Analytical Thinking | Applying Principles |
Argument Formation | Assessing Arguments |
Bias Recognition | Big Picture Thinking |
Cognitive Flexibility | Comparative Thinking |
Conceptual Thinking | Conceptual Understanding |
Considering Alternatives | Counterfactual Thinking |
Data Analysis | Decision Modeling |
Deductive Reasoning | Design Thinking |
Developing Explanations | Drawing Conclusions |
Empirical Thinking | Evaluating Sources |
Evaluation | Fallacy Detection |
Hypothesis Formation | Inference |
Intellectual Curiosity | Interpretation |
Logical Analysis | Mathematical Thinking |
Objective Reason | Openness |
Pattern Analysis | Problem Solving |
Questioning Assumptions | Rational Thinking |
Reasoning | Reflection |
Scientific Reasoning | Skepticism |
Sustained Attention | Systems Thinking |
Objectivity
First and foremost, critical thinking requires objectivity, the process of seeking authoritative evidence and weighing such evidence in an honest way that is not motivated by an agenda. For example, a news reporter who reports on an environmental problem using authoritative scientific publications as a source without giving much weight to non-authoritative and biased sources.Open-Mindedness
Critical thinking requires open-mindedness such that you form a judgement as a process of exploration as opposed to starting with a conclusion and seeking to prove it based on selected evidence.Socialization
Critical thinking does not hide from criticism but instead seeks validation of ideas by socializing them. For example, a researcher who seeks peer review of a theory in order to find the flaws in their thinking.Emotion & Culture
Critical thinking need not be robotic thinking that is emotionless and cultureless. For example, a film reviewer may suspend disbelief to see an film much as the audience sees it. Otherwise, a film critic many end up being overly focused on technical execution and miss the point of a film altogether.Logic
Applying logic such as inference. Another critical aspect of logic is the detection of logical fallacies. Fallacies can be extremely difficult to spot and can often be found in the work of highly intelligent individuals. As such, a critical thinker may study known fallacies in order to improve their thought processes.Skepticism
Skepticism is a questioning attitude that bravely challenges ideas that aren't well supported by evidence. A purely skeptical attitude doesn't tend to be creative and a purely optimistic attitude isn't conductive to identifying errors. As such, critical thinking may use both optimistic and skeptical frames of mind in order to both generate non-obvious ideas and validate them.Abstraction
Developing and applying abstract ideas. For example, using an analogy to model a problem.Thought Experiment
The use of abstractions to experiment with ideas. For example, Einstein used a thought experiment about a street car moving away from a clock tower at the speed of light to develop his theory of special relativity. This thought experiment resulted in a moment of serendipity as Einstein realized that time would appear to be stopped from the perspective of people on the street car looking back at the clock.Analysis
Analysis is the systematic process of breaking information down into its component parts to develop knowledge. For example, a salesperson who carefully analyses the content of conversations that result in a no and yes answer from the customer to determine where they are going right and wrong.Formal Methods
The use of formal methods such as mathematics to calculate values or estimate future probabilities.Design Thinking
Design thinking is the application of design to solve problems that aren't traditionally considered design. Design is a process of synthesis that creates what didn't previously exist. For example, a critical thinker may design a set of decision criteria in order to make a decision.Systems Thinking
Systems thinking is the process of considering the broad impact of things. For example, an engineer who is not lost in technical details but can consider complex systems in their designs such as society, culture, human factors, ecosystems, risk and business operations.First Principles
Using foundational principles that you know to be true or that you hold to be true in order to infer new knowledge from them. For example, a designer who uses the principle of least astonishment to make design decisions for a user interface.Summary
Critical thinking is a common way to describe all the thinking processes that are required for academic work. This includes evaluating sources, assessing arguments, questioning assumptions and developing analysis, evaluations, hypotheses and reasoning.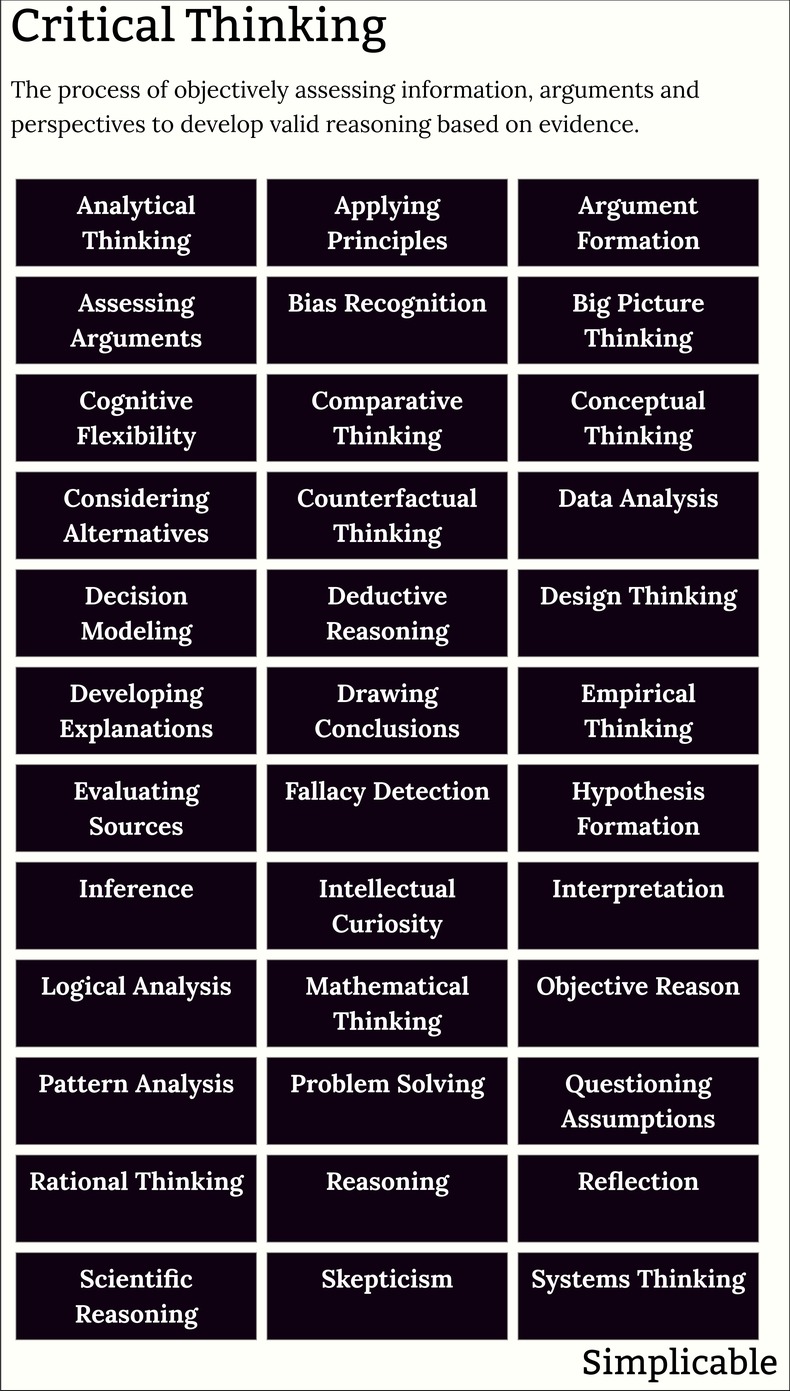
| Overview: Critical Thinking Examples | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | Thinking that questions itself. | |
Definition (2) | The process of objectively assessing information, arguments and perspectives to develop valid reasoning based on evidence. | |
Related Concepts | ||