Optimism
Forward thinking is linked to optimism, particularly the practice of viewing the problems of today as opportunities. For example, if an industry is damaging the environment, there is an opportunity to replace that industry with products and services that serve the same need but cause far less damage.Investment
Investment is the dedication of capital and labor today to strategies intended to produce future benefits. For example, a student who invests their time and money into education in order to improve their future earning prospects.Prediction
Efforts to predict the future in order to adapt strategy and decisions. For example, a technology enthusiast who wants to be the first to own a new technology but also wants to choose the technology that everyone else will be using in five years.Agent of Change
An individual who shapes the future in some way. For example, an inventor who develops a method of transport that is faster and more efficient than existing methods. Such an inventor is only an agent of change if their idea is actually implemented.Risk Management
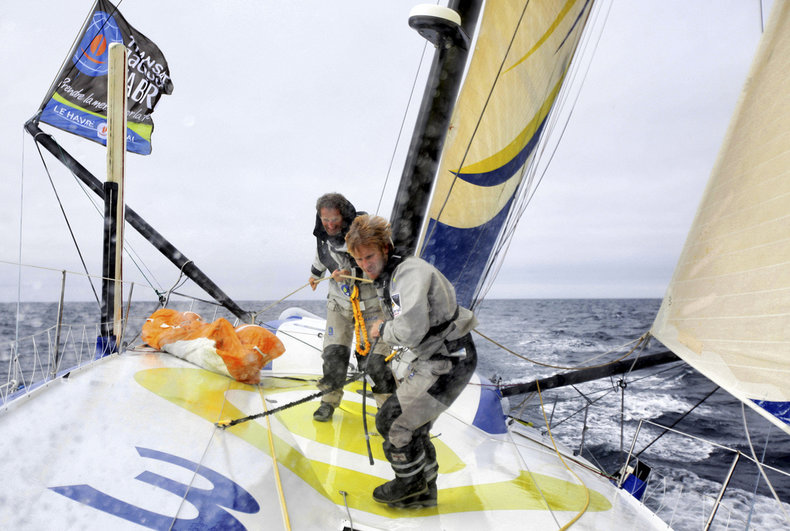
The process of identifying and treating risk. Risks are future losses that have some probability of occurring. For example, a sailor may identify the risk of severe weather and take steps to avoid such weather. They may also invest in equipment and training that reduces the likelihood of a poor outcome in bad weather.Resilience
The development of systems to be fundamentally resilient to stress such that they are likely to survive into the future. Resilience is similar to risk management with the difference being that resilience doesn't anticipate specific risks but instead adopts approaches that reduce a broad range of risks. For example, a sailboat that is designed to be extremely strong such that its main components are practically unbreakable.Anticipating Objections
The practice of planning for resistance and criticism of your ideas in advance to mount a more effective defense. For example, a salesperson who brainstorms the reasons a customer might resist a deal. This allows the salesperson to prepare effective pitches to overcome such objections.| Overview: Forward Thinking | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The process of anticipating the future to improve strategies and decisions. | |
Related Concepts | ||