Charities | City Governments |
Cultures | Education Systems |
Families | Financial Systems |
Firms | Healthcare Systems |
Industries | International Organizations |
Justice Systems | Languages |
Legal Systems | Markets |
Media Organizations | Military Organizations |
Monetary Authorities | National Governments |
Non-Profit Groups | Organized Labor |
Political Parties | Regional Governments |
Regulatory Agencies | Religions |
Research Organizations | Space Agencies |
Special Interest Groups | Traditions |
Transportation Systems | Universities |
Government Institutions
Structures established by governments to administer a society and provide public services.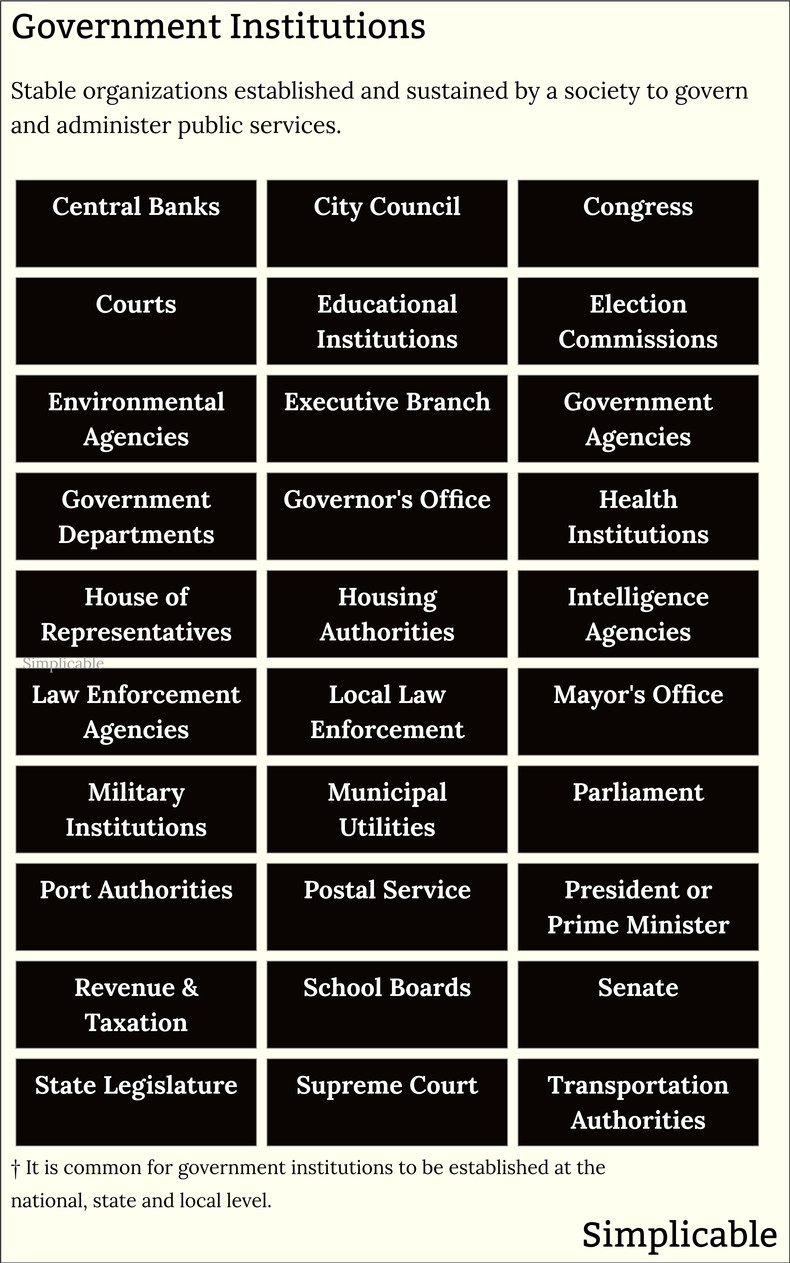
Social Institutions
Systems, structures and other enduring elements of a society that serve a social purpose.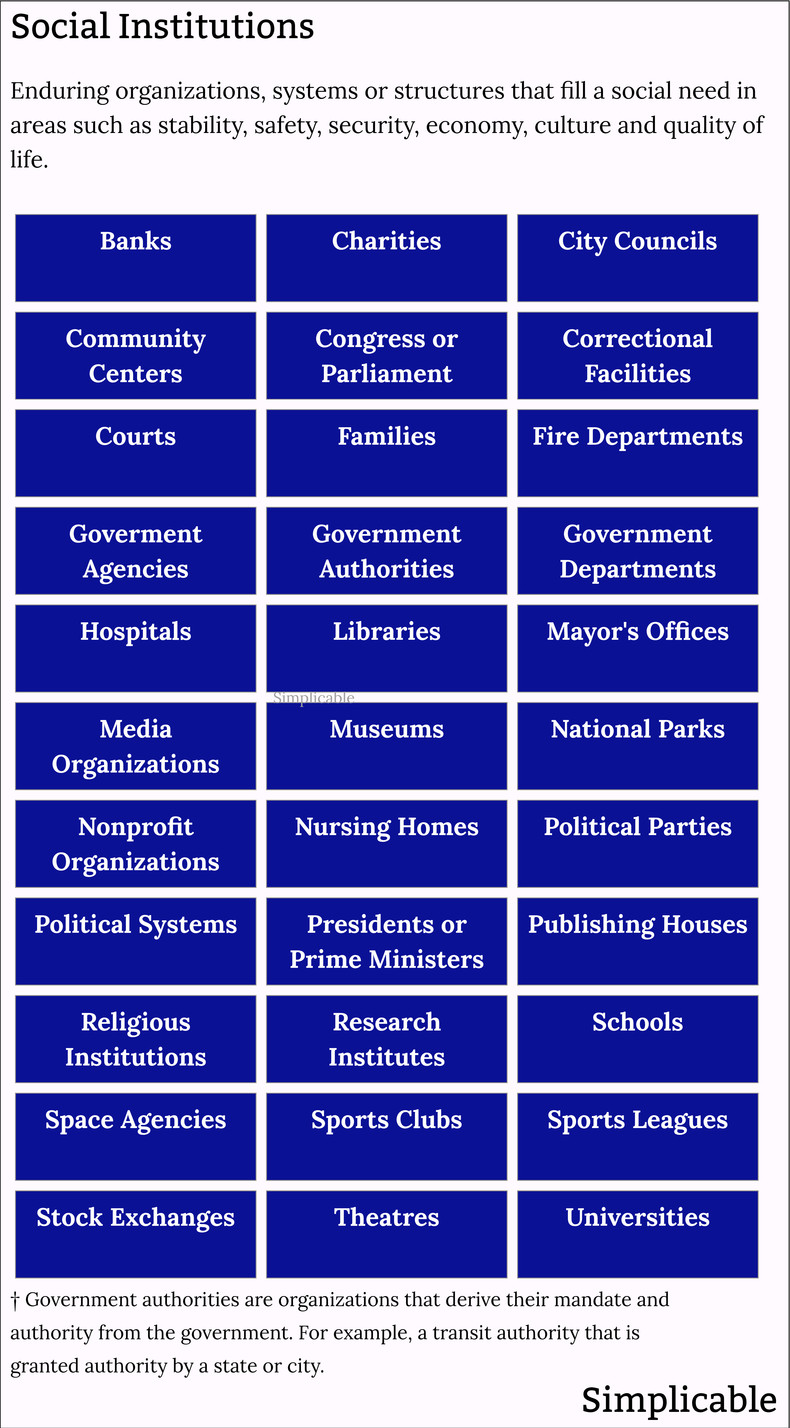
Media Institutions
Media organizations, platforms and channels that are sustained over time such that they provide stability to a communication environment such as a society.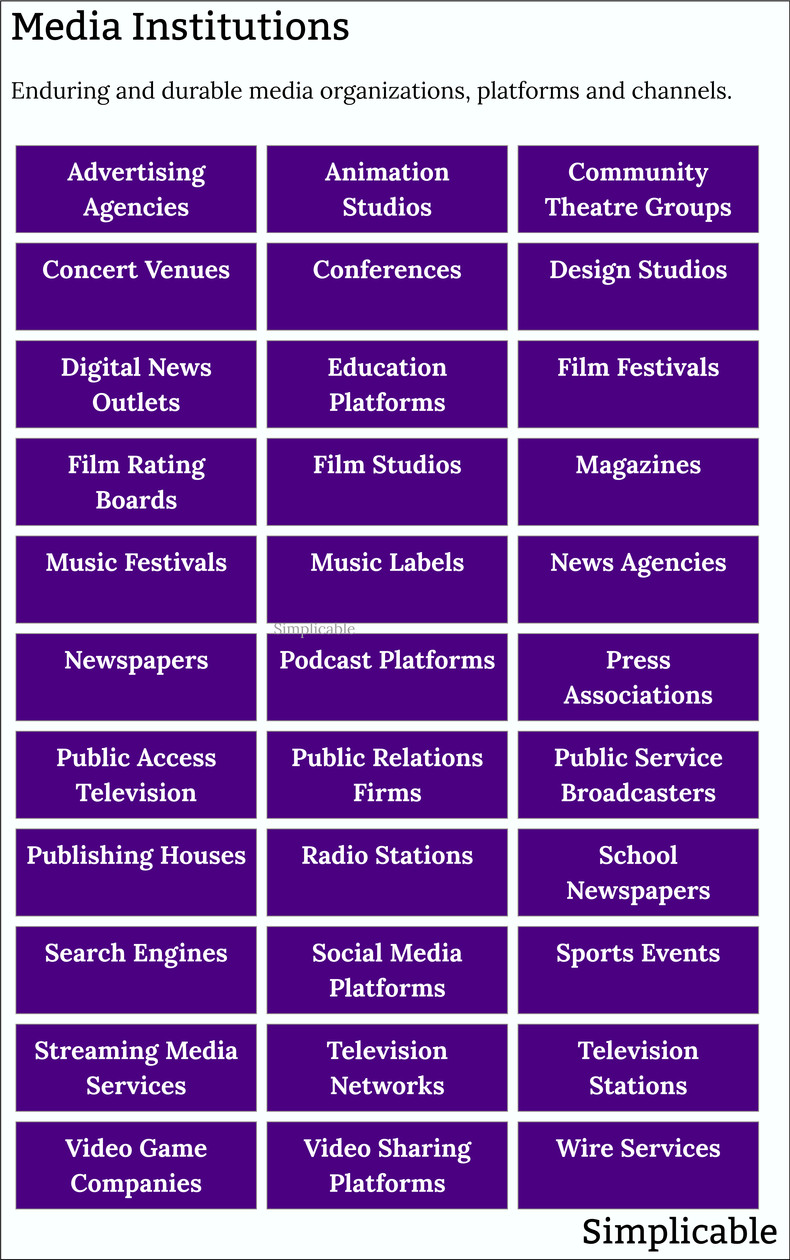
Economic Institutions
Complex and sustained structures, large and small, that play an important role in the economy.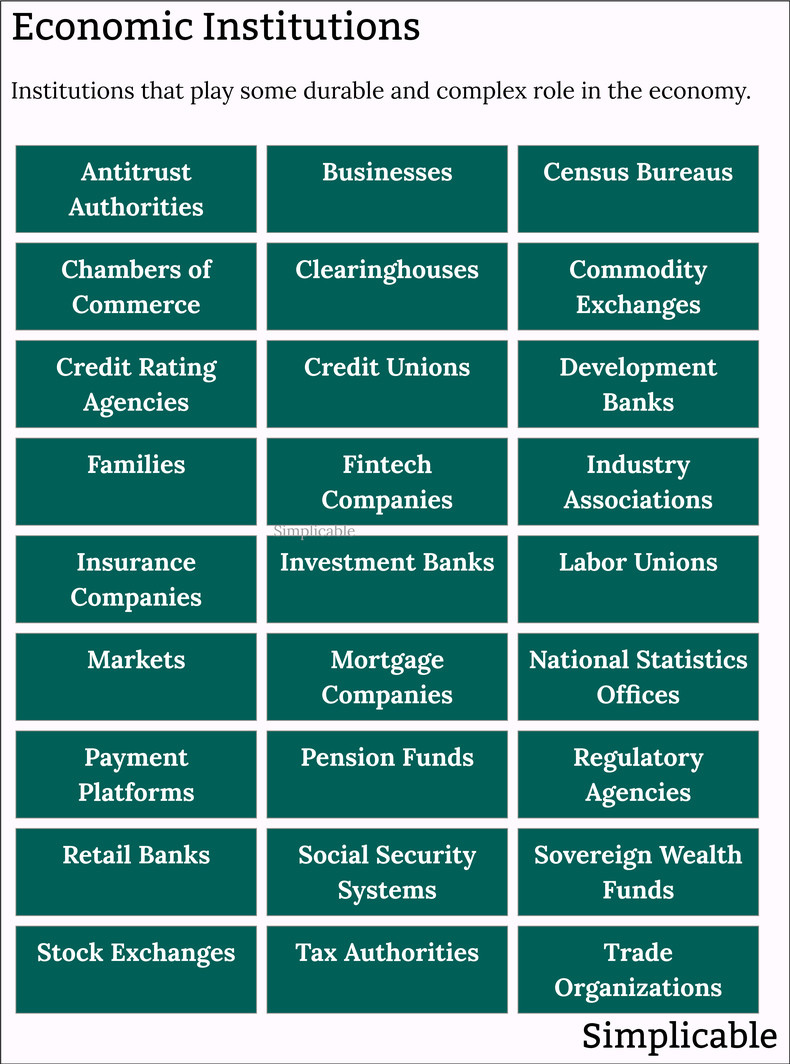
Community Institutions
Local institutions that benefit the quality of life of a city, town or neighborhood in a sustained and durable way.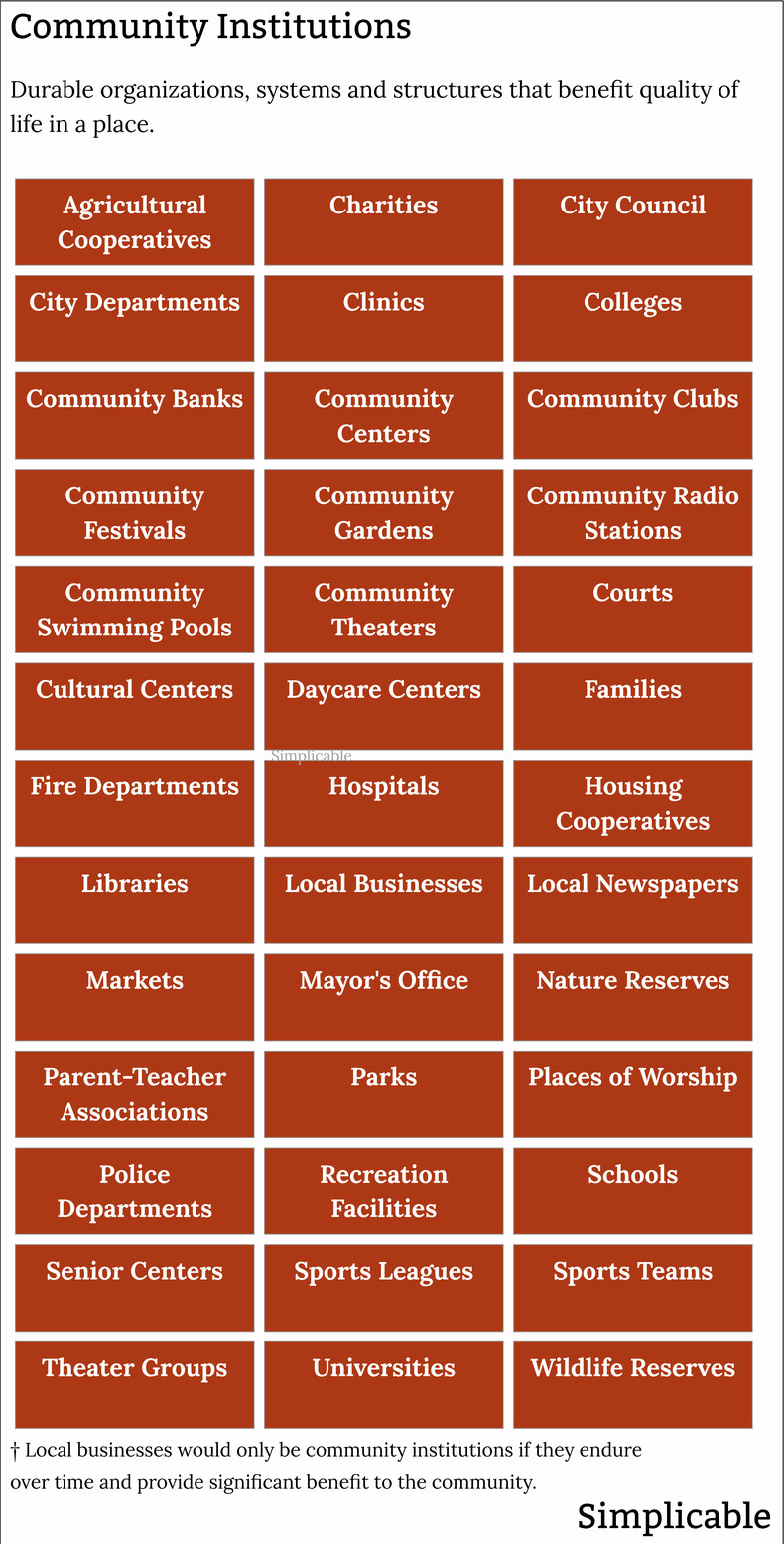
Cultural Institutions
Institutions that are important to a culture. This includes places that are important to a living culture such as a music venue that's important to a music scene.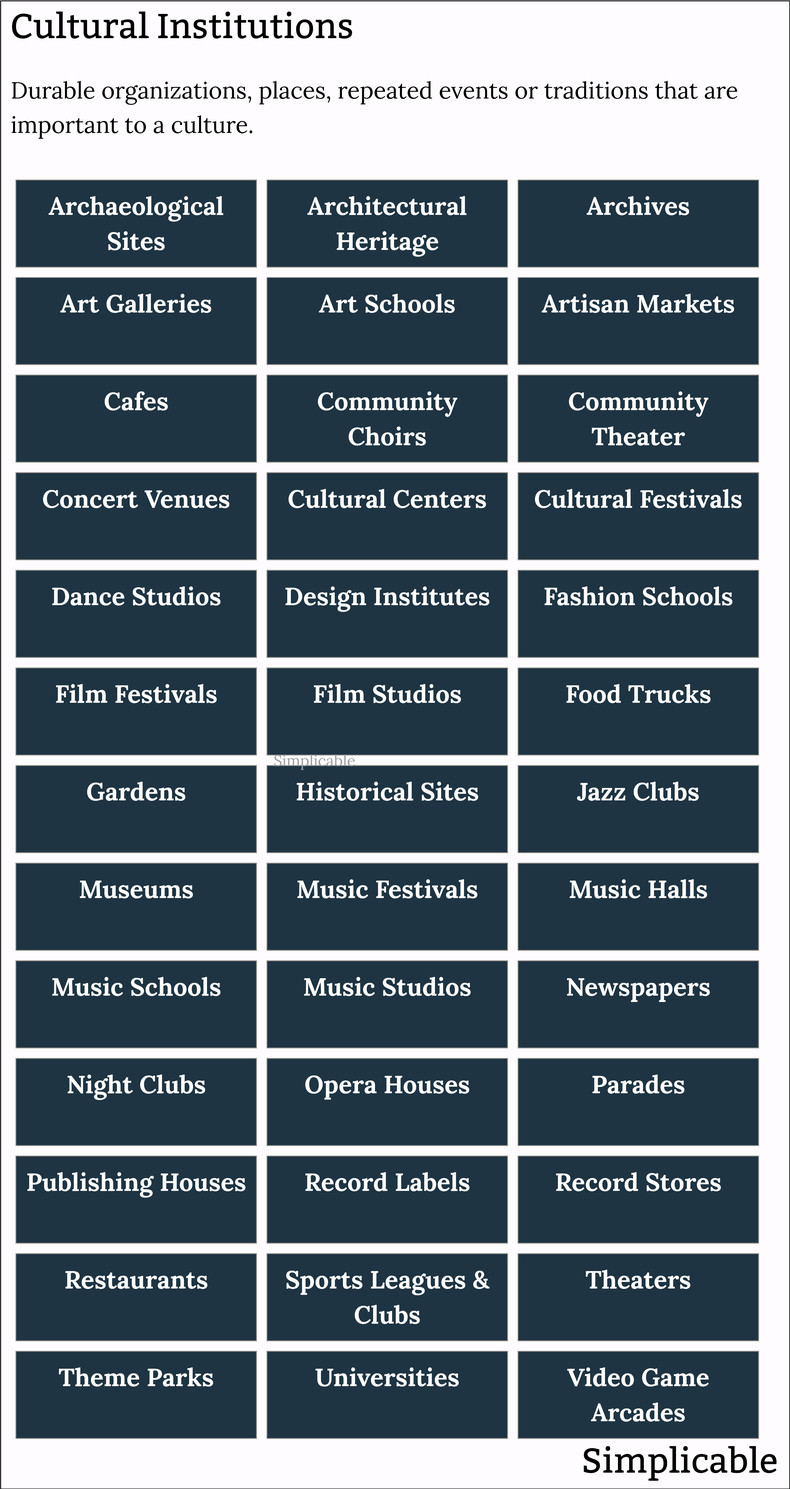
Summary
Institutions are enduring elements of society that provide stability. These can be government, non-profit or business organizations. Institutions can also be intangible non-organization things such as a tradition.
Notes
Institutions can be viewed at many levels. For example, the top level of "government" can be decomposed into dozens or perhaps hundreds of large institutions.| Overview: Institutions | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Complex and enduring features of societies. | |
Related Concepts | ||