risk.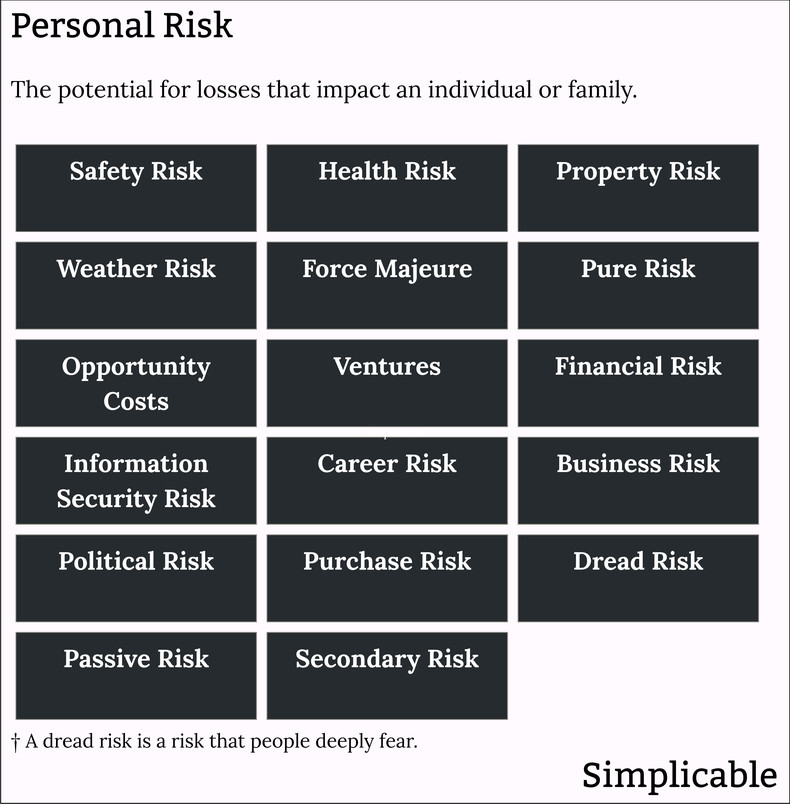
Overview
The risks to individuals, families and households such as health, safety, financial and property risk.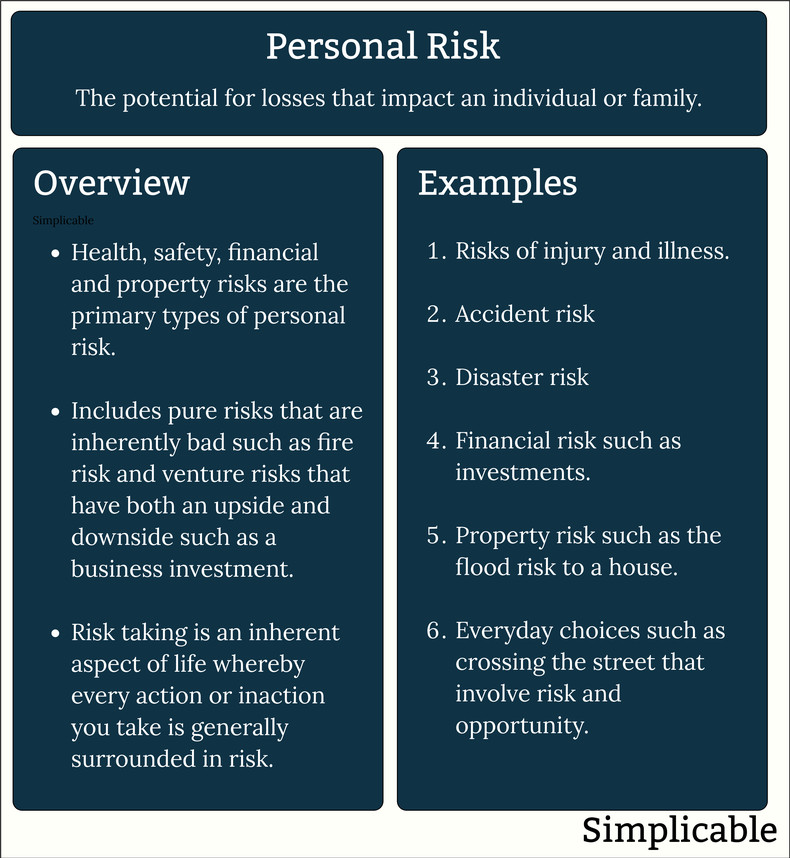
| Overview: Personal Risk | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The potential for losses that impact an individual or family. | |
Related Concepts | ||



































