Moral Duty
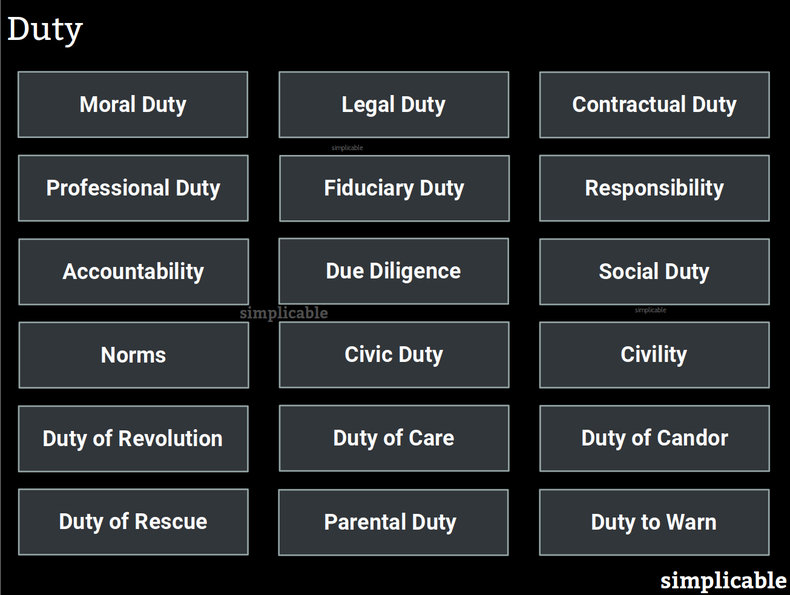
An obligation that is created by principles of right and wrong. For example, the moral duty to be honest with others.Legal Duty
A duty created by the laws and regulations of a society. For example, the duty to report your income to a tax authority.Contractual Duty
A duty created by agreement between parties. For example, a company director that has a duty to disclose any conflicts of interest by the terms of their employment agreement.Professional Duty
A duty to comply with the ethics and norms of a profession. For example, journalists that have the duty to verify the accuracy of their reports according to a code of ethics.Fiduciary Duty
Fiduciary duty is an obligation to act in the best interest of another party. This comes up in business where you are representing someone else in a transaction. For example, a real estate agent representing a buyer has a fiduciary duty to tell the buyer if they are aware of a problem with a property. This is a type of legal duty.Responsibility
Responsibilities of a role such as a job or social role. These can be dynamic such that they change from day to day. For example, an accountant that has a responsibility to reconcile bank records with journal entries.Accountability
Accountability is like responsibility except that it can't be delegated. For example, the VP of Operations for an airline can delegate safety related maintenance to mangers but remains accountable for safety.Due Diligence
The level of care that can be reasonably expected of a task. For example, the duty to investigate the labor and environmental practices of your partners such that ignorance can't be used as an excuse.Social Duty
Social duty is an informal duty defined by society and culture. For example, the Japanese concept of giri (duty) and ninjo (true feelings) whereby social duty often comes into conflict with one's true feelings and desires. For example, a father who wants to spend time with his children each evening (ninjo) who has a social duty (giri) to stay at the office until his boss goes home. Generally speaking, Japanese culture respects those who put duty ahead of feelings. Some cultures reverse this where following your true feelings despite your duty is glorified.Norms
Norms are rules of behavior that are enforced with social processes. This respects the intelligence and freedom of individuals by not making everything a formal law, regulation or rule. It's an informal social duty to follow norms if you want to fit in with a society or culture. For example, the norm that you thank someone who offers you a courtesy.Civic Duty
Civic duty are ethical obligations expected of all members of a society. For example, the duty to vote in elections.Civility
Civility is the duty to resolve disputes in a reasonable way using the systems and norms offered by a society. This assumes a society has rights, freedoms and reasonable systems for resolving disputes.Duty of Revolution
The right or duty to overthrow a government that has ceased to function as a democracy or that has turned against its people.Duty of Care
A legal duty to apply a reasonable standard of care if you are doing something that could harm another person. For example, the duty to pay attention when you're driving.Duty of Candor
Duty of candor is the principle that a government not try to win lawsuits at all costs but to admit to mistakes, errors, omissions and fault even if it isn't beneficial to their case. For example, the responsibility of a public hospital to report mistakes in a procedure even if this creates liability.Duty of Rescue
The duty to come to the aid of someone who is in danger. A moral duty that isn't always a legal duty.Parental Duty
Duties to protect, nurture and provide children with every chance to thrive. For example, parents, guardians and babysitters have a duty of rescue.Duty to Warn
The duty to warn others of danger that you are aware may harm them. For example, an employer has a duty to inform employees of workplace hazards such as a dangerous or unhealthy chemical.Notes
The examples above include legal, moral, social and role-based duties.| Overview: Duty | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An obligation to act or not act in a particular situation. | |
Related Concepts | ||