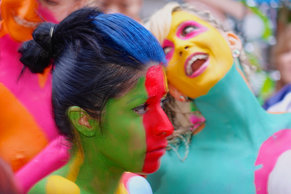Physical
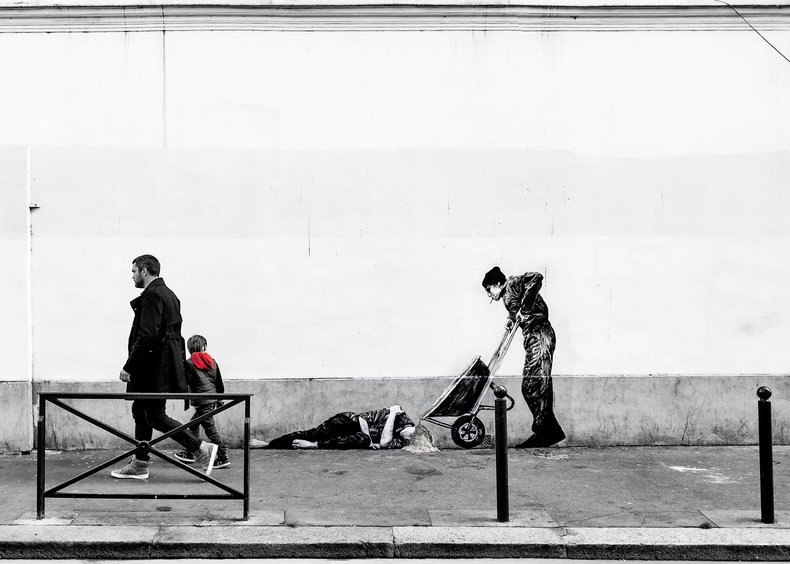
Noticing things that stand out physically such as something that is moving or a bright color. Salience can be overridden by higher level thinking processes. For example, if you are at a night club you may override your responses to loud sounds and sudden bursts of lazer lights.Emotion
Things that have emotional significance to an individual tend to be more salient. For example, a cartoon character that you were fond of as a child that stands out in a sea of product advertising in a supermarket.Motivation
Motivation can influence salience. For example, if you are hungry your brain may begin to notice things related to food.Directed Salience
Humans appear to be able to tune their salience to try to achieve a goal. For example, if you are trying to catch a mosquito you may tune your salience to the slightest of movements.Adaptive Salience
Humans adapt their salience to filter out repeated patterns as meaningless. For example, a person living in a highly urban area who pays no attention to the sound of sirens where someone in a rural area may detect this as salient information.Society & Culture
Society and culture influence salience. For example, clothing that attracts little attention in one culture may stand out with high salience in another.Social Information
People automatically seek out social information such as faces and voices. For example, people will automatically focus in on faces in a photograph and ignore other visual elements such as greenery. This is the reason that advertising and product packaging often features people.Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is the ability to understand fast moving situations. Salience is a critical low level cognitive ability that supports situational awareness. For example, a driver going at 40 miles per hour who is able to quickly focus on relevant things such as pedestrians, bicycles, vehicles and traffic lights from a fast moving stream of visual information.Artificial Intelligence
Salience is an important concept in artificial intelligence and computing in general. For example, an information security system that is able to detect salient threats in a stream of event information.Bizarreness Effect
The bizarreness effect is the tendency for people to remember highly unusual things over ordinary things. This indicates that salience affects memory. This is the reason that advertising is often designed to be bizarre as this helps it to be both noticed and remembered.Salience Bias
Salience bias is an irrational focus on that which stands out. For example, if there are 50 people attending a conference, a person wearing a bright red dress might be noticed far more than anyone else as this is a rare and emotional color. This can occur even if there are more remarkable people in attendance who are wearing less remarkable colors. It is more accurate to think of salience as a heuristic as opposed to a bias. As with most heuristics, salience is not completely accurate but is efficient and fast. This can beat accuracy, depending on the situation.Summary
Salience is the degree to which something sticks out in a sea of information.
| Definition: Salience | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The ability to quickly detect things of possible importance in a stream of sensory information. | |
Definition (2) | The degree to which something sticks out in a sea of information. | |
Related Concepts | ||