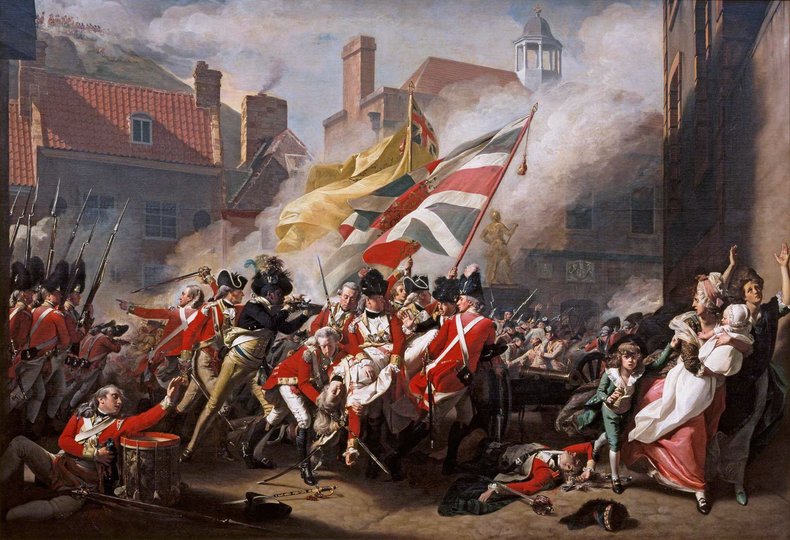
Taxation without representation. | The French and Indian War of 1754 to 1763 were costly for Britain leading to determination to tax the colonies. |
Taxation Acts of 1764 | Sugar Act placed taxes on sugar, molasses, coffee and cloth. |
Stamp Act taxed newspapers, documents, playing cards and dice. | Townshend Acts put taxes on tea, glass, paint and paper. |
Mercantilist practices that limited colonial trade and favored British merchants. | Presence of British troops in the colonies was viewed as oppressive. |
Writs of Assistance that gave British soldiers the right to search and seize property and abuse of this power. | Quartering Act of 1765 that required colonists to house British soldiers. |
Proclamation of 1763 that prohibited colonial settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains. | Boston Massacre of 1770 in which British soldiers killed five colonists |
Acquittal of six British soldiers involved in Boston Massacre with only two soldiers dishonorably discharged. | Boston Tea Party of 1773 |
British reaction to the Boston Tea Party with punitive measures in the Intolerable or Coercive Acts of 1774. | The Enlightenment and its philosophy and social movements around rights, liberty, the social contract and popular sovereignty. |
Common Sense published by Thomas Paine at the beginning of 1776 that became an influential pamphlet calling for independence. | Religious beliefs of Protestant groups in the colonies that did not view the King as having divine rights. |
Geography of the colonies and distance from Great Britain. | Mindset and character of colonists who went to the New World seeking opportunity and freedom. |
Existence of colonial legislatures and growing ability of colonies to administer themselves. |