Counterfactual Thinking
Counterfactual thinking is the process of considering how the past could have been different. This includes instances of staircase wit whereby you regret not saying something more intelligent in a particular situation. Counterfactual thinking also includes thoughts of regret and gratitude for the past.
Simulations
Imagining how the future will play out as a means of practice. For example, a public speaker who imagines the audience's reaction to parts of their speech such as a joke that might bomb.
Play
Play is the work of children as it helps to develop the mind. A key element of play is exercising the imagination such as a child who imagines they are a superhero. Play is also known to benefit the productivity, creativity and happiness of adults. Adult forms of play tend to be less imaginative and more competitive than play that comes naturally to children. However, adults do engage in imaginative forms of play such as video games, cosplay and improvisation.
Perception
Imagination plays a role in perception as the brain actively interprets information from the senses by making guesses that require the imagination. This can be seen in people's reactions to 3d chalk art whereby they may automatically imagine a 2d image is 3 dimensional.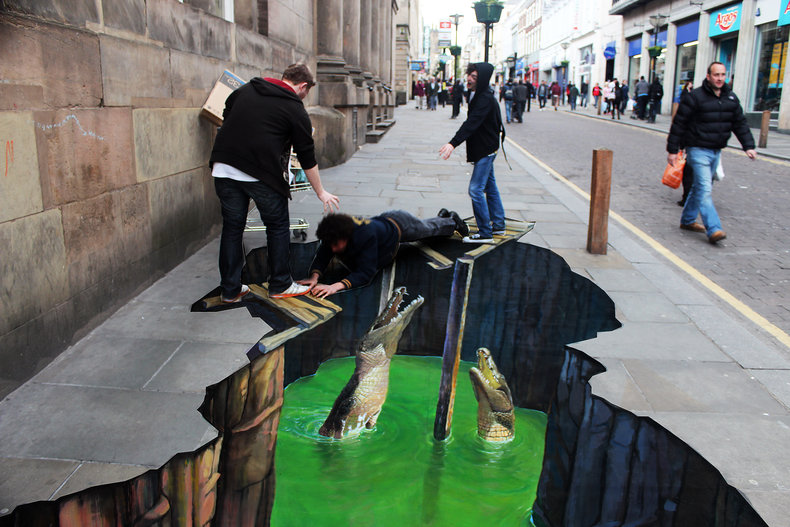
Visualization
The ability to visualize concepts and events. The imagination is the basis for visual thinking and related functions such as dreaming. People also visualize characters and scenes when they read fiction.
Storytelling & Fiction
Storytelling both fictional and non-fictional requires the imagination.
Suspension of Disbelief
Suspension of disbelief is the willingness of audiences to put critical thinking on hold to enjoy a story such as a film or theatrical performance with the imagination.
Memory
Imagination plays a role in memory. For example, visualizations of the past are largely painted by the imagination as opposed to being direct recordings from your senses.
Imagination Inflation
Imagination inflation is the theory that if you imagine something enough you can begin to believe its a real memory. This can be demonstrated to occur in some individuals.
Introspection
Introspection is the process of developing self-knowledge. This can involve the imagination whereby you imagine how you are perceived by others.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability to understand and respond to emotion in an intelligent way. This often involves imagining how people feel or how you will feel in the future in response to possible situations.
Creativity
Creativity is the process of creating non-obvious value. This requires a leap into brave new directions by the imagination.
Identity
Imagining yourself in order to define and develop your identity. For example, a fashion enthusiast who imagines how they want to look.
Dealing With Ambiguity
The imagination can be used to deal with unknowns. For example, a surfer who imagines how a particular wave is going to play out.
Forecasting
Imagination plays a role in forecasting whereby an individual can see beyond current trends to imagine a change that may occur.
Exaggeration & Deception
The imagination is often used to exaggerate or lie.
Delusion
Delusion is a wide range of negative mental states whereby an individual mistakes imagination for fact.
Failure of Imagination
Failure of imagination is the expectation that the future will resemble the past. This neglects the constant change that surrounds all things. Failure of imagination is common in risk management whereby societies and organizations expect the status quo to continue despite clear evidence of mounting risk.
| Overview: Imagination | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The ability to form ideas and images that do not originate with your senses. | |
Related Concepts | ||