Quartz
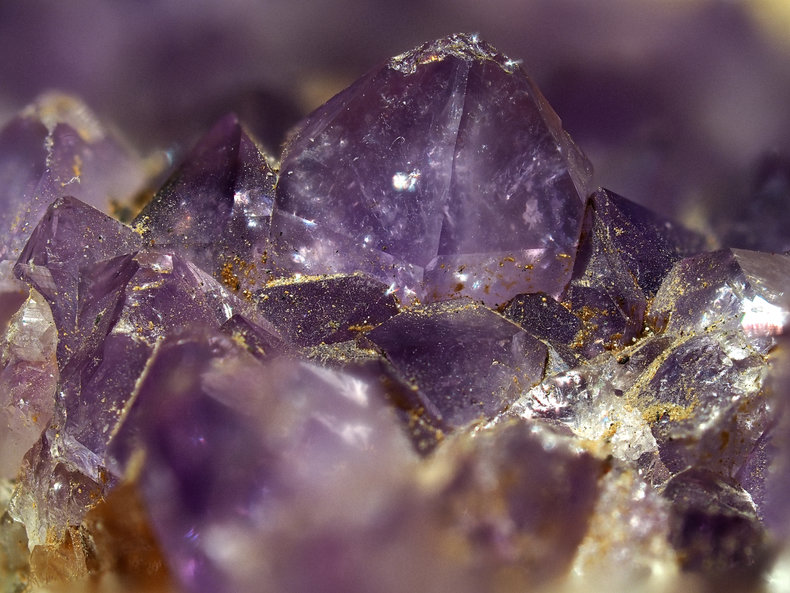
Amethyst is a variety of quartz that has a crystal structure. Like quartz, it is composed of silicon and oxygen. Amethyst also has impurities such as iron that give it its unique color.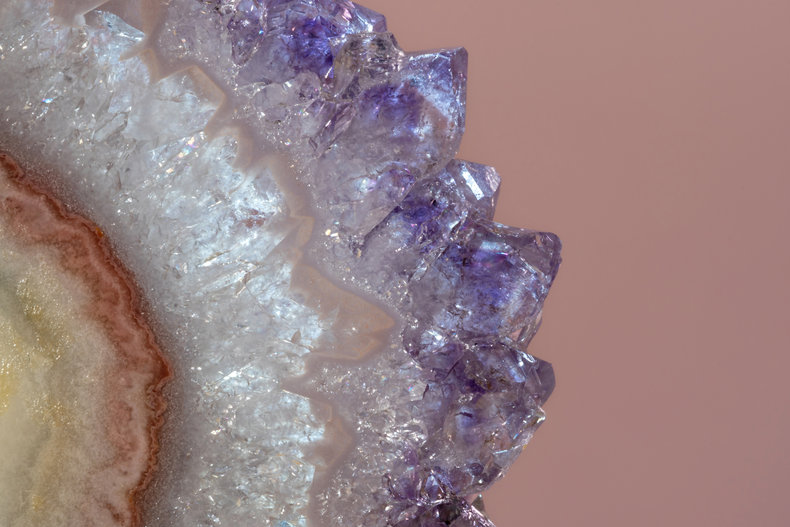
Cardinal Gem
Amethyst was historically considered a cardinal gem meaning that it was viewed as one of the few precious gems alongside diamonds, rubies, sapphires and emeralds. This term has fallen into disuse. Amethyst is now considered semi-precious due to the discovery of large deposits, particularly in Brazil.
Color
Amethyst is valued for its violet color that is created by the irradiation of trivalent iron embedded in the crystal. The highest grade amethyst is a dark purple color known as Deep Russian.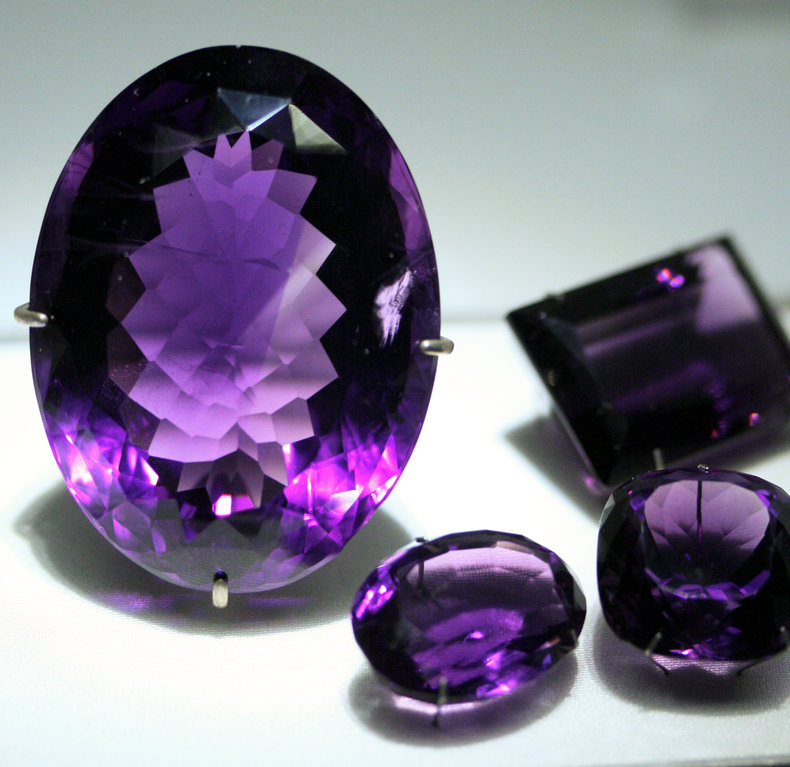
Irradiation
One of the modern factors that holds down the price of amethyst is that its color can be darkened with irradiation with high energy particles such as gamma rays. Regular quartz can also be treated with iron and gamma rays to make it a violet color. Where high energy radiation can darken the violet in amethyst, regular light can cause it to fade with time.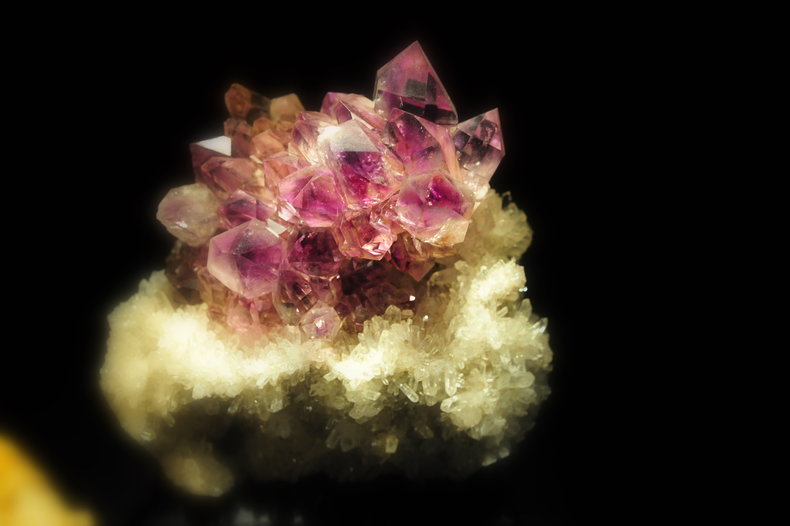
Heat
Amethyst's color is damaged with heat such that it becomes yellow-orange or yellow-brown. In this case, it resembles another type of quartz called citrine. For this reason, citrine is sometimes referred to as "burnt amethyst." Indeed, citrine and amethyst are commonly found together such that citrine often results from heat exposed amethyst.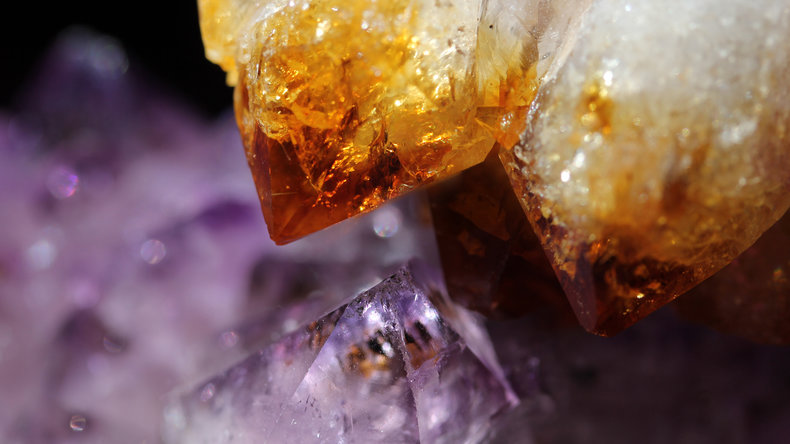
Hardness
Amethyst is quite hard with a mohs hardness of 7. This is the same as quartz. Quartz is one of the reference minerals for the mohs scale meaning that geologists in the field may try to scratch materials with quartz and vice versa to identify them.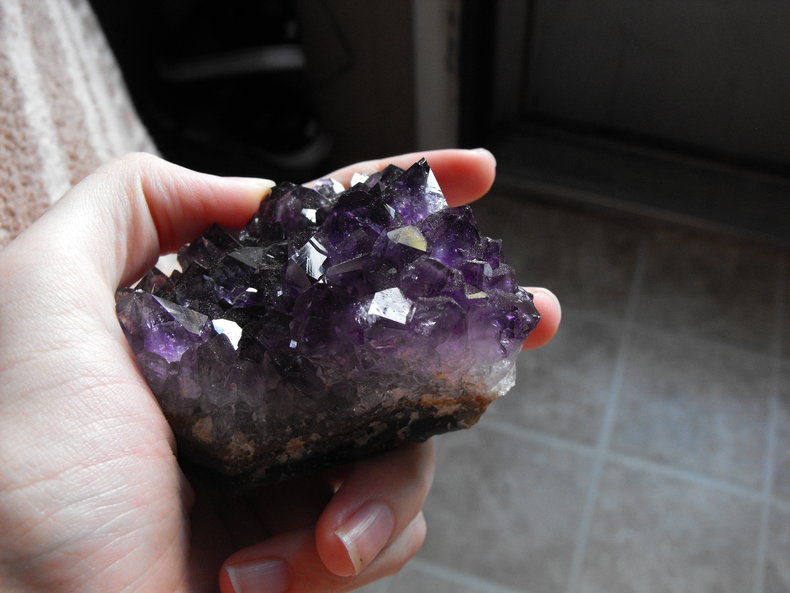
Medieval Europe
Throughout the middle ages, amethyst was used in amulets and other charms due to various myths surrounding its powers. For example, medieval European soldiers wore amethyst as it was believed to have healing powers and to keep warriors coolheaded in battle.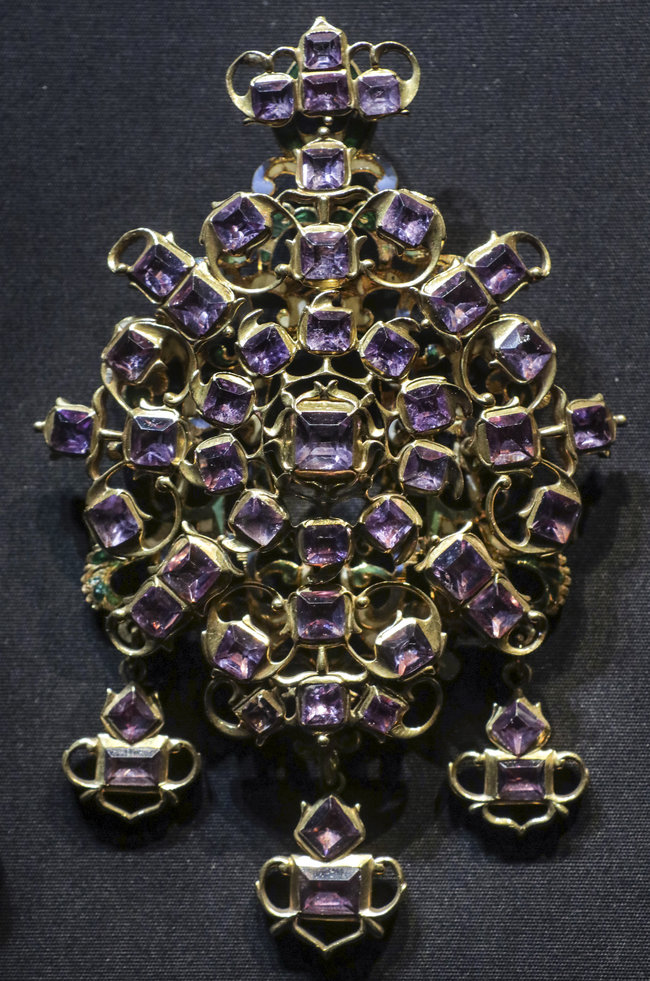
Ancient Greeks
The Ancient Greeks believed that amethyst prevented drunkenness and crafted drinking vessels from it. This belief is demonstrably false. However, amethyst now symbolizes sobriety and some Christians use amethyst for this purpose. The word amethyst originates with the Hellenistic Greek word amethystos meaning intoxicate. In the middle ages, writers invented Greek myths related to the gods, amethyst and drinking. These aren't true Greek myths. The single such reference in antiquity is by Nonnus of Panopolis who writes that the titan Rhea presented Dionysus, the god of fertility and wine, with an amethyst gemstone to preserve the drinker's sanity.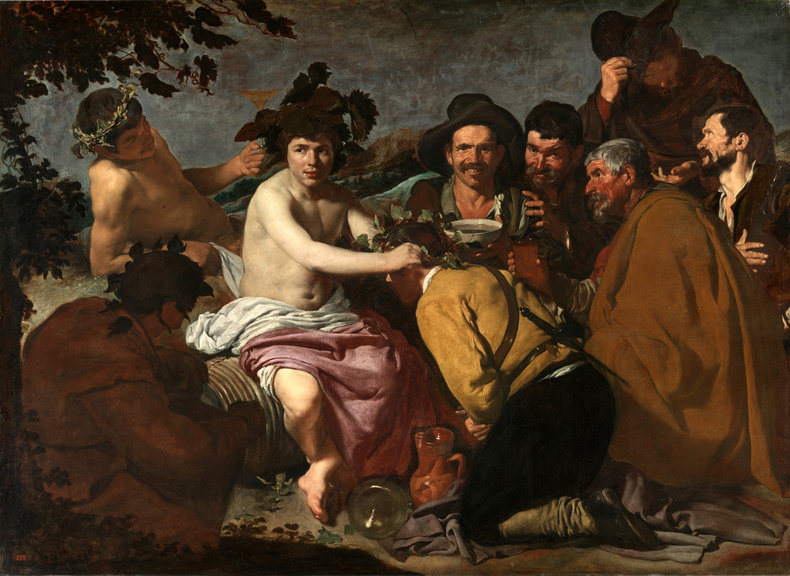
Ancient Egyptians
The ancient Egyptians commonly carved and inscribed amethyst. As with quartz, amethyst is reasonably hard and durable and is also somewhat workable.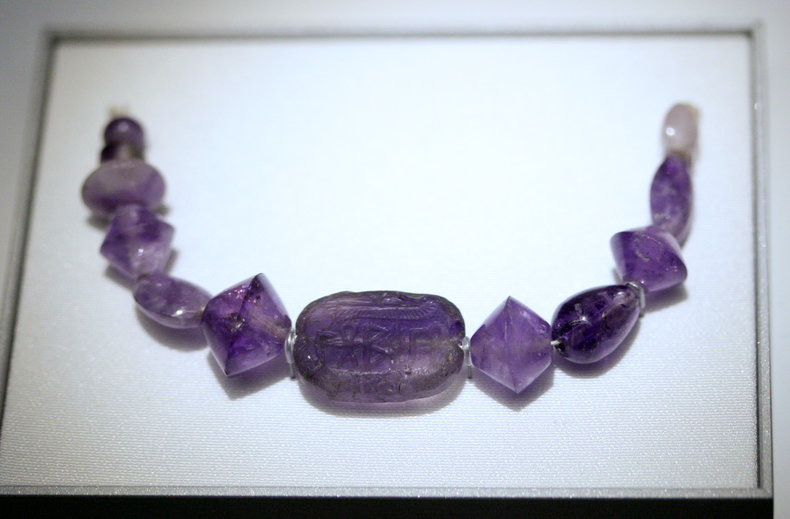
| Properties: Amethyst | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A violet variety of quartz | |
Composition | Silicon, Oxygen, Iron | |
Structure | Crystal | |
Texture | Vitreous (glass-like) | |
Type Of | Quartz | |
Value | Semi-precious Gemstone | |
Color | Light to dark violet. | |
Mohs Hardness | ||
Symbolism | SobrietyHealingCoolness in Battle | |
Color Fades With | SunlightHeat | |
Color Darkens With | Irradiation | |
Artificial Varieties Exist | Yes | |
Misnomers | Green amethyst doesn't exist as amethyst is always violet. The correct name is green quartz. | |
Etymology | Word originates with the Ancient Greek amethystos meaning intoxication. | |
History | Used as a gemstone since antiquity. Discovered in prehistory. | |
Related Concepts | ||