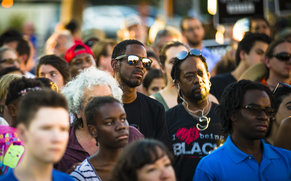Society
The study of societies, complex social structures that organize human affairs in a place.
Culture
Meaning and behaviors that emerge from the shared experiences of groups. This includes national cultures, traditional cultures, super culture and subcultures.
Traditions
Traditions are stable and enduring elements of culture that provide shared experiences across generations.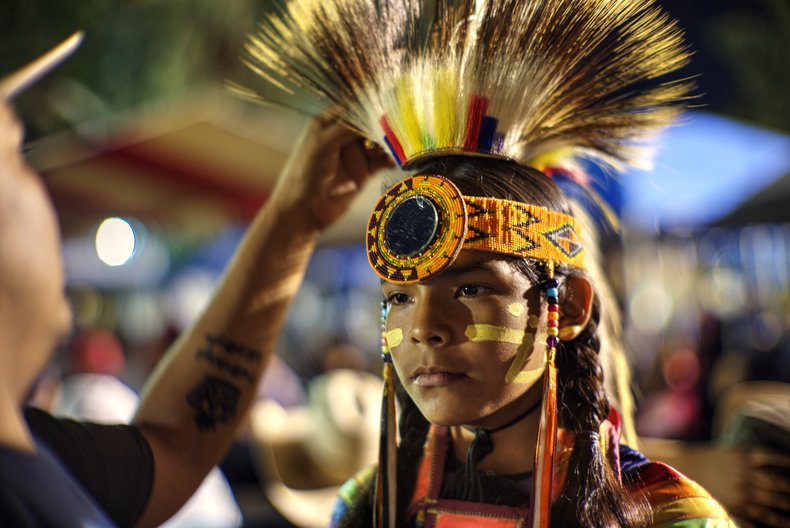
Norms
Norms are shared expectations of behavior that emerge in a culture. Sociology looks at how norms emerge and how they influence social behavior.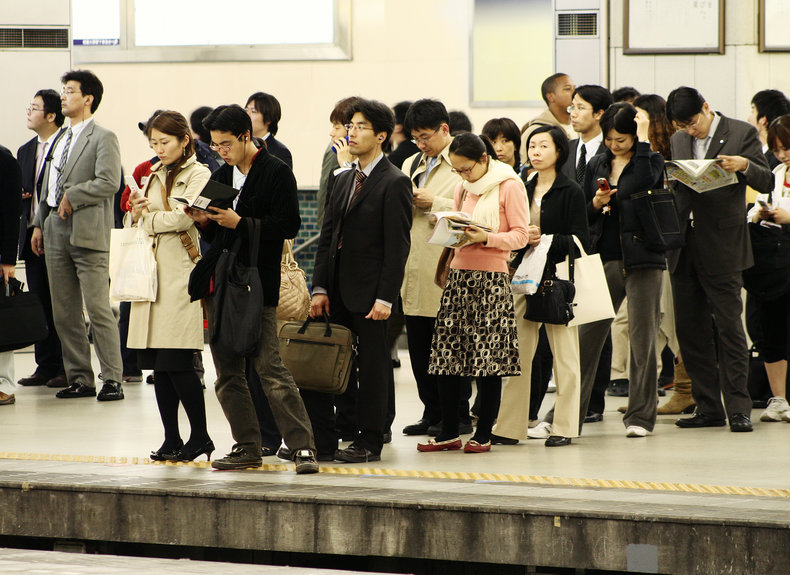
Social Behavior
Social behavior such as communication, leadership, motivation, engagement, cooperation, competition, conflict, altruism, friendship, family and courtship.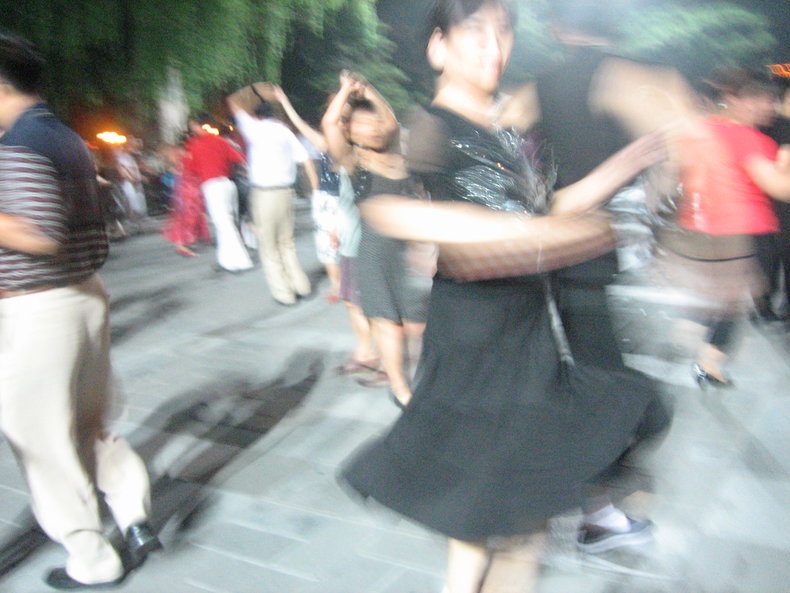
Politics
Politics is the means by which social groups make decisions and allocate authority. Sociology looks at the structure, systems and policies of governments and their impact on human behavior and quality of life.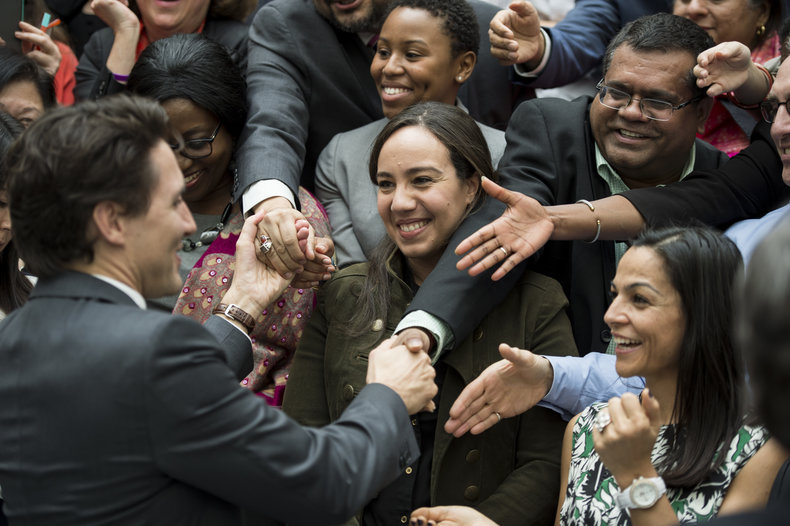
War & Conflict
War, conflict, diplomacy, peace and related issues such as refugees.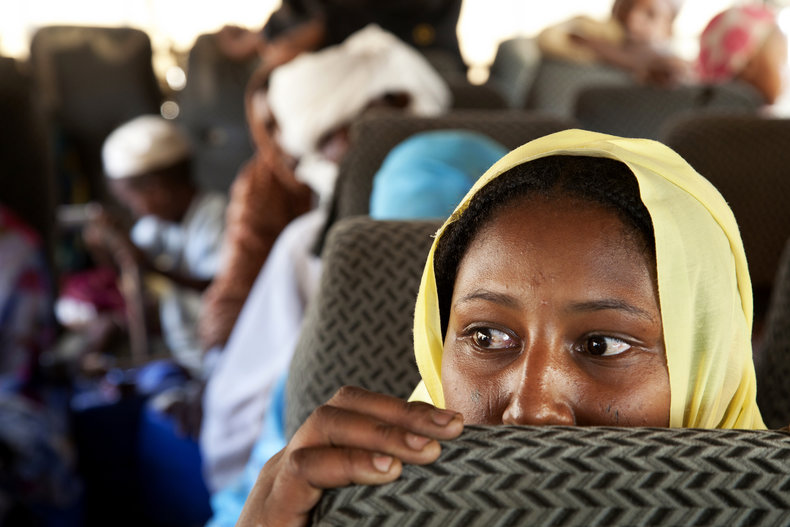
Institutions
Sociology defines institution in broad terms as any enduring and stable practice adopted by a society. This includes elements of culture such as family and language. It also includes the systems of a society in areas such as education, knowledge, media, justice, law, health, finance and religion.
Criminality & Law
Behavior that exceeds the tolerances of a society and rules that are enforced with the power of a state.
Roles
Roles are responsibilities or expectations assigned to an individual by a society or institution. These include political, economic and social roles. For example, a family role such as parent or a professional role such as train conductor.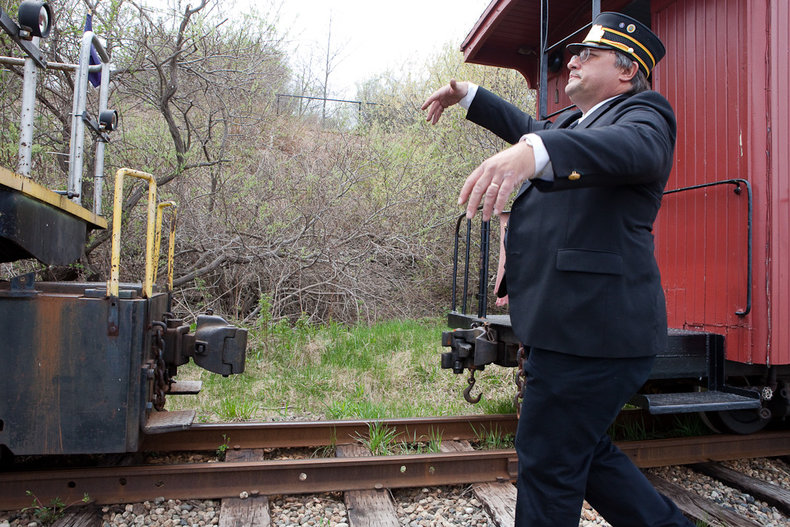
Demographics
Demographics is the composition of a society, place or group. For example, the study of the population of a city including dimensions such as age, gender, socioeconomic class and ethnicity.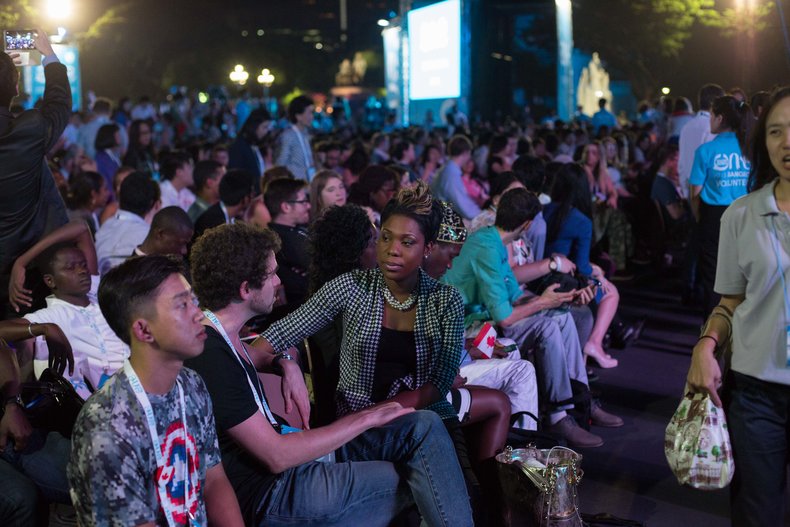
Economics
Economics is a distinct academic discipline from sociology but the two are hopelessly intertwined such that you can't understand one without the other.
Social Structure
Social structures are patterns of group membership. For example, socioeconomic classes such as the upper class, bourgeoisie, middle class and working class.
Social Mobility
Social mobility is the potential to improve or worsen your position within the social structures of a society. This is mostly associated with an ability to transition to a higher socioeconomic class. Generally speaking, a society with social support such as government funded healthcare and education has higher social mobility. Economies based on competition, entrepreneurship and meritocracy have higher social mobility than economies based on rent seeking.
Social Issues
Social issues such as poverty, addiction, disease, crime, instability, inequality and pollution.
Development
The process whereby countries with a high poverty rate work towards becoming developed countries with a high quality of life.
Identity
The degree to which individuals identify with the social groups that they belong to by default and seek to define their identity in terms of optional group memberships and individual expression.
Social Change
Society and culture aren't static items that can be understood in a timeless way but are rather complex, dynamic systems that constantly change.
Power
The control of resources within a society including elements such as authority and wealth. One approach to sociology, known as critical theory, views every relationship in society as a materialistic power struggle. Other approaches, such as structural functionalism, view society as cooperative and rational such that those with power serve some function.
| Overview: Sociology | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The study of human social behavior and structures. | |
Related Concepts | ||