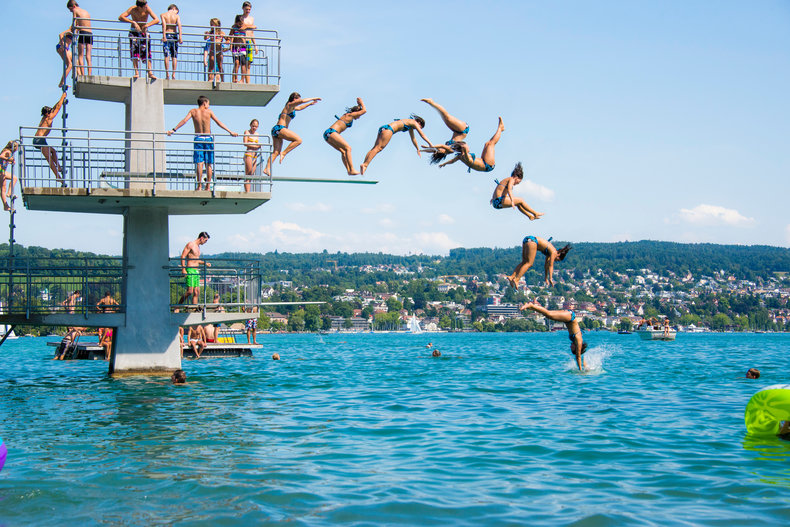
Arrow of Time
Arrow of time is the observation that time moves in one direction from past to future.Cause and Effect
Cause and effect is the observation that one thing causes another. Due to the arrow of time, these sequences of events can never be changed once they occur. For example, if you jump off a diving board, this jump can't be reversed such that your landing becomes inevitable.Entropy
Entropy is the observation that things (isolated systems) move in one direction from simple to complex. For example, the information required to describe the universe is constantly increasing as it expands and ages. As such, time could be described as a process of entropy -- ever increasing complexity, decay and chaos.Spacetime
The theory that time is a forth dimension alongside length, width and height. Time is unique amongst these dimensions because it can only be traveled in one direction.Time Preciousness
The observation that time is the most constrained thing that humans need whereby you can get more water, food, space, love or money but lifespan appears to be inherently limited.Nostalgia
As you can only travel in one direction in time, you can never return to a moment. This creates melancholy feelings about time known as nostalgia.We Are Time
The idea that the past and future do not independently exist but are part of the human experience in forms such as memory, nostalgia, anticipation and prediction. If time were nothing more than a human cognitive device, it may be difficult for us to understand a timeless universe.Subjective Time
The theory that humans perceive time differently such that things are moving faster for some people than others. For example, the theory that time moves faster as you age.Biological Time
Perception of time is related to the size of an organism and its metabolism. For example, birds appear to perceive visual information in faster streams than humans. As such, a human generally appears to be slow from the perspective of a bird. Humans may appear to be fast from the perceptive of an animal with a slow metabolism such as a turtle.Time Dilation
According to the General Theory of Relativity, time slows down as you move faster. This has been repeatedly confirmed with experiments and is hard science.Time At Speed of Light
Due to time dilation, time stops at the speed of light. If you are moving at the speed of light away from a clock you can look back forever but the clock will never move from your perspective.Time Distortion
Time distortion, better known as Gravitational time dilation, is the observation that time moves slower at high gravity (created by proximity to a large mass). For example, time moves faster on an airplane than on the ground. As with speed dilation, time can stop with high enough gravity such as on the surface of a black hole that theoretically has infinite gravity.Wheel of Time
Several religions and philosophical theories view time as a cycle that is repeated. This is similar to the Big Crunch hypothesis of physics that predicts that expansion of the universe will eventually reverse. This would imply that the size of the universe would ultimately approach zero, presumably creating the conditions for another Big Bang.Notes
Biological time is the reason that it is generally difficult for a human to capture a bird with our hands. Even if we move as fast as a bird such as a chicken, the bird perceives events quickly such that we appear to be moving in slow motion from the bird's perspective.| Overview: Time Examples | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The movement of events from past to future. | |
Related Concepts | ||