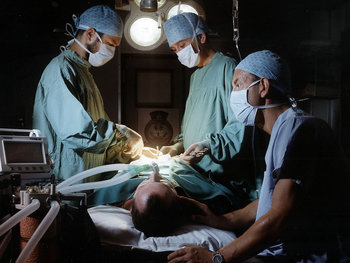
Environmental Justice
Ending the situation where the poor suffer unhealthy environmental conditions that the rich escape.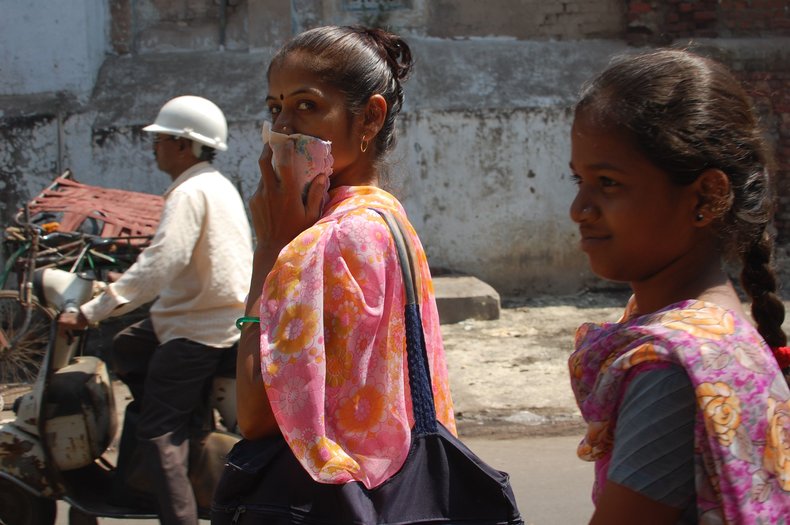
Economic Opportunity
Sustainability isn't viewed as a prioritization of the environment over communities. People need to thrive and pursue a high quality of life. Sustainability requires solutions that are win-win for people and planet.
Air Quality
Discontinuing and modifying processes that put particles and gases into the air. This would address air pollution and climate change.
Water Quality
Ending practices that pollute water sources with things such as plastic, chemicals and agricultural runoff.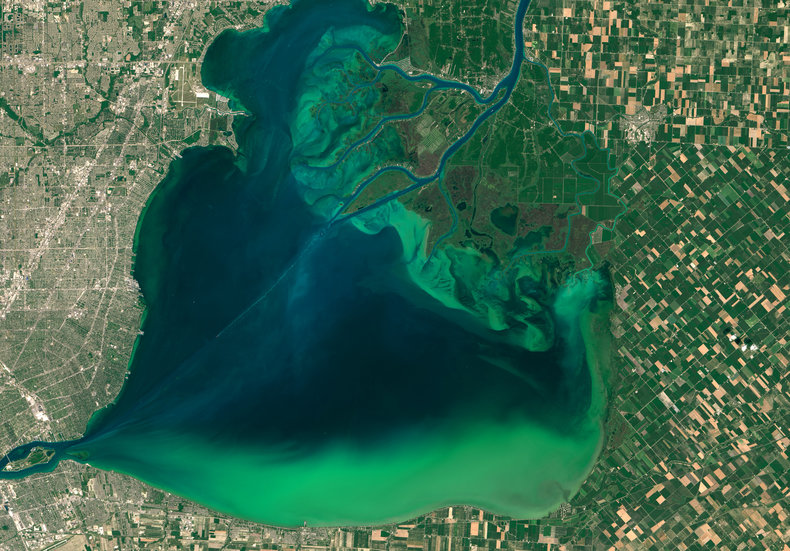
Efficiency
Using resources such as energy, water and materials in an efficient manner. This doesn't mean that resources as minimized but rather that you maximize value for a unit of a resource.
Reduce
Reducing the consumption of resources where this doesn't produce much value. For example, questioning the need to drive a heavy vehicle everywhere.
Reuse
Structuring an economy, society and culture for reuse of things. At the cultural level this includes things like repair cafes. At the economic level this could include tax incentives for used goods and industry regulations that ensure goods can be repaired or disassembled and reused.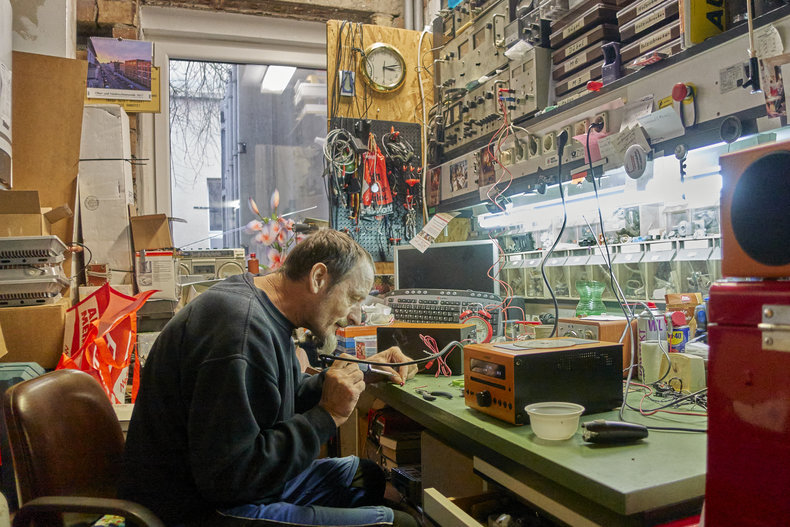
Circular Economy
An economic system that reuses or recycles all goods and other things such as buildings and infrastructure. This can be based on two principles: extended producer responsibility and waste is food.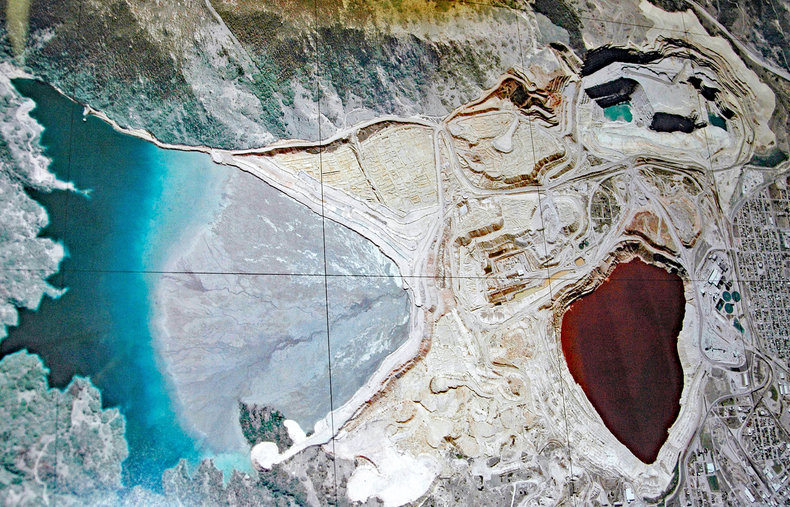
Stewardship
Exercising responsible stewardship over the natural world whereby we don't destroy ecosystems in pursuit of resources and land. This includes elements such as nature conservation -- the moral duty to prevent human caused extinctions of species.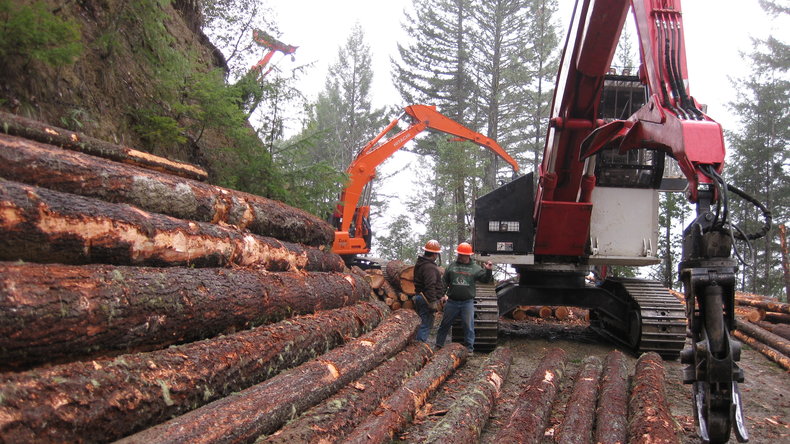
Resilience
Building societies, cities and communities to endure stresses such as disasters or supply chain disruptions. For example, an area that produces much of its own energy and food may be somewhat resilient to supply chain disruptions.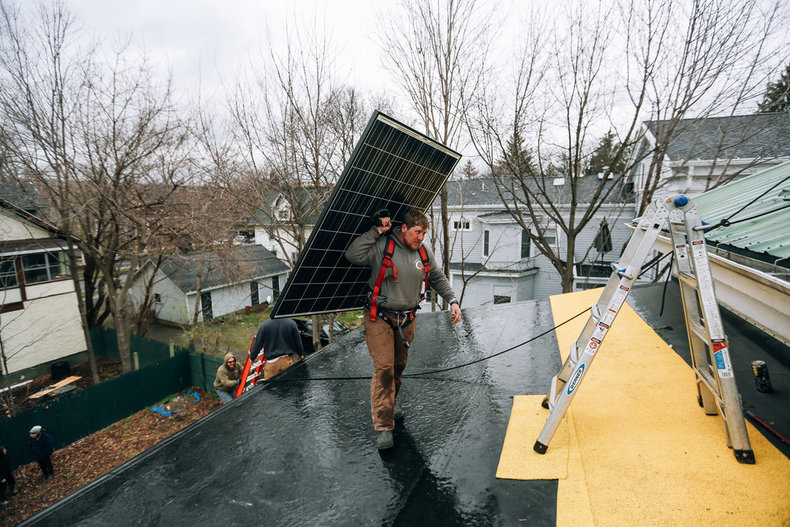
Limits
Sustainability includes the sense that excessive consumption, environmental destruction or environmental risk must be prevented. Excessive consumption mostly relates to wealth such as a single individual with a gigantic environmental footprint. Limits to risk and destruction relate to the actions of large organizations such as governments and corporations.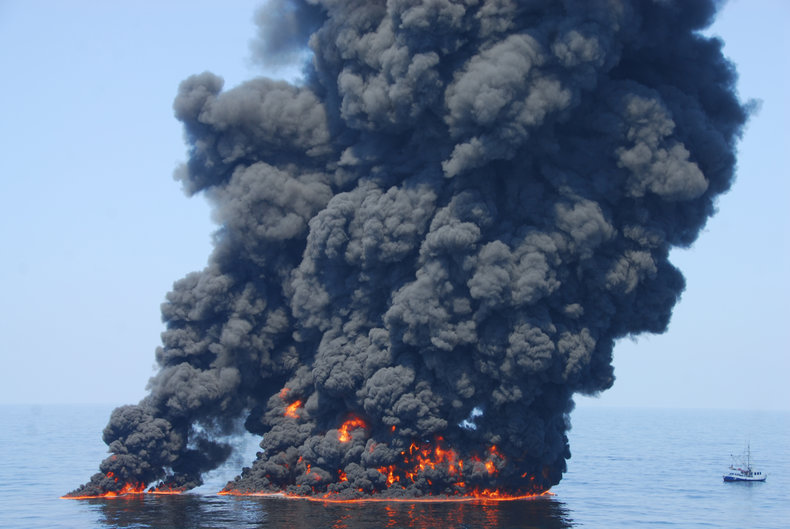
Precautionary Principle
The precautionary principle is the principle that products and emissions be proven safe before being released. This places the onus of proof on the producer and prevents the common situation where something that is almost certainly harming people and planet isn't pulled from the market because there is a small amount of uncertainty surrounding a large body of proof.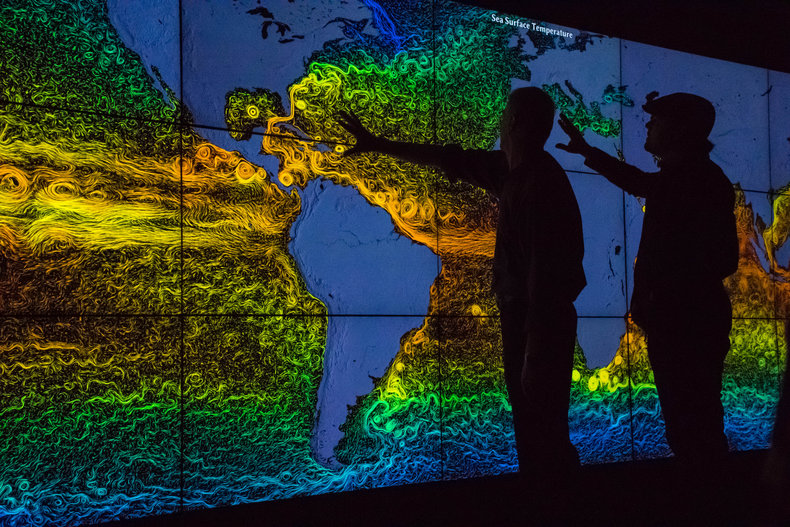
Right to Know
The right to know about hazards that you are exposed to such as particles in air that are introduced from a specific source.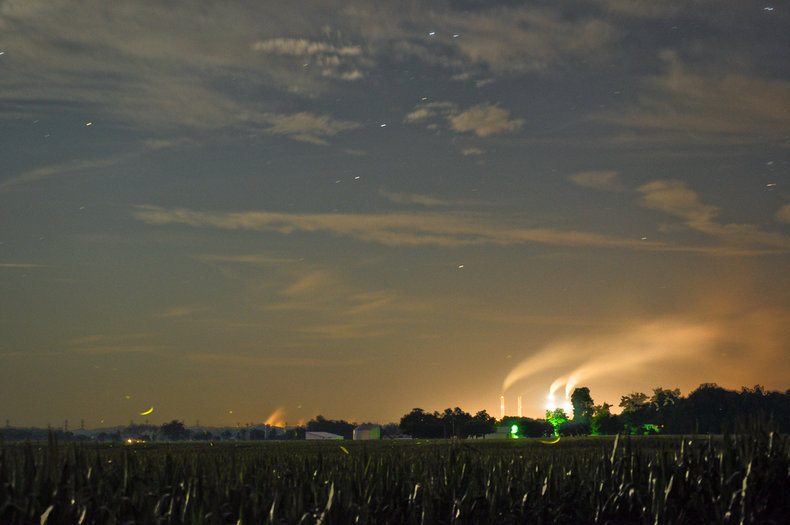
Transition
Systems, processes and practices that are supporting the livelihood of billions of people can't be instantly replaced at a point in time. As such, sustainability involves pragmatism and the sense that things must quickly get better but that there is a transition phase whereby current practices may be required until there is some reasonable replacement.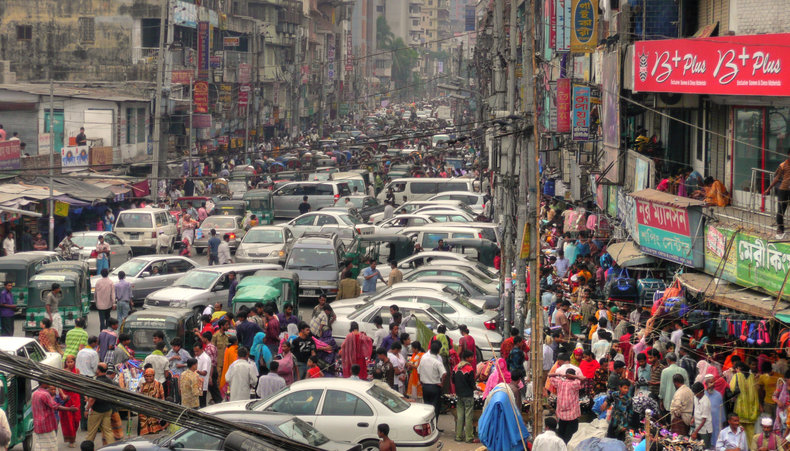
Cultured Living
Giving people the rights, freedoms, public services, working conditions and wages required to live a cultured life above the harsh austerity of basic survival.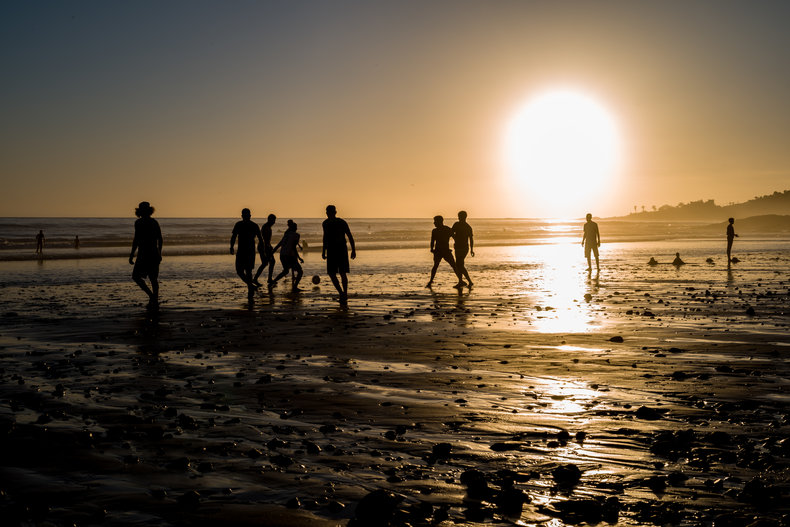
| Overview: Sustainability | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The prioritization of quality of life and environmental protection in government policy, business strategy and personal action. | |
Related Concepts | ||