Morals
Standards of right and wrong such as the principle that you won't work for a firm that has a poor environmental record.Mastery
The standard that you will do what it takes to reach the top of your profession, or at least realize your full potential in an area that is important to you.Self-discipline
The principle that you concentrate for long periods of time when there is something to be completed.Work Ethic
The rule that you work a reasonable number of hours each day.Work-Life Balance
The principle that work is time-boxed so that you can live a full life.Work Quality
The philosophy that you be happy with the quality of your work before submitting it.Social Comparison
The rule that you neither be jealous nor arrogant and that you focus on correcting your own faults over rebuking others.Good
The principle that you try to be a good person and perform random acts of kindness.Wonder
The philosophy that you try to see the wonder of life and pursue senseless acts of beauty.Humility
The rule that you not virtue signal and remain humble about your good deeds and attributes.Taking the High Road
The principle that you not change your behavior to match the poor behavior of others.Tolerance
The standard that you treat people equally and be tolerant of differences between people.Honesty
The principle that you tell the truth.Authenticity
The rule that you be yourself and not try to pretend to be anything else.Culture
Adopting elements of culture as a rule. For example, a parent who adopts the practice of cooking a proper meal and eating as a family each evening.Norms
Committing to certain norms of behavior. For example, the principle that you will try to avoid excessive noise in the evenings and early morning so as not to disturb your neighbors.Appearance & Hygiene
Standards of person hygiene and appearance such as the rule that you will pursue your personal sense of style and dress well in the office.Risk Taking
The principle that you will take calculated risks and do things that make you a little nervous in order to build resilience and grow.Risk Avoidance
The rule that you won't take excessive, naive or destructive risks that are counterproductive.Introspection
The rule that you will review your own behavior each day to identify your failures and try to improve.Intuition
The rule that you will remain mindful of your intuition and correct things that don't feel right.Optimism
The rule that you will try to view people and situations with a sense of optimism.Pragmatism
The principle that you will deal with the world as it is in reality and not retreat into inflexible idealism whereby you expect the world to bend to you.Sidelining
The rule that you will sideline negativity and not allow the negativity of others to become a dominant force in your life.Unaffectedness
The standard that you will try not to worry about what others are thinking without going so far as to ignore valuable criticism.Quality of Life
Quality of life standards such as the rule that you will avoid any work that involves a long daily commute.Health & Fitness
Health related standards such as the rule that you try to exercise each day.Forgiveness
The rule that you try to free yourself of resentment and bitterness and consider forgiving others.Gratitude
The standard that you will approach life with a sense of gratitude.Loyalty
The rule that you will be loyal to those who you love.Negative Personal Standards
Personal standards can be used in negative ways that are likely to backfire and cause painful failures. For example:
Elitism
Elitism such as a CEO who has a standard that they not waste time talking to anyone under the director level.Selfishness
Setting "high standards" that you don't apply to yourself but rather apply to other people.Biases
Setting biased standards for who you are willing to accept as a social equal.Perfectionism
Setting high standards for your work and the work of others such that you become inefficient, slow, unresponsive and inflexible.Social Isolation
Setting social standards that isolate you from the world. For example, an academic at the top of their field who can't stand socializing with those who don't understand their work despite the fact that their work is obscure.Mediocrity
Standards can be used as an excuse to avoid change, risk taking and creative tension. For example, an administrator who adopts the principle that all rules are to be followed at all times without exceptions no matter how illogical the application of rules may become.Summary
Personal standards are rules that you adopt for your future behavior, problem solving and decision making. These are designed to align your behavior to your ideals but can have a dark side as an excuse for inflexibility.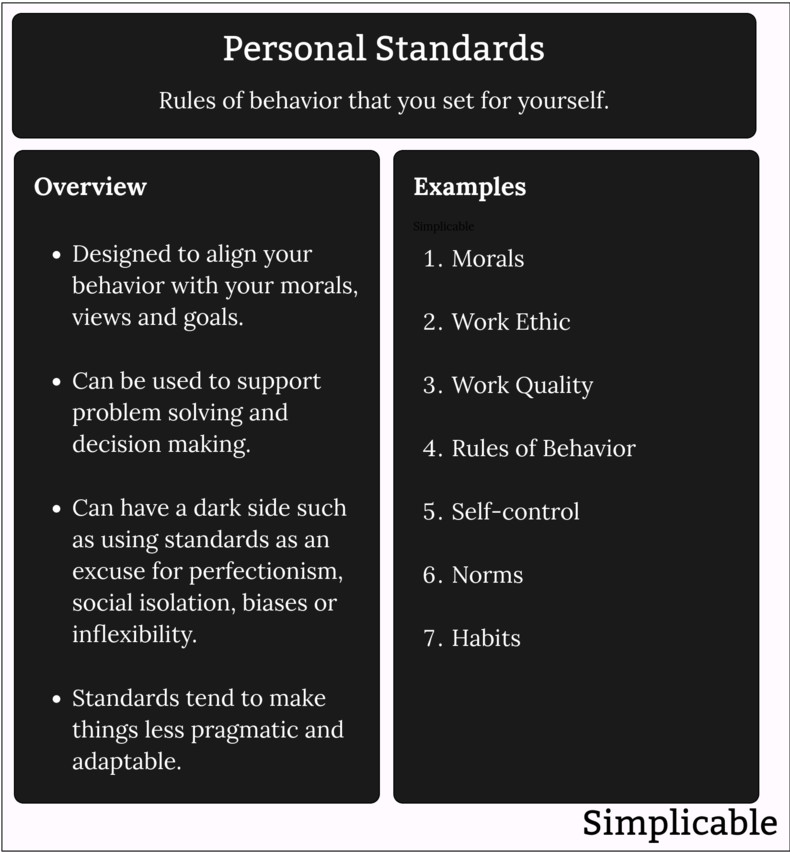
Notes
Standards do not bend to the behavior and expectations of others. For example, if you have set a high standard for your work ethic you don't abandon it simply because others are slacking.It is the inflexible nature of standards that can make them problematic as they can reduce the dynamism of an individual.| Overview: Personal Standards | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Rules of behavior that you set for yourself. | |
Related Concepts | ||