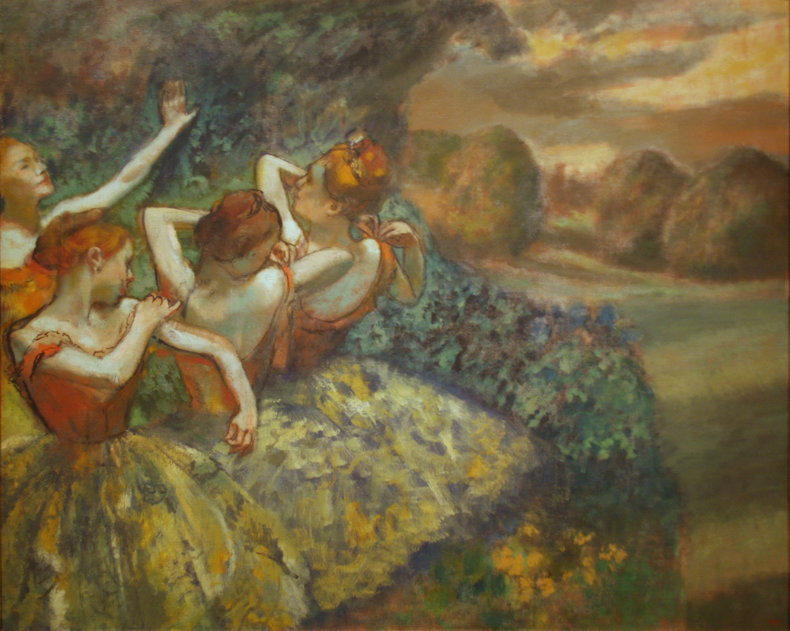|
| |
Elements of art are compositional and expressive characteristics of artworks. These are used in art education, critique, evaluation, appreciation and by artists themselves in creating a work. The following are common elements of art.BalanceBalance is the sense that a work is equally weighted on both sides of its center. This can be easily be achieved with symmetry but is more commonly achieved with asymmetrical balance whereby unlike elements are perceived to have equal weight.CohesionThe degree to which elements in a work look like they belong together.ColorThe use of color and color theory. For example, using color temperature to indicate a physical temperature or emotion.
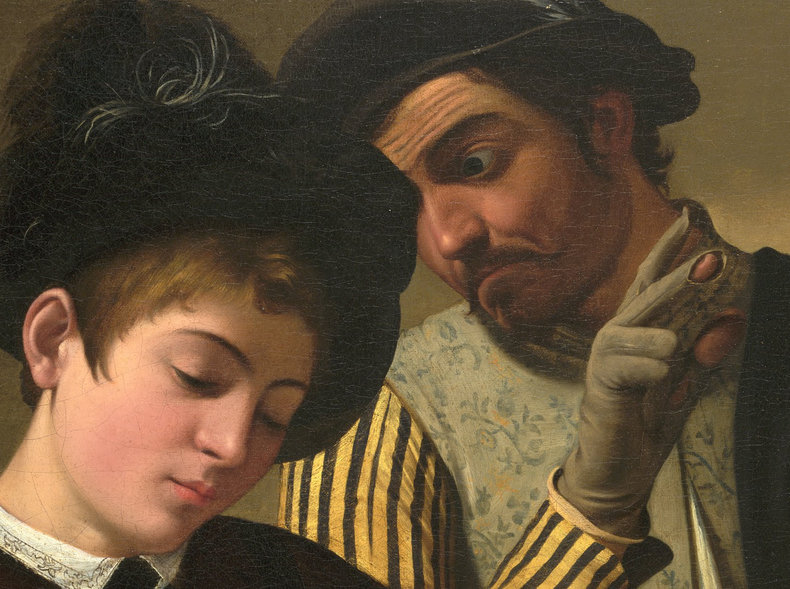
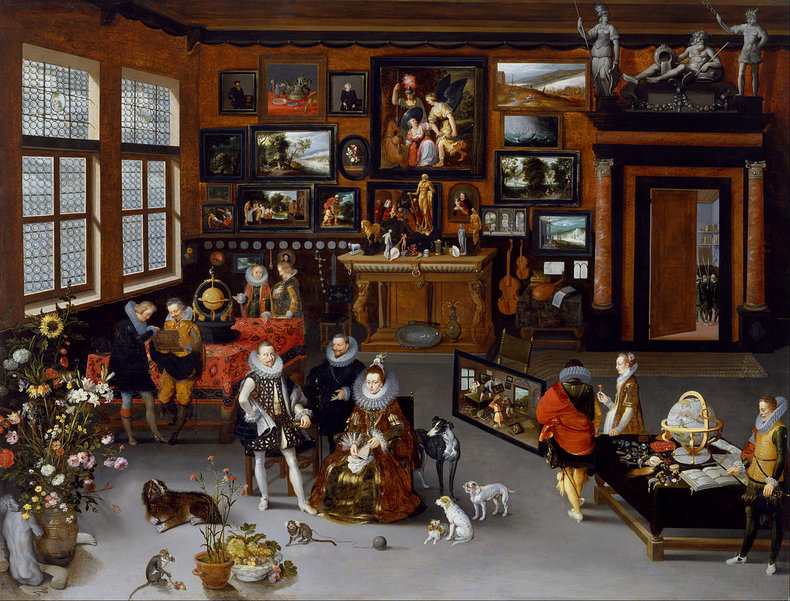
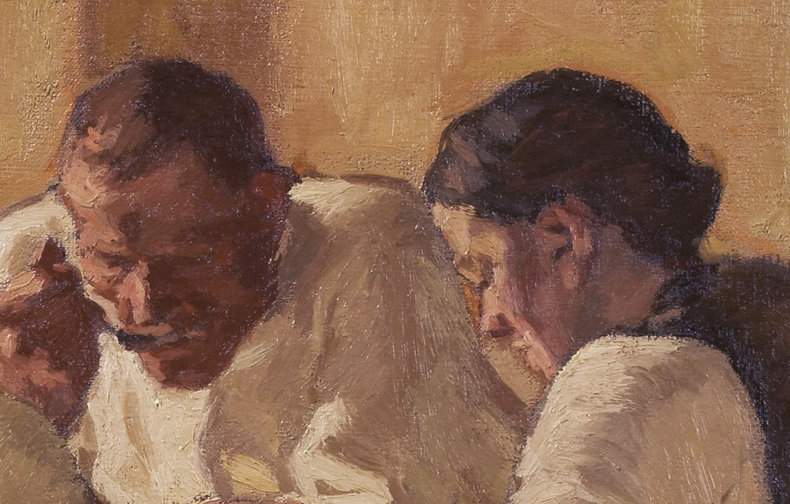
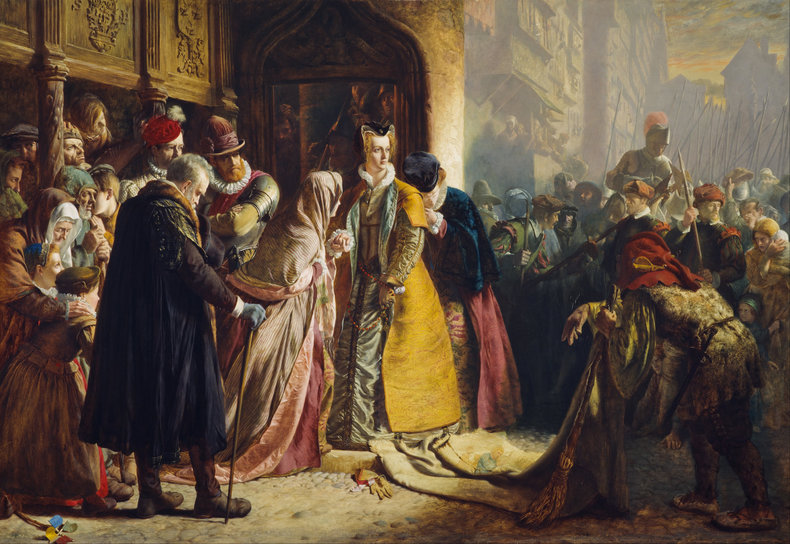
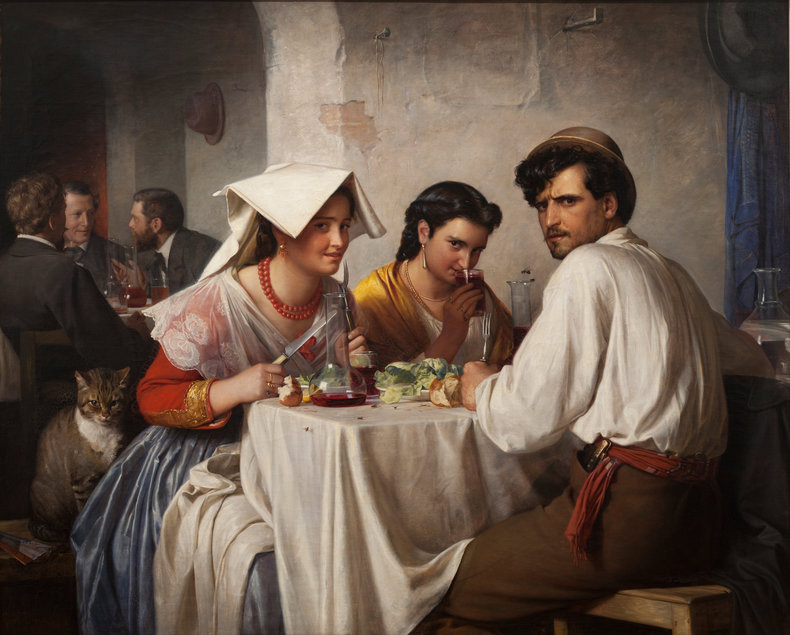
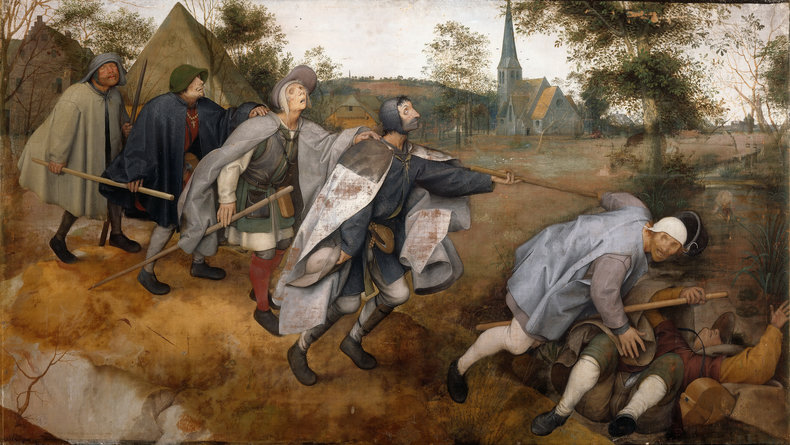
ToneTone, also known as value, is the lightness or darkness of objects.Above: Rembrandt, The Man with the Golden Helmet (Detail)CompositionComposition is the overall arrangement of the elements of a work including considerations such as balance, cohesion and effect.Above: Giuseppe Arcimboldo, Summer (Detail)ContrastThe use of differences to create effect. For example, the use of a contrasting color to draw attention to a dominant part of a work. Contrast isn't confined to color and can be created with other elements such as form, texture and size.DominanceDominance is the practice of attracting the eye to one part of a work.EffectThe ideas and emotions that are generated by a work. For example, a work that is gloomy and bleak.EmphasisAnother term for dominance, the element of a work that attracts the viewer's attention.Above: Henri Toulouse-Lautrec, Moulin-RougeExpressionWhat the artist seeks to communicate with a work.Focal PointAnother term for dominance or emphasis that suggests an attempt to direct the eye to a particular point in the work.BackgroundThe components of a work that are conceptually furthest away from the viewer.ForegroundThe parts of a work that are conceptually closest to the viewer.Middle GroundAn area between the background and foreground that adds additional depth to a scene.Above: Edgar Degas, Four DancesShapeTwo-dimensional shapes formed by color or line.FormThe multidimensional shapes in a work. For example, the sense that elements have depth.HarmonyA sense of togetherness whereby parts of a work are in agreement.Tradition & MovementArt never occurs in a vacuum. Where it does, it would be extremely primitive such as a cave drawing. As such, influences of culture, traditions and artistic movements can be seen in any work.Above: Egon Schiele, Portrait of Eduard KosmackArrangementThe organization of the components in a work such as figures, trees and buildings.LayoutLayout is another word for composition, the process of arranging the elements in a work.LightingLighting a scene with strategic use of color temperature and tone. This may consider light sources, shadow, reflective light and ambient light. Lighting isn't necessarily realistic as light that appears to defy physics can add a mysterious element to a work. MoodMood is the emotion or emotions expressed by a work.Above: Caravaggio, The Cardsharps (Detail)LineLines and implied lines. Important to technical aspects of art such as perspective and scale.Above: Albert Bloch, The Green Domino (Detail)PerspectiveThe process of adding depth to a work so that it appears to be 3-dimensional like the real world. It is also possible, but rare, to depict other dimensions in an abstract way.Vanishing PointA vanishing point is the place where the horizon disappears. A element of perspective.ScaleThe relative sizes of things. Most works depict human scale.ProportionThe perceived size, weight and dominance of things with respect to each other. This includes elements such as size, position and color. For example, things get smaller as you move towards the horizon.Above: Hieronymus Francken, Archdukes Albert and IsabellaMark MakingMark marking are traces of the artistic process that remain in a work such as the brush strokes of a painting. These are often considered a key element of a work. For example, rough unfinished brush strokes that add to the austere mood of a composition.Above: Albin Egger-lienz, Lunch (Detail)MaterialityChoice of materials and emphasis of these materials in the work. For example, a painting that allows the canvas to add to the texture of the work.Above: Paul Gauguin, Washerwomen Movement Creating the impression of movement. For example, adding a blur and positioning things so that they look like they are moving. TimeA work that expresses the passing of time. For example, a scene that feels slow or fast.NarrativeA story that is told by a work.Above: James Drummond, The Return of Mary Queen of Scots to EdinburghPositive SpaceOccupied areas in a composition.Negative SpaceNegative space is the use of emptiness.Above: Odilon Redon, Baroness Robert de DomecySubjectsThe people depicted in a work.Subject MatterThe people, places, animals, things, events or concepts in a work.PresenceThe presence of the artist in their work. For example, what you can sense about the artist from how the subjects of a composition look at them.Above: Carl Bloch, In a Roman OsteriaRhythmA pattern that can be found in the repeated elements of a composition.StructureThe basic relationships between forms in a composition.SymbolismSymbolism is abstract meaning that is widely understood in the context of a culture.StyleThe distinctive character of an artist's work. Above: Amedeo Modigliani, Lunia Czechowska (Detail)TextureThe way that parts of a work look like they would feel if you could reach out and touch them.ArtificeA device that is used to deceive the viewer often to create a delightfully complex work that defies analysis.AllegoryMeaning and symbolism embedded in a work using an extended type of analogy known as allegory.Above: Pieter Brueghel, The Parable of the Blind, 1568 NotesHeader Image: Alexej von Jawlensky: Portrait of Alexander Sakharoff, 1909
Art Elements
This is the complete list of articles we have written about art elements.
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|