Risk Tolerance
The risk taking spirit of an organization or team. In many cases, an organization specifically recruits talent for their risk taking prowess in areas such as innovation, design and sales.Checks and Balances
A culture of balancing risk taking functions with control functions. This can include structural balances such as risk management teams and lower level balances such as segregation of duties. For example, a bank where no trader can take a risk that goes unobserved by teams with accountability for risk exposure.Risk Awareness
The degree to which employees are aware of risks that are relevant to their job. For example, factory workers that know the common types of injury and health hazard associated with a production process and are well versed in risk reduction procedures.Due Diligence
The expectation that employees perform due diligence in managing risk. For example, a firm where it is understood that no project is approved without sufficient risk identification and analysis.Values
The values of an organization that are relevant to risk such as prioritizing safety, health, environmental and financial sustainability.Tone at the Top
Leadership that serve as exemplary examples of the values and diligence required to manage risk. Where tone at the top is lacking values may be viewed as flexible.Awareness & Participation
The degree to which everyone in an organization is aware of risk and participates to identify and treat risk. An organization with low participation may see risk management consigned to an isolated team that is disconnected from operational realities.Authority
The distribution of the authority to identify and treat risk. For example, a factory where any worker has authority to stop a production line for a safety issue versus a factory where such authority lies in an executive who is rarely on site. This is an element of culture because an employee may technically have authority that they feel they are unable to use due to norms and expectations.Accountability
An organization that holds leadership accountable for unmanaged risk. In some cases, leadership is rewarded for risk taking but not penalized for a lack of due diligence in managing risk. This is mostly cultural as organizations simply get in the habit of rewarding successes and hiding failure.Failure of Imagination
In some cases, an organization takes risk management seriously but has a lack of imagination in identifying risk and risk treatments. This can manifest itself as an obsession over minor risks whereby bigger risks are neglected such as a society that is focused on dread risks while ignoring large scale environmental risks. A failure of imagination can also cause a society or organization to overfocus on recent events in identifying risk. For example, a banking regulator that focuses on the managing risks related to the causes of a recent financial crisis without managing emerging threats.Resilience
Resilience is a society, organization or individual's ability to withstand stresses. Risk management can be stuck in a reactive mode of identifying emerging risks to a poorly structured and designed system. Alternatively, risk management can drive the fundamental restructuring and redesign of a society or organization to reduce risk. For example, a city can develop an emergency response plan for a flood to reduce risks to life and property. Resilience would call for the city to avoid floods in the first place with techniques such as infrastructure and land use planning.Summary
The following are common elements of a risk culture: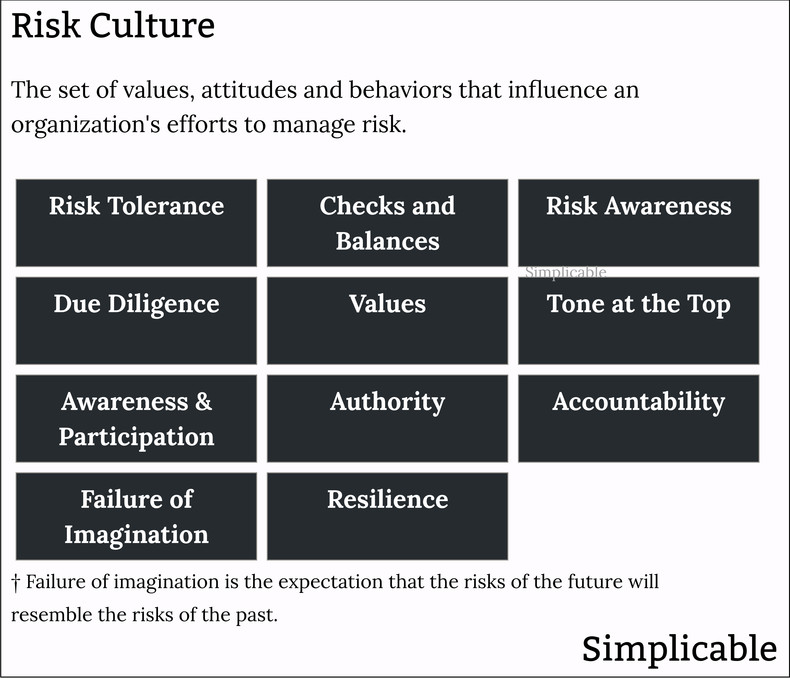
Overview
The habits, norms, attitudes and behaviors towards risk that are pervasive in an organization.
| Definition: Risk Culture | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | Elements of risk management that can't be controlled directly because they are embedded in the culture of an organization. | |
Definition (2) | The habits, norms, values and expectations of a society or organization that impact risk management. | |
Related Concepts | ||