Rights & Freedoms
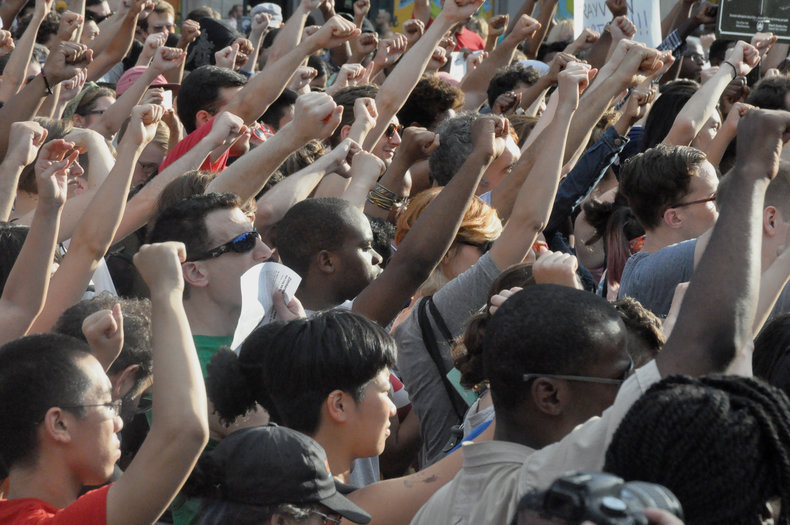
Strong individual rights and freedoms, particularly freedom of speech.Democracy
Liberalism supports a strong form of democracy where all people can vote and participate in the political process. This is based on freedom of speech and other freedoms such as freedom of the press and freedom of association.Secularism
Separation of church and state and a government that is neutral to all religions while protecting freedom of religion.Free Markets
Economic rights such as the right to start a business, freely engage in commerce and own property.Capitalism
Liberalism is based on the economic freedoms of capitalism but may seek to support free markets with interventions and regulation to protect fair competition, consumers and the environment.Equality Before The Law
Equal political and legal rights for all people. Liberalism is consistent with equality of opportunity whereby all people are treated the same by the systems of society.Limited Government
Liberalism prioritizes rights and freedoms and views the government as a means for maintaining these. A large government that regulates every aspect of life is inconsistent with liberalism.Free Trade
Liberalism is consistent with globalism and the freedom to interact with people, communicate and engage in commerce at the global level. It is inconsistent with international agreements that take away democratic rights and shift power to private interests.Liberalism vs Social Market Economy
Modern liberals typically embrace a social market economy whereby the government plays a role in taxing the wealthy to provide limited redistribution of wealth in the form of free public services such as healthcare and education. This is perhaps not pure liberalism that would tend to support economic rights and a limited government.Liberalism vs Socialism
Liberalism is based on freedom and control of government by the people. Socialism is based on equality of outcome whereby the government controls all capital and economic processes to ensure that all people receive the same material outcomes. As such, these two political ideologies are essentially opposites.Liberalism vs Conservatism
Conservatism is a political ideology that prioritizes tradition and stability over rapid change. This tends towards focusing on what the individual owes society over what society owes the individual. In other words, it tends to prioritize community rights over individual rights where liberalism tends to prioritize in the opposite direction.Liberalism vs Progressivism
Liberalism is about freedom and says nothing about progressivism but tends to be on the side of rapid change. For example, in its support of individual rights liberalism races to change society to support new values where conservatism seeks to preserve traditional values.Liberalism vs Libertarianism
Libertarianism is a term for political philosophies that support complete liberty. This can be compared to the practice of liberalism that tends to adopt elements of big government, particularly public services designed to improve quality of life. In practice, many liberals support a society based on a social market economy whereas libertarians seek to minimize government involvement in life and reduce or eliminate taxation.The outline above relates to liberalism as a political ideology. Political parties that are referred to as "liberals" don't necessarily align to the values above. For example, it is common for progressivism or socialism to be mislabeled liberal.
| Overview: Liberalism | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A political philosophy based on liberty and equality before the law. | |
Related Concepts | ||