|
| |
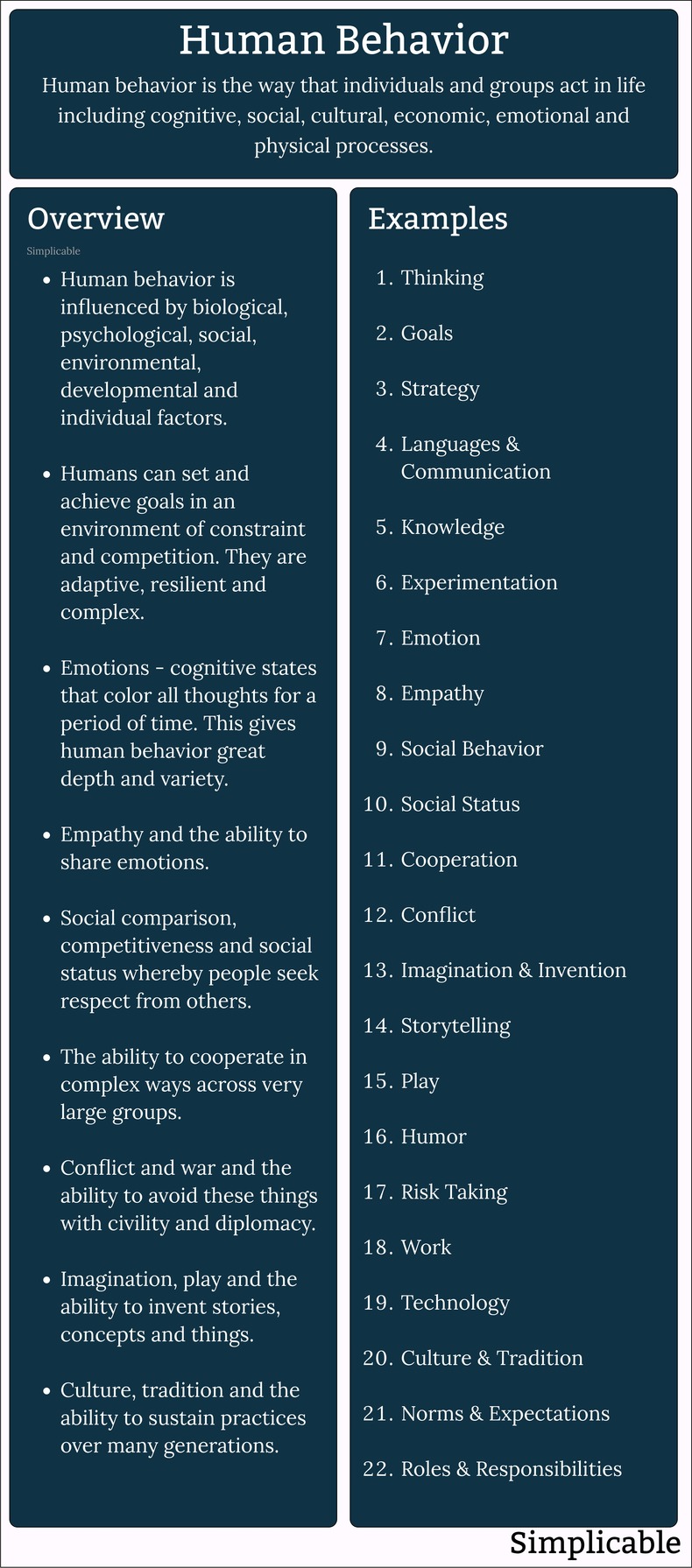
Human behavior is the range of thoughts, emotions and actions of people. The following are illustrative examples.StrategyThe process of setting goals and plans to achieve these goals in an environment of constraint and competition. Humans can apply systematic analysis to form strategies based on established knowledge and reasonable predictions.
CommunicationHumans have a tool called language that includes a wide range of fully developed concepts that can be used and communicated. They also communicate visually with pictures, symbols, body language and eye contact. Languages include sign languages expressed with the hands and face, spoken languages and written language.
ThinkingHumans are able to think in a range of modes. The concepts provided by language allow for advanced abstract thought. Humans can also think with visual information. The result of human thinking can be rational, irrational or coldly rational.KnowledgePeople have a curiosity that drives the development and acquisition of knowledge. Humans devote much of their life to learning and may spend more than 20 years in school.ExperimentationTrying things to see what will happen. A type of knowledge and experience acquisition.EmotionHuman thoughts are colored by a diverse range of mental states called emotions. EmpathyHumans have significant capacity to understand how others feel. In fact, they can share emotions with others in a process known as empathy.MotivationHumans have intense motivations such as angst, greed, competitiveness and fear that drive them into action and inaction. Generally speaking, they feel motivated to engage in the human experience. The strongest motivations are for basic human needs such as oxygen, water and food. Where these are satisfied motivation may move on to high level achievements such as self-fulfillment.Social BehaviorHumans are social beings that organize into societies, communities, organizations, groups and families. They establish a wide range of relationships such as leaders, followers, mentors, friends, adversaries, neighbors, romantic partners and families. Social StatusHumans desire respect from other humans. This often takes the form of social status based on things like wealth, youth, appearance, coolness, style, intelligence, authority, popularity, position, recognition and association with high status people and institutions. Social status has also been commercialized and commoditized as brands, products and services that signal these things. Human behavior regarding social status is amazingly complex. For example, they may countersignal to show strength such as an executive who dresses informally to pretend to downplay their authority and position. CooperationHumans demonstrate an ability to cooperate as very large groups using processes such as politics, leadership, organizations, agreements and communication. It isn't unusual for millions of humans to cooperate on a strategy or as a society. This allows them to create immense works such as cities and infrastructure.ConflictHumans don't always cooperate. Civility and diplomacy can break down resulting in conflict. Humans have a fearsome capacity for this, particularly as groups. Due to technology, they have the potential to create large scale destruction and misery.CompetitionAll species compete for resources. As the dominant species on Planet Earth, humans mostly compete with each other. Humans are hardwired for competition with emotions such as jealousy and envy. Positive emotions such as feelings of comradeship are also conductive to competition. Humans are so competitive that they compete for the fun of it in the form of games and sport.PlayThe ability to pursue joy for the sake of joy. This appears to play a role in human development, creativity and social skills.HumorHumor is essentially the mental equivalent of play whereby people find ways to think that create joy.Risk TakingHumans are risk takers that demonstrate initiative, courage and tenacity. They are also able to calculate risk and manage it.WorkHumans demonstrate the diligence and concentration required to complete complex tasks. They may constantly improve their work and eliminate toil. Attitudes towards work, work habits and talents differ greatly between individuals. TechnologyHumans transform their environment, create tools and automate things. They are quite weak without technology and can become completely dependent and absorbed by it. TraditionDespite their capacity to constantly change, humans do value stability and are able to maintain traditions for hundreds or perhaps thousands of years. This can serve as a common experience across generations and provides a sense of continuity and connection with the past.CultureCulture is a collection of shared meanings, norms and behaviors that emerges in groups through the process of shared experience. This has no central design and emerges within any group that spends time together. NormsA norm is a shared expectation that occurs in a culture. This allows people to align their behavior to get along.MediocritySome humans seek to minimize effort, maximize comfort and minimize risk. This is achieved by seeking to belong to large groups and pursuing harmony by avoiding any conflict or competition. This is a common behavior that can be described as mediocrity, complacency or conformity.ImaginationImagination is the ability to think in ways that differ from reality. This often ends up defining the future such that imagination and reality are intertwined. EscapismEscapism is the tendency of humans to spend time doing things that aren't directly related to their goals in life. This includes day dreaming, play, entertainment, leisure and recreation. CreativityDue to their capacity for imagination humans can create non-obvious solutions to problems. They also have an appreciation for things like art, music, film, performance art, fashion and cuisine that derive their value from the imagination.ResilienceHumans can endure stress and continue on without loss of enthusiasm. With exposure to stress, humans improve their resilience to it such that stress can benefit them. For this reason, they may intentionally seek experiences that are mildly stressful.AltruismAltruism is the human capacity to make sacrifices to help each other. This can also apply to efforts to help animals and the planet. IntrospectionIntrospection is the human ability to objectively examine their own emotions, thoughts and behavior to improve.SummaryHuman behavior is the range of thoughts, actions and experiences demonstrated by individuals and groups. This is influenced by biological, psychological, social, environmental and developmental factors and demonstrates great breadth and variety.Next: Human Experience
Human Behavior
This is the complete list of articles we have written about human behavior.
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|