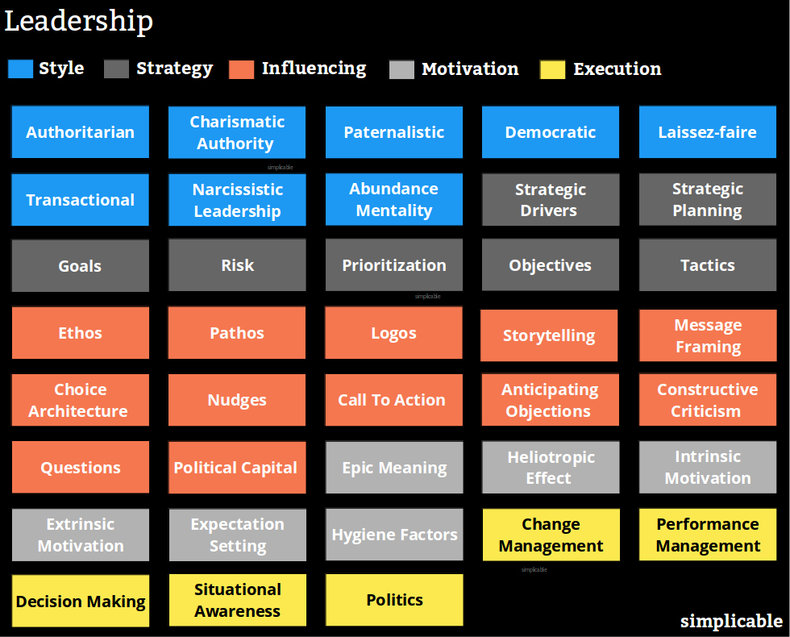
Style
Leadership style is the basic approach of an organization, team or individual to setting direction and getting people to follow it.Leadership that relies solely on formal authority and a rigid system of command and control. This requires systems, process, rules, regulations and punishment for non-compliance. | |
A leader who extends their influence beyond their authority with the force of their personality. | |
A leader who views their team much like a family whereby they help members to grow and reach their potential. This can result in an extensive professional network of loyal allies over time. | |
Democratic | A leader who orchestrates social processes as opposed to dictating a direction. |
Laissez-faire | A leader who gives individuals freedom to achieve a set of goals as they see fit. This suits creative processes. A laissez-faire leader serves as a role model or mentor and leads by example. |
Transactional | Influencing and motivating with reward and punishment. |
Narcissistic Leadership | A leader who is only concerned with themselves. For example, a leader who is willing to follow irrational strategies that damage an organization if it enhances their own position. Narcissistic leaders have poor relationships with almost everyone and are in a constant state of conflict. They gain influence by developing a reputation for being "tough." |
The opposite of narcissistic leadership. Leaders with an abundance mentality believe that most situations are win-win. For example, the belief that if a leader does what is good for the organization and their team they will reap rewards. Focuses on results over political battle. Tends to sideline people who are negative, dramatic or unproductive. |
Strategy
Strategy is a plan for the future. If leaders get people moving in the same direction, strategy serves as the direction.Identifying the forces that shape strategy such as customers, competition, technology and regulations. | |
The process of developing a strategy. | |
Developing a set of goals. | |
Prioritizing strategies to recognize constraints such as time, budget and feasibility. | |
Identifying risks and considering probability and impact. | |
Breaking strategies into a series of objectives and using these to divide work between teams and individuals. | |
Taking advantage of fast moving situations to take quick wins. Tactics are essentially the flexible element of strategy that responds to realities that don't match your plan. |
Influencing
Influencing is the process of selling goals, strategies, objectives, tactics, policies and actions to teams. Leadership often involves influencing beyond your formal authority. In other words, leadership is mostly about convincing people to follow as opposed to dictating commands.Convincing people using your credibility or authority. | |
Appealing to emotions. | |
Appealing to logic and rational thought. | |
The art of making information interesting and memorable. | |
Crafting information to influence ideas, emotions and reactions. For example, a pitch for a business case designed to generate excitement and optimism in your audience. | |
Structuring choices to influence results. | |
Using gentle suggestions to influence. | |
Directly requesting action with a concise command. For example, "give him a call tonight" or "get this fixed." | |
Anticipating negative responses and working out how you will address them in advance. | |
Finding a positive way to convey criticism. | |
Using questions as a tool of influence. | |
Building trust and goodwill in order to build up influence that can be spent when you need it. |
Motivation
If you influence people to follow direction, they still require the motivation to do well. As such, motivating people is a basic function of leadership.Giving people the sense that they are part of something that's big, important and positive. | |
The tendency for people to want to live up to positive views people have of them. People will tend to perform well when you recognize their talents, ambitions and unique contributions. | |
Giving people a sense of purpose, relatedness, challenge and creative freedom in the hopes that they will feel intrinsically motivated to do well. | |
Structuring things to be win-win so that people feel they will be rewarded if they do well. | |
Setting clear expectations for work including requirements, objectives, schedule and quality expectations. | |
Hygiene factors are basic things that team members expect. Such factors don't add to motivation when they are satisfied but severely reduce motivation when they aren't satisfied. |
Execution
Leadership practices that ensure that strategies are implemented.The process of leading change. This is often focused on defeating resistance to change with communication. It also involves sidelining people who aren't being helpful and empowering those who are moving the change forward. | |
Regularly evaluate performance based on the expectations that were communicated. Quickly and candidly communicate low performance to give people a chance to improve. | |
Decision making is one of the basic functions of leadership. Providing reasonable and timely decisions helps people to move in a common direction. | |
Leaders are typically expected to know what is happening in their industry, organization and amongst customers. | |
Leaders represent their team with external groups. This often involves engaging in office politics such as diplomacy and negotiation to earn wins for your team. |
| Overview: Elements Of Leadership | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The practice of getting groups of people moving in the same direction towards common goals. | |
Related Concepts | ||