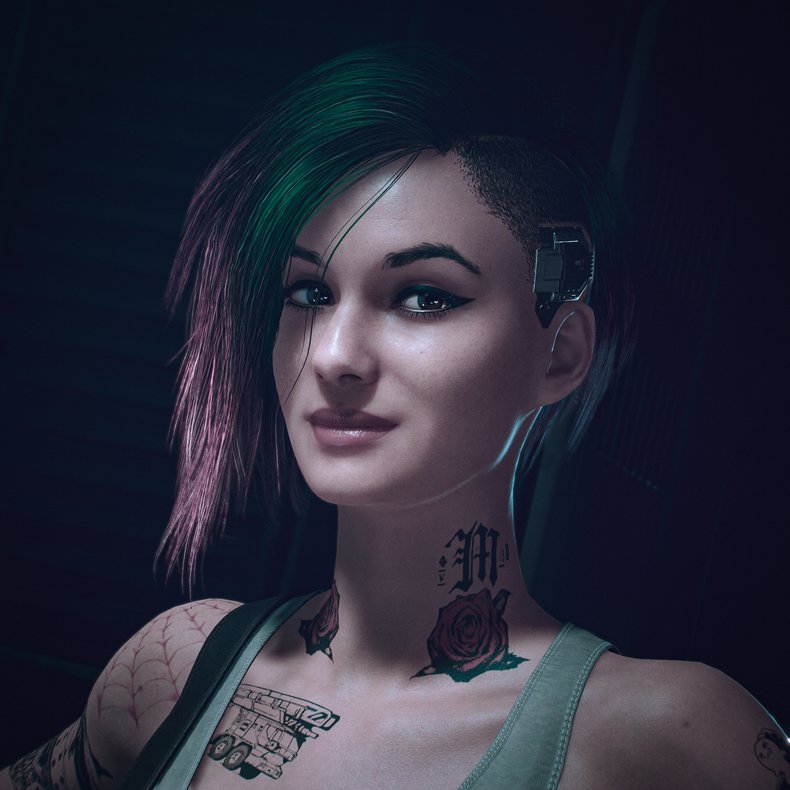|
| |
Art is visual expression. This is considered fine art where it is the product of an artist who is unconstrained. Art is considered a priceless element of culture, heritage and the human experience. More than any other artifact, great art captures the spirit of a time and place. For this reason, art movements occur at a point in time, never to be repeated. The following are illustrative examples.
RenaissanceAccording to the traditional historical narrative, after the fall of the Roman Empire, Europe went into a long period of barbaric decline known as the middle ages only to emerge into a period of cultural progress again in the 15th and 16th centuries. This argument is supported by art of the period that took an obvious leap forward, particularly in Italy and the Netherlands.
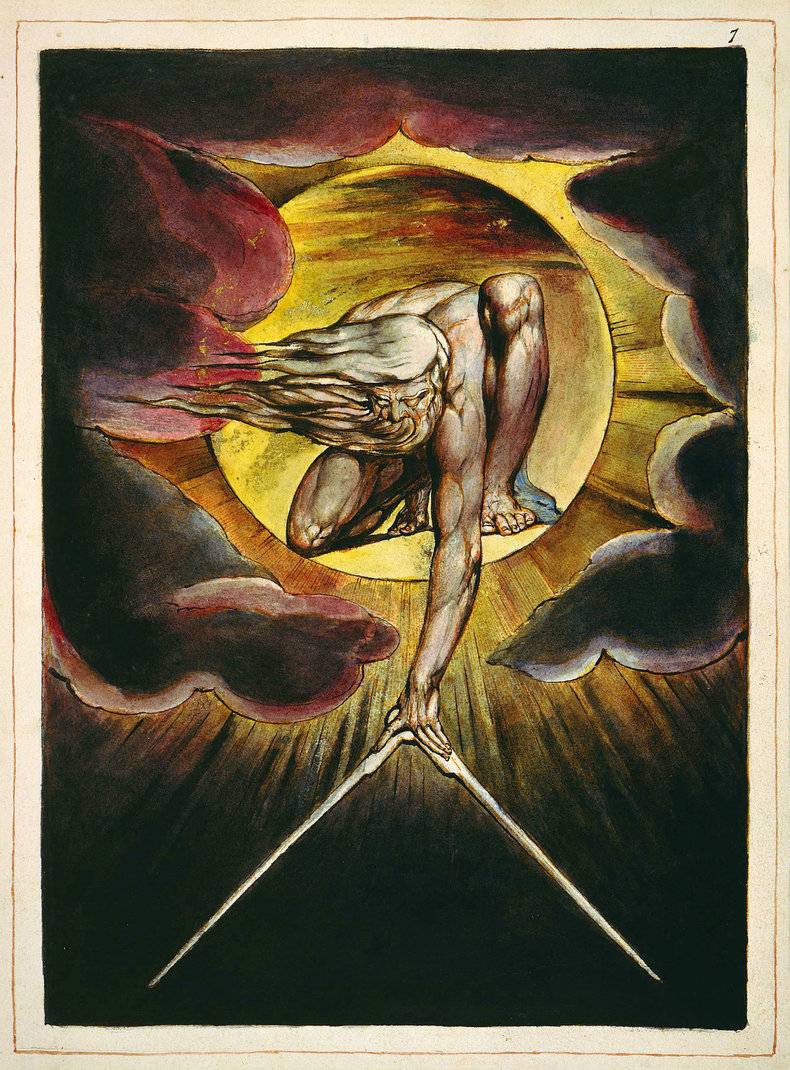
Medieval Art Generally speaking, modern audiences don't find medieval European art very appealing as it tends to be serious, stark, pious and often contains technical flaws such as unrealistic perspective. However, it is certainly a myth that the middle ages was a period of decline as Europe produced significant advancements in architecture in this time, particularly Gothic architecture.Dutch Golden AgeThe Dutch Golden Age was a time of cultural abundance in the Netherlands whereby the nation was economically and militarily dominant such that they ended up funding a great deal of art. This produced the masters Rembrandt, Johannes Vermeer and Jan Steen.Ancient ArtAncient art primarily refers to the art of early civilizations such as Babylonia, Assyria, Ancient Egypt, Indus Valley Civilization, Ancient China, Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome and the Roman Empire. These were sophisticated and powerful cultures that produced great works of creative expression and crafts that demonstrated significant mastery.NeoclassicismThe Renaissance sparked a multi-century obsession with all things ancient known as neoclassicism. This thrived throughout the 18th and 19th century with a focus on drama over accuracy or realism. Academic ArtThe brilliance of the Italian Renaissance and Dutch Golden Age collapsed into a period of decline in the 18th and early 19th whereby art was standardized by prestigious institutions with a style appropriately known as Academic Art. The religious themes and bland portraits of the middle ages were abandoned in favor of sensationalized scenes from myth, popular lore and history.RomanticismRomanticism was a mid 19th century rejection of Academic Art that sought the unique style and expression of the artist over rigid standardization. This was also a reaction against industrialization with themes of nature, idealized rural life and individualism. Romanticism was the first revolution in art whereby art become anti-establishment. This produced several remarkable artists such as William Blake who experimented with abstraction and surrealism way beyond his time.Ukiyo-eUkiyo-e is a term for 17th to 19th century Japanese art that was widely distributed as woodblock prints. In the 1850s, the American navy forced Japan to open its markets to the world. This suddenly ended the Edo-era and threw Japan into turmoil. One of Japan's first exports to the world was ukiyo-e. This greatly influenced European artists and is one way to explain the explosion of avant-garde art that begins in the 1860s and arguably continues to this day. Ukiyo-e was unlike anything Europe had ever seen with its unusual viewing angles, asymmetric composition, saturated unrealistic color, highly stylized works and imaginative subject matter.RealismRealism is a broad category of art movements that begin around 1850 and extend to the present day. This avoids style and abstraction to depict things as they are perceived by the eyes. Realism has a tendency towards depicting everyday subjects in slice of life situations.NaturalismNaturalism is a broader term for realism that is often used to describe realism in a rural setting. This emerged in the middle of the nineteenth century as a reaction against industrialization and urbanization. Naturalism most typically portrays the countryside in a somewhat idealistic light whereas realism is more commonly stark. Exceptions do exist such as the 1893 work Under the Yoke by Finnish painter Eero Järnefelt that doesn't gloss over the poverty and harsh conditions of rural life at the time.SymbolismSymbolism was a late nineteenth-century movement that uses symbols and imaginative elements that tell a story. This is largely viewed as a reaction to naturalism and realism that featured everyday life. ImpressionismImpressionism was a 19th-century art movement that depicts scenes as they are perceived by the artist without any particular abstraction. This emphasizes accurate light with delicate brush work. Impressionism is also known for its sense of movement and the passage of time.Post-ImpressionismPost-Impressionism was a late 19th century reaction against impressionism that embraces unnatural light, unrealistic angles and veers towards abstraction. This was a short lived movement that faded into the explosion of avant-garde movements of the early 20th century.Neo-ImpressionismNeo-impressionism continues with the accurate light, movement and passage of time of impressionism but tries to impose "scientific order" on scenes with the use of geometric shapes.PointillismPointillism is a painting or drawing technique that grew out of neo-impressionism that involves composing entire works from points of color. This began with fine dots with works that resembled impressionism and evolved into larger points with works that began to look increasingly abstract. Pointillism is considered one of the precursors to cubism as pointillist artists such as Jean Metzinger composed works from cube shaped points.CubismCubism was an early 20th century art movement based on highly stylized abstraction build up with geometrical shapes and multiple view points. These works have a multidimensional and deconstructed quality that are unlike any art that proceeds them. In other words, they represent a modern brilliance that was beyond the imagination of the past.FauvismAnother early 20th century reaction against impressionism that emphasizes the painterly quality of works with visible brush strokes. It is interesting to note that photography was well established by this time such that realism perhaps began to feel mechanical. Fauvism is a French term that can be translated "the wild beasts."Les NabisA small group of French artists who all knew each other that produced remarkable art in the brief period 1888 ~ 1900. This type of short movement was a common way for art to take leaps forward as artists inspire and challenge one another in a time and place. Prehistoric ArtPrehistoric art is any art that predates writing systems in a particular region. This includes the early stone etchings that begin around 73,000 years ago and includes works from the Stone Age, Bronze Age and Iron Age. In every region, prehistoric art demonstrates advancements over time whereby early works appear to be primitive attempts at realism and later works may include complex symbols and elements of style.Naive ArtNaive art is art that is produced by a person who is immersed in a modern culture but is not immersed in an art scene or trained as an artist. This produces interesting results as an individual essentially needs to invent styles and techniques from scratch. For example, the works of Henri Rousseau, a French tax collector who didn't start painting until his 40s, are now considered fine art that played a role in post-impressionism.ExpressionismExpressionism was a late 19th and early 20th movement that built upon the subjective expression of Romanticism by depicting scenes colored with cognitive states such as emotion, memory and perception.Abstract ExpressionismExpressionism was taken to its logical conclusion by a post-WWII American art movement known as Abstract Expressionism that embraced fully random processes such as throwing paint onto a canvas.FuturismAn early 20th century art movement centered in Italy that glorified modernity and industrialization with themes of youth, violence, speed, movement, automobiles, aircraft and other technology. Futurism emerged in Italy and involved some interesting characters such as musician/artist Luigi Russolo who is considered the first musician to produce music made exclusively with noise. Russolo's first concert in 1914 caused a riot.Art NouveauArt Nouveau was an early 20th century movement that mixed fine art and design. At the time, design was emerging as an important discipline as industrial products and societies were designed as opposed to crafted.MinimalismInitial mixes of art and design in the early 20th century were highly decorative and crafty. This didn't suit the requirements of an industrial economy that needed to scale out bland but unoffensive designs to millions. In this context, art and design movements such as Bauhaus that supported industrial needs rose to the forefront advocating minimalism and form follows function. These approaches dominated art and design between 1940 and the 1990s. The world filled with unadorned concrete, white rooms and corporate art.Commercial ArtCommercial art is any art that is produced with commercial constraints such as advertising, product designs, packaging, entertainment and publishing. This is an incredibly rich body of art that is considered ineligible to be considered high culture. For example, comic books such as manga are considered commercial because they are sold.Pop ArtIn the second half of the twentieth century, minimalism and abstraction dominated art, architecture and industrial design. The austere bleakness of 20th century minimalism can be contrasted with the color, bizarreness, personality and sensationalism of mass media of the same period. This fed back into art as a movement of the 1950s ~ 1960s known as pop art. This copied cliche styles and iconography from mass media in a way that was supposedly ironic.Street ArtStreet art is likely to be the art which comes to represent the current period in art history. It has a risk taking and competitive culture that is far more poignant, timely and culture-rich than any other art scene today. This has drawn institutional interest such that it is already considered high culture.Installation ArtInstallation art is art that is installed into a physical location such that it may be multidimensional and immersive. As contemporary art, this has a more academic and less edgy feel than street art. Modern technology allows for extremely compelling immersive experiences but video games are arguably ahead of installation art in this regard.Postmodern ArtPostmodern art is a broad and incomprehensible term for contemporary art. Generally speaking, this has moved beyond the pretentious minimalism and abstraction of late modern art to seek the emotional, bizarre and human. Hyperrealism mixed with absurdity is a common theme. Digital ArtDigital art is art that is produced and experienced in digital environments. This includes fine art produced with digital tools and commercial art such as video games. Digital art is potentially multisensory and immersive such that it has far more possibilities than traditional art. It seems likely that future people will spend much time in virtual or mixed reality worlds such that stepping into art will be the norm.
Art
This is the complete list of articles we have written about art.
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|