Acting | Adventure sports |
Analysis | Archery |
Architectural design | Astronomy |
Beauty artistry | Business acumen and commercial awareness |
Calligraphy and lettering | Carpentry |
Character design | Chemistry |
Choreography | Coaching |
Coding | Community building |
Cooking | Costume design |
Crafts | Creative writing |
Cultural activities and traditional crafts | Customer advocacy |
Customer service | Dancing |
Diy projects | Drawing and illustration |
Environmental action | Establishing credibility and trust |
Experiments | Explaining the complex in simple terms |
Fashion design | Film making |
Fishing | Game design |
Gardening | Geography and maps |
Geology | Graphic design |
Helping others | Housework |
Influencing and persuading others | Interior design |
Journalism | Languages |
Leading teams and groupwork | Listening |
Magic tricks | Makeup artistry |
Management | Martial arts |
Mathematics | Media production and editing |
Music composition and performances | Music instruments |
Nature talents such as botany | Negotiation |
Origami | Outdoor activities such as hiking |
Painting | Performance art |
Pet training | Photography |
Physics | Presentations and presentation design |
Problem-solving | Public speaking |
Quilting | Relationship building |
Reliability and diligence | Research |
Resolving conflicts | Resourcefulness and inventiveness |
Running | Sailing |
Sales and marketing | Science |
Self-improvement such as time management | Set design |
Singing | Skiing and snowboarding |
Solving problems with design | Songwriting |
Space related pursuits and interests | Sports and athletics |
Storytelling | Strategic thinking and planning |
Studying and test-taking | Swimming |
Teaching | Technology |
Theater directing | Traditional arts |
Traditional dance and performances | Typography |
Video games | Visual design |
Visual effects and animation | Wayfinding, navigation and orienteering |
Woodworking | Writing non-fiction |
2024 Additions

Aerial photography | Art direction |
Artificial intelligence | Creative vision |
Cybersecurity | Data curation |
Data science | Digital art |
Hybrid work fluency | Immersive experience design |
Machine learning | Market research |
Natural language processing | Risk management |
Robotics | Sound design |
User experience design | Videography |
Visual communication | Voice acting |
Key Talents
The following talents are foundational such that they are valuable to the pursuits above.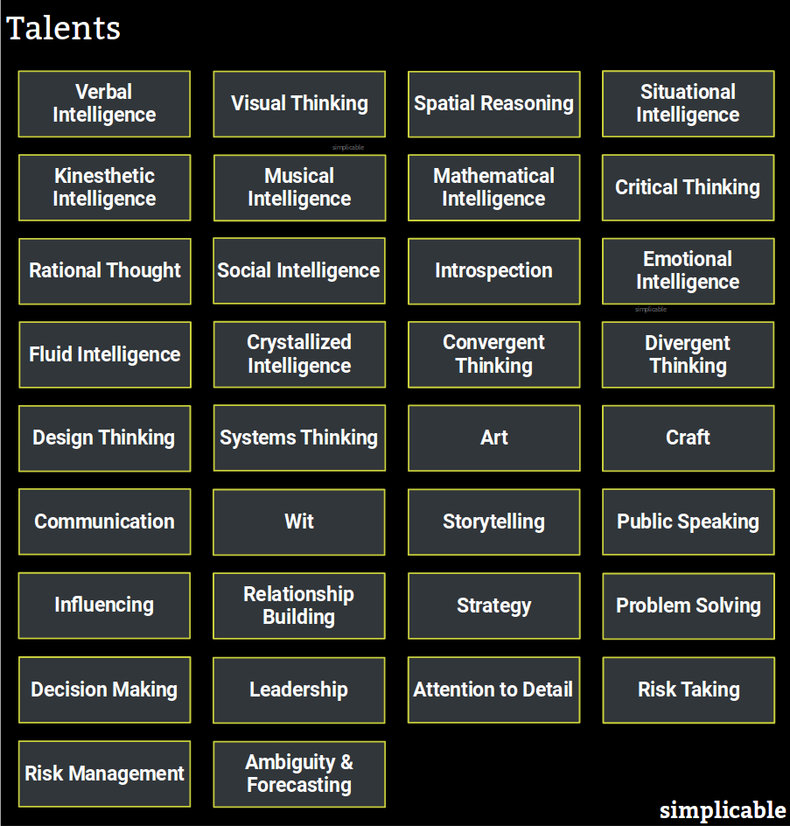
Verbal Intelligence
The ability to reason using a natural language such as English, Spanish or Mandarin Chinese. This includes thought processes based on language as people commonly think with words. As such, verbal intelligence has a wide range of applications in areas such as communication, strategic thinking, decision making and problem solving.Visual Thinking
Reasoning using visualization. As with verbal intelligence, this is applicable to a wide range of problem spaces and includes thought processes and communication. For example, the ability to make a production line more efficient by visualizing the process on paper to identify inefficiencies.Spatial Reasoning
Perception of 3-dimensional space and the ability to solve problems in areas such as pattern recognition, navigation and design. For example, a product designer who is able to make the interior of a vehicle feel roomy despite space constraints.Situational Intelligence
A talent for handling fast moving and complex situations such as a chaotic video game.Kinesthetic Intelligence
Perceptual-motor skills that allow an individual to use the body with precision and grace. This is the basis for talents in areas such as sports, dance and acting.Musical Intelligence
Musical intelligence is considered a foundational type of thought that is independent of verbal, visual and kinesthetic intelligence. This is related to talents in music composition and performance.Mathematical Intelligence
Talents related to math and logic.Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is any thought process that is disciplined, objective and systematic. For example, the ability to see logical flaws and biases in your own analysis in order to improve it.Rational Thought
Rational thought is the ability to think logically and to apply reasonable thinking to human complexities that aren't always completely logical such as emotion and culture. In other words, rational thought is thinking that can be viewed as reasonable within the context of a society and culture.Social Intelligence
The ability to navigate society and cultures. This goes beyond intelligence as it benefits from character traits such as patience, emotional maturity, kindness or fearsome competitiveness. For example, the ability to get along with difficult neighbors by taking the high road.Introspection
Introspection is intelligence related to the self such as an ability to understand and improve your own morality, character, personality, thought processes, knowledge, emotions and performance.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability to read and respond intelligently to emotion. For example, a customer service agent who can see that an customer is upset at a perceived injustice who is able to influence the customer to reduce these negative emotions and reach a solution that strengths the customer relationship.Fluid Intelligence
Fluid intelligence is the ability to adapt your thinking and acquire new knowledge. For example, a musician who appears to easily acquire the ability to play new instruments.Crystallized Intelligence
Crystallized intelligence are acquired abilities and knowledge such as a musician who knows how to play 5 instruments due to years of experience.Convergent Thinking
Convergent thinking is the ability to find the correct answer to problems based on existing systems and methods. For example, a structural engineer who can correctly calculate the loads a building can sustain in an earthquake.Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking is the ability to use creativity to develop new and non-obvious things such as a structural engineer who develops a new method for upgrading old buildings to be earthquake resistant.Design Thinking
Design thinking is the ability to solve problems using design. For example, a hotel manager who solves customer satisfaction problems by designing a new incentive program for customer service staff.Systems Thinking
Systems thinking is the ability to think through the impacts of change on complex systems to develop solutions to problems that don't have unintended consequences. For example, a solution to an environmental problem that doesn't cause other environmental problems.Art
Artistic talent is the ability to create works of aesthetic value. For example, a painter who is eventually recognized for creating priceless works of art. Artistic talent is a strange domain whereby talent often goes unrecognized for an extended period of time. This is due a tendency for art to defy criticism and valuation.Craft
A talent for creating objects of value with your hands.Communication
Communication related talents such as writing, speaking, reading comprehension and listening.Wit
Communication skills at speed that allow you to say something intelligent or humorous when the moment presents itself.Storytelling
Storytelling is the ability to make information interesting. This applies to communication of fact and the crafting of fiction.Public Speaking
A talent for communicating to groups such as the only speaker at a conference who wakes an audience up and invigorates them with ideas, emotion and humor.Influencing
Influencing is the process of changing the ideas, emotional state and actions of others. For example, a crisis negotiator who is able to exert a calming effect on someone who is in an agitated mental state.Relationship Building
A talent for establishing and sustaining productive relationships with others.Strategy
Identifying effective plans to achieve goals in an environment of competition and constraint. For example, an entrepreneur who quickly gains market share against a larger competitor by serving niche markets that are ignored by the larger firm.Problem Solving
A talent for solving problems such as an individual who is able to quickly determine the root cause of technical issues and design a fix.Decision Making
The ability to make reasonable and timely decisions in an environment of ambiguity, risk and opportunity.Leadership
A talent for leading groups to achieve common goals, solve problems and work together productively and creatively.Attention to Detail
The ability to work with diligence to produce high quality work.Risk Taking
A talent for taking calculated risks such as a trader who has demonstrated an ability to identify and execute trades with a highly favorable risk-reward ratio.Risk Management
Talents related to the identification, analysis and treatment of risk such as a stunt coordinator in the film industry who is known for their ability to make the most daring of stunts safe.Ambiguity & Forecasting
Dealing with ambiguity and the ability to develop reasonable estimates and forecasts. For example, an entrepreneur who is known for entering markets just as they are about to experience explosive growth and exiting before they fall into decline.| Overview: Talent Examples | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Mental strengths that are useful to a pursuit, art, profession, activity or task. | |
Related Concepts | ||