Visual Perception
Visual experiences such as swimming underwater with swim googles.
Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is the ability to understand and react to fast moving situations in an intelligent way. Visual perception is a key element of situational awareness alongside processing of other senses such as hearing. For example, a quarterback in a football game who needs to know about the location, speed and direction of multiple players over a period of several seconds in order to complete a pass and avoid injury.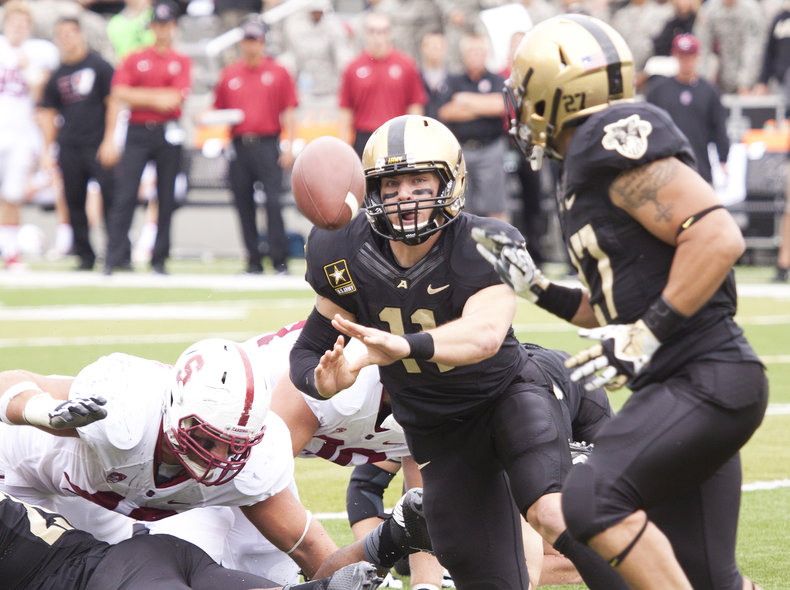
Memory
The ability to bring up visual images of the past. It is believed that the imagination often fills in gaps in these images such that they aren't as accurate as a photograph. Indeed, visual memory is often fuzzy such that images feel fragmented or faded.
Recognition
It is common for people to remember faces better than names. This is the reason that brand logos and other visual symbols are considered essential elements of communication, marketing and user interface design as visual memory can be more vivid than verbal memory.
Visualization
The ability to develop imaginative mental images in your mind. For example, picturing landscapes, scenes and characters as you read fiction.
Dreams
A dream is a succession of ideas, storylines, emotions and visualizations that occur during certain stages of sleep. Visualizations are a prominent element of dreaming and it is common to visually remember a dream upon waking up. The function of dreams is not well understood with various theories proposing that dreams play a role in memory formation, problem solving or regulating mood.
Visual Learning
The process of understanding information using visual images. For example, looking at a chart of data or experiencing a virtual environment that illustrates concepts.
Visual Communication
Communicating with visual elements such as a drawing, graph or photo. Verbal communication is often more efficient than visual communication and this is the reason it tends to dominate in areas such as business and education. It is easier to tell someone "I'm from California" than to draw them a picture of the state. However, some ideas are far easier to communicate with visuals or may be impossible or difficult to accurately communicate with words. For example, it is easier to communicate the architecture of a building with a drawing or model than with textual information.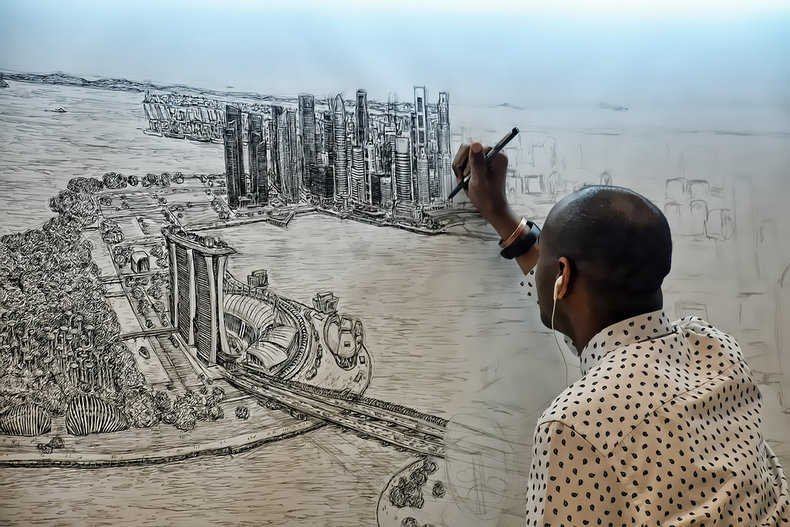
Visual Expression
Expressing meaning such as culture, stories, ideas, emotions and identity with art, media, film, performance art, fashion and other visualizations.
Spatial Reasoning
The ability to visualize and solve problems involving 2d or 3d space. For example, an astronaut who is able to fit parts together to perform a maintenance procedure in a disorienting and constrained environment.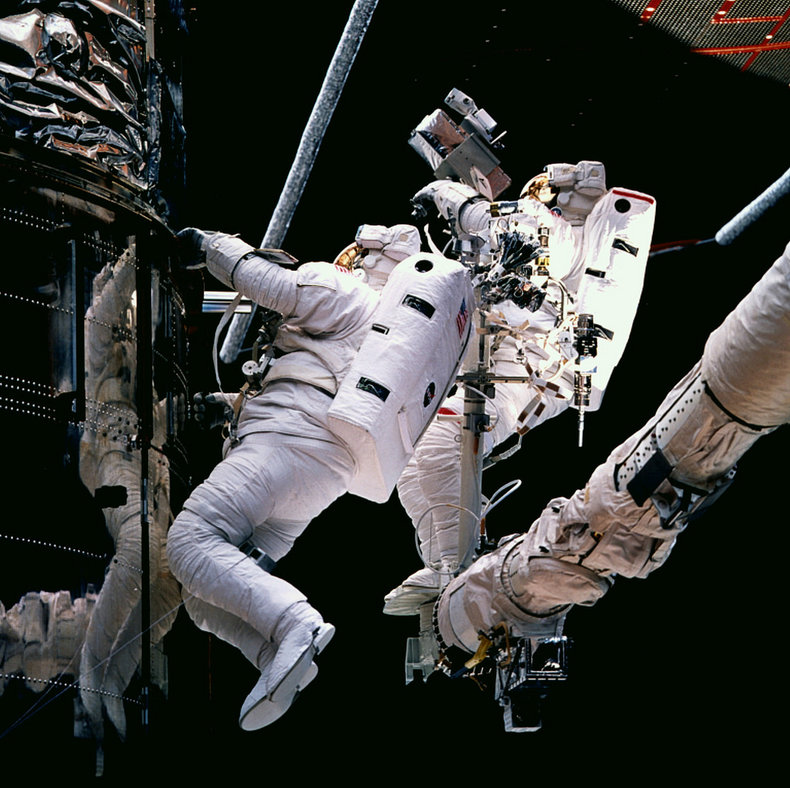
Spatial Memory
The ability to remember 2d or 3d space independently of verbal information. For example, a diver who remembers a path through a cave based on visual cues.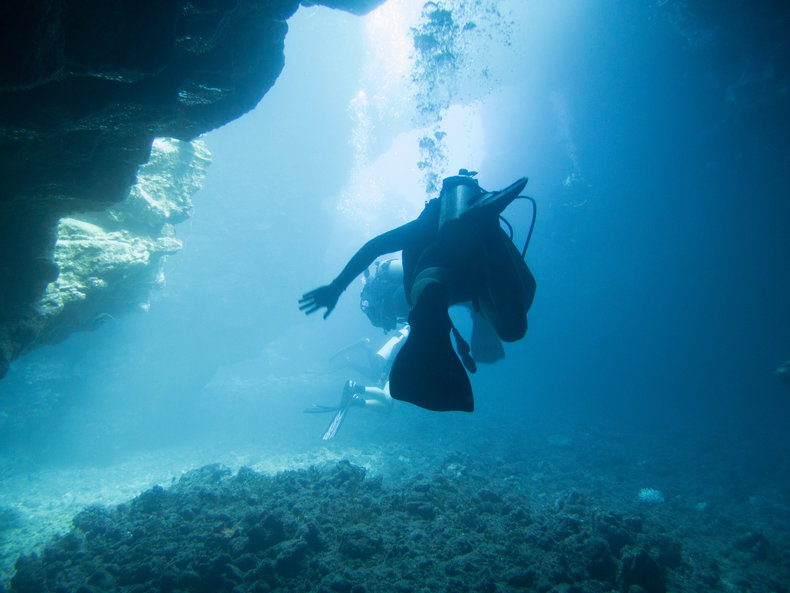
Abstraction
The ability to develop visual abstractions such as a visual metaphor that can be used to influence people. For example, scales are often used in art as an metaphor for justice.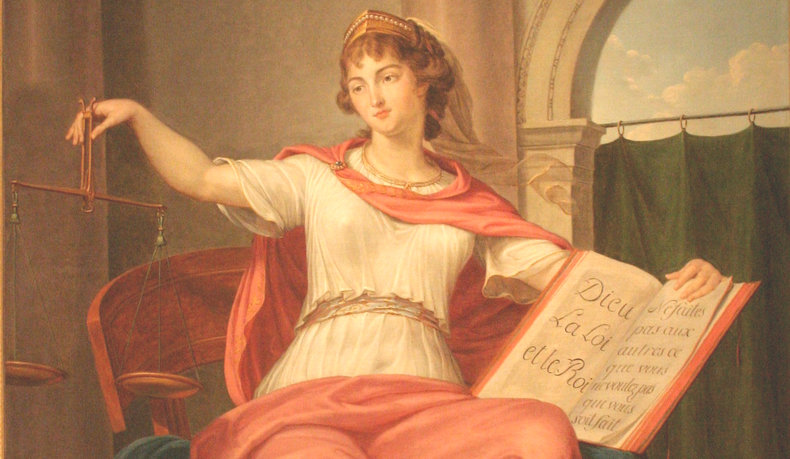
Thought Experiments
Using visual metaphors as thought experiments that can be used to simplify complex problems. For example, Einstein's thought experiment of a streetcar racing away from a street clock at the speed of light such that time would appear to stand still from the perspective of people on the street car looking back at the clock.
Design
Visualizing a design on paper or in your head. This can include both visual design that obviously lends itself well to visualization and non-visual design such as the design of a computer system, business process or machine.
Simulation
The ability to run through visual simulations in your head. For example, a chess player who can see a chess board in their head such that they can model the possible future states that can result from a move.
Visual Thinkers
Most people have both visual and verbal thinking abilities to varying degrees with other types of thinking such as musical thinking playing a secondary role. People who strongly rely on visual thinking or who perform well in areas that require visual thinking such as spatial reasoning are known as visual thinkers.
| Overview: Visual Thinking | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Any mental process that is based on the visual processing capabilities of the mind. | |
Related Concepts | ||