Concept
A concept is any idea that has no specific physical manifestation. For example, a brick is not a concept because it physically exists but respect is a concept because it is completely intangible.Emotions
Abstractions are mostly concepts with the exception being abstract feelings. An emotion can directly relate to physical reality such as a sense of pleasure you get from eating ice cream. Emotions can also be extremely detached from your current physical experience. For example, a sense of angst driven by a desire for a life of purpose.Imagination
Imagining events, people, concepts, things and experiences that don't physically exist is completely based on abstraction.
Synthesis
Synthesis, also known as design, is the process of creating new entities that never existed before you imagined them and created them.Language
Most language is abstract in nature with the exception being nouns and verbs that describe physical things and actions. For example, words like "freedom" or "the" have no direct physical manifestation. It is common for humans to process a large number of abstract concepts every minute.Generalization
Generalization, also known as compression, is the process of mapping many things to a single concept. For example, mapping thousands of events to the concept of experience. This is a foundational element of human thinking.First Principles
A first principle is a rule, theory, law or guideline that has broad explanatory power. For example, the principles of gravity that explain why things fall towards the Earth.Analogy
Analogy is the use of comparison to develop meaning.If people were like rain, I was like drizzle and she was a hurricane.
― John Green
Visual Abstraction
Visual abstraction is the use of pictures to understand or communicate abstract concepts and emotion.Abstract Art
Any art that intentionally differs from reality can be considered abstract.
Computer Science
Abstraction in computer science is the practice of reducing complexity by arranging code and data into a conceptual framework. For example, a software developer may develop an object called Document that is abstract such that it can't be used directly but instead defines common characteristics of entities such as a HtmlDocument. In this case, the HtmlDocument may inherit functions and structure from Document that are common to all documents such as an data field called author.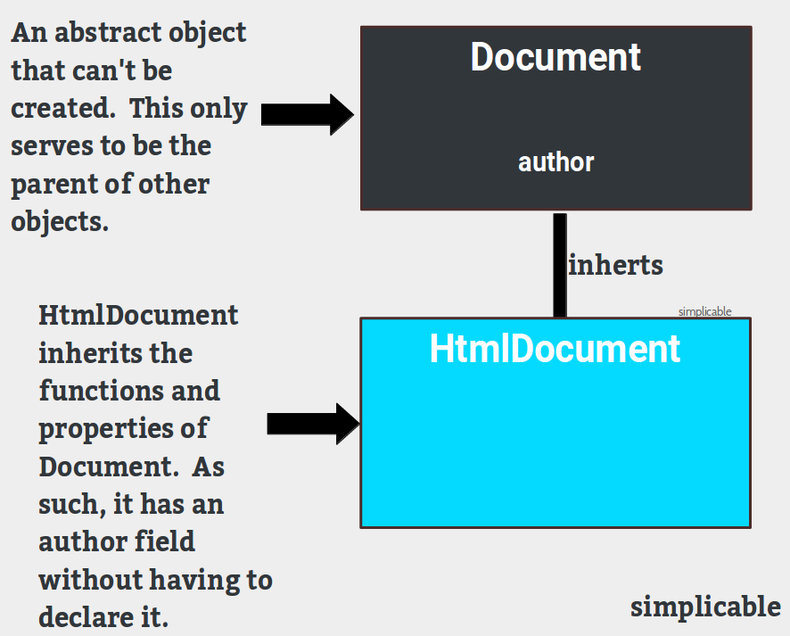
Labeling
Humans understand things quickly but inaccurately but labeling things with abstract concepts. This is suboptimal but fast and lazy. For example, an individual might label another person a "jerk" based on their facial expression without evaluating the reasons the person might have that look on their face.Overview
Abstractions are information and visualizations that differ from concrete physical reality. Humans mostly experience abstractions and they are common in our languages, thinking, emotions, thoughts, media, stories, communications, analysis and perceptions.
Discussion
The human experience is mostly about abstractions. Even our senses such as color vision are abstractions. Color doesn't exist beyond perception although it somewhat corresponds to wavelengths of light. This mapping is an abstract representation of physical reality. For example, humans perceive unbelievably colorful light from many wavelengths as white.| Summary: Abstraction | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The process of thinking or communicating using concepts that differ from concrete reality. | |
Related Concepts | ||