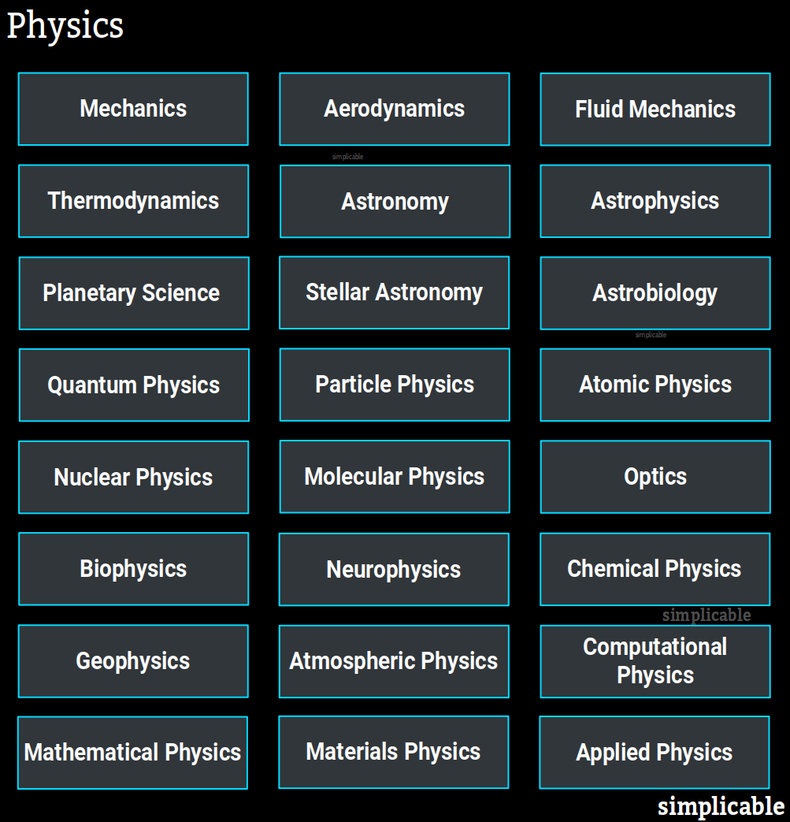
Mechanics
The physics of moving physical elements and objects.Aerodynamics
The study of the motion of air.Fluid Mechanics
The study of the motion of fluids.Thermodynamics
The branch of physics that deals with heat and work.Astronomy
The study of the universe beyond Earth. A broad field that includes many branches.Astrophysics
The branch of astronomy concerned with the physics and chemistry of astronomical objects such as galaxies, stars, planetary systems, planets, moons and asteroids.Planetary Science
The study of planetary systems, planets and moons. This includes Earth and the Solar System.Stellar Astronomy
The study of stars and stellar evolution.Astrobiology
The scientific study of life in the universe including its origins, early evolution and future. This also concerns the question of whether extraterrestrial life exists and what characteristics it may demonstrate.Quantum Physics
Quantum physics, also known as quantum mechanics, is a cornerstone of theoretical physics that describes the physical properties of the universe at atomic and subatomic scale.Particle Physics
A brand of physics that mostly deals with the smallest detectable particles and their behavior and interactions.Atomic Physics
The study of atoms including electrons and atomic nuclei.Nuclear Physics
The study of the atomic nuclei. Primarily concerned with nuclear power and nuclear bombs.Molecular Physics
The science regarding the physical characteristics and movement of molecules.Optics
The branch of physics that deals with light.Biophysics
The use of physics to study biology. An interdisciplinary science.Neurophysics
The branch of biophysics concerned with the nervous system.Chemical Physics
The study of chemistry from the point of view of physics.Geophysics
The study of geology from the perspective of physics including elements such as the Earth's shape, gravity, magnetic fields, internal structure, volcanism and plate tectonics.Atmospheric Physics
The application of physics to the atmosphere of Earth. Closely related to meteorology and climatology.Computational Physics
The computational science that solves problems in physics with computing techniques such as algorithms.Mathematical Physics
The application of mathematics to problems in physics.Materials Physics
The physics component of the interdisciplinary field of materials science that looks at the properties of materials.Applied Physics
The application of theoretical physics to solve problems and develop know-how.| Overview: Physics | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The science that deals with the basic elements of the universe such as matter, space, energy, motion and force. | |
Related Concepts | ||