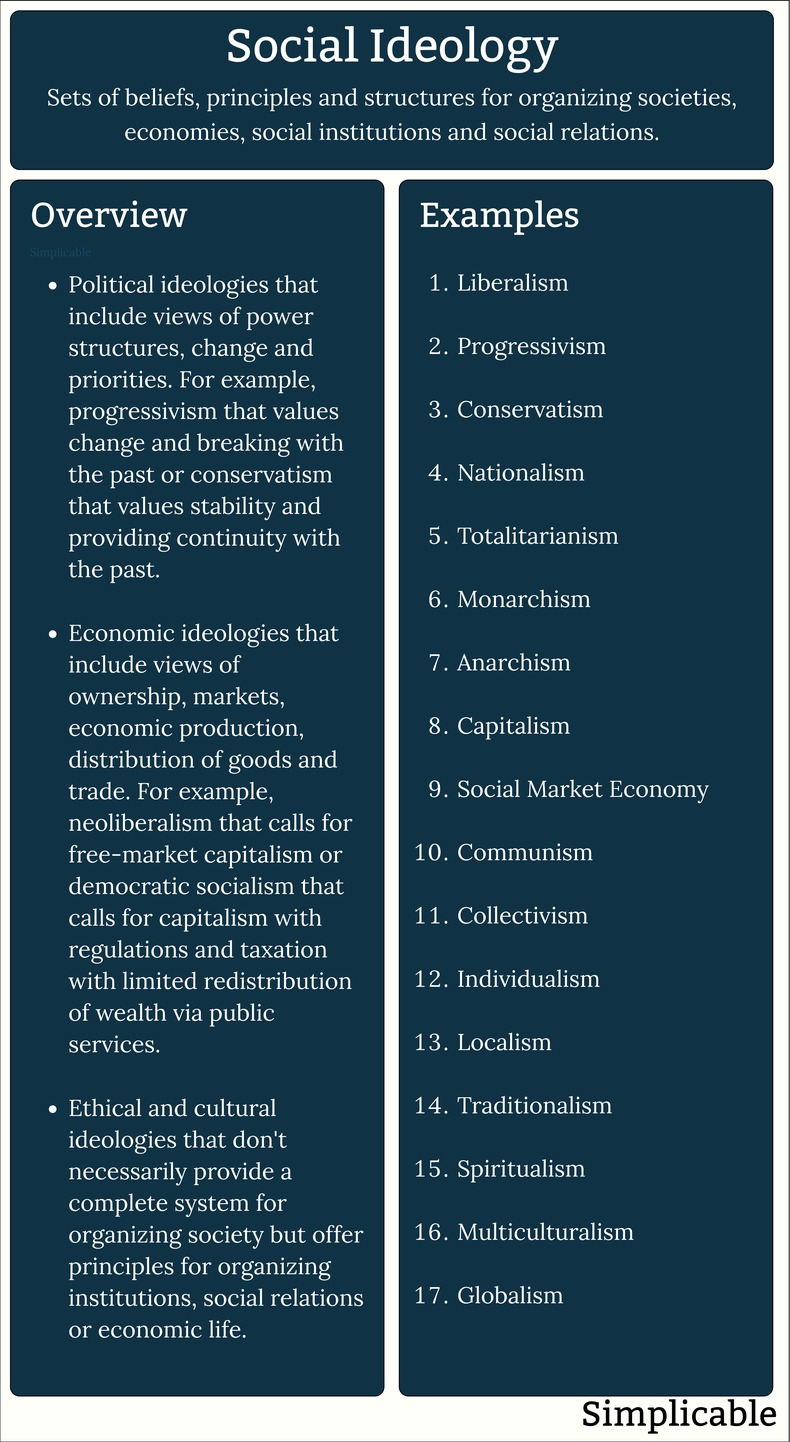
Political Ideology
Political ideologies are comprehensive sets of principles for organizing a society. These are each based on bodies of academic knowledge and the political traditions and institutions of nations such as political parties.Anarchism | Authoritarianism |
Conservatism | Liberalism |
Libertarianism | Monarchism |
Nationalism | Progressivism |
Reactionary | Republicanism |
Totalitarianism |
Economic Ideology
Economic ideologies are structures for organizing economic ownership, production, markets, distribution and trade.Anarcho-Capitalism | Capitalism |
Communism | Democratic Socialism |
Feudalism | Globalism |
Neoliberalism | Protectionism |
Social Market Economy | Socialism |
Ethical & Cultural
There are many social ideologies that don't provide a full system for organizing society or the economy. These are typically referred to as ethical & culture ideologies that offer principles for structuring social institutions and relations.Collectivism | Conservationism |
Consumerism | Environmentalism |
Ethical Consumerism | Feminism |
Humanism | Individualism |
Isolationism | Localism |
Materialism | Multiculturalism |
Pacifism | Secularism |
Spiritualism | Traditionalism |
Summary
Social ideologies are established sets of beliefs, values and principles related to the organization of society, the economy, social institutions and social relations.