Health
A health outcome such as the prevalence of a disease. In this case, an independent variable may be a harmful substance, a healthy food or a medicine.Safety
Safety related outcomes such as the results of a crash test on a vehicle. An example of an independent variable in this scenario is a design variation such as different materials used in key structures.Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of a building, facility, infrastructure component, machine or product. For example, testing different data center configurations to reduce the power required to cool racks.Ecosystems
Outcomes in an ecosystem such as the population of an endangered species. This would typically be a natural experiment based on independent variables that are a threat to the species.Material Properties
Material properties such as the amount of sound absorbed by a foam pad. Here the independent variable might be the formulation or structure of the foam.Choice
Consumer choice such as a taste test whereby consumers choose a product variation they prefer.Conversion Rate
Marketing experiments are often designed to improve conversion rate. This is defined as the percentage of visitors who complete a goal.Customer Satisfaction
Experiments to test improvements to products, services or customer experience are often measured with customer satisfaction as the dependent variable. For example, a hotel may experiment with two different models of interior design for its rooms to gauge customer satisfaction with their stay.Efficiency
Experiments with business processes, practices and facilities are often measured in terms of efficiency. For example, an experimental change to a production line may be measured in terms of unit cost as the dependent variable.Overview
The variable of interest to an experiment that is predicted to change in response to change to the independent variable.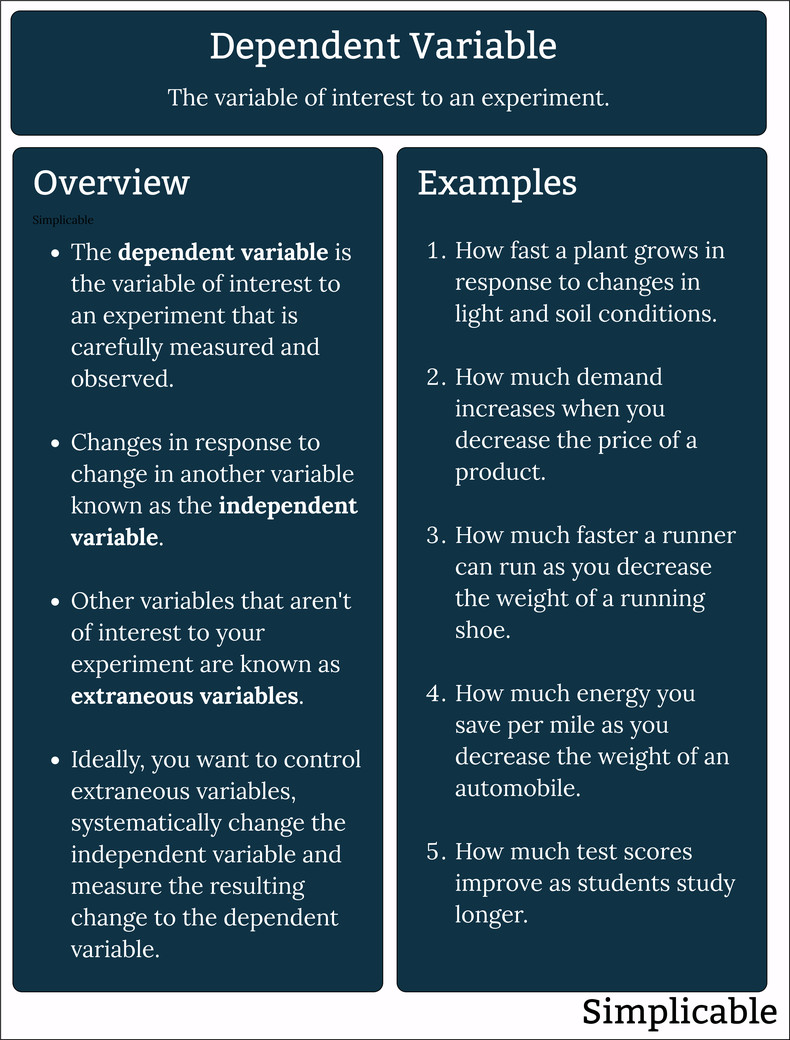
| Definition: Dependent Variable | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | A measurable result of interest in an experiment. | |
Definition (2) | A variable that is predicted to change with changes to independent variables in an experiment. | |
Related Concepts | ||