Need
Humans are born with emotional and physical needs that must regularly be satisfied to avoid pain and decline. For example, the need to eat or to be safe.Instinct
Humans have instincts and are able to override these with higher level thought processes. For example, a person may feel a strong urge to flee from danger but may override this to face the danger where it makes sense.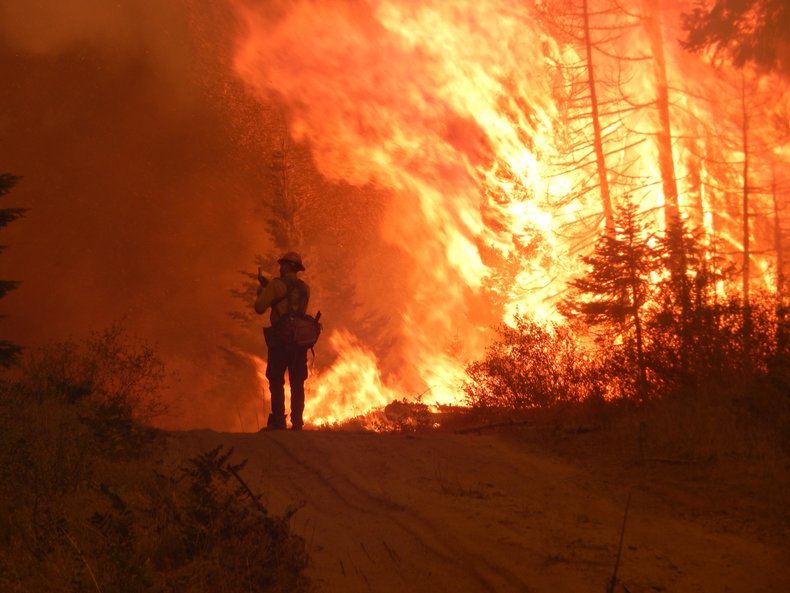
Self
Humans have a sense of self such that they defend what they view as their self interests and have a sense of self-esteem and self-importance.Relatedness
A desire to be connected and to interact with other people.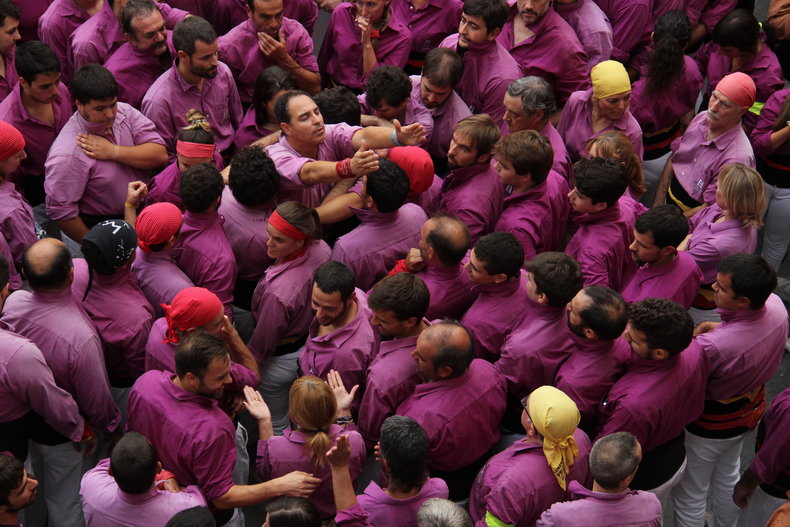
Motivation
Humans have desires known as motivation that are amazingly diverse as compared to animal instincts such as the drive to find food.Emotion
Emotions are mental states that color all thought for a period of time.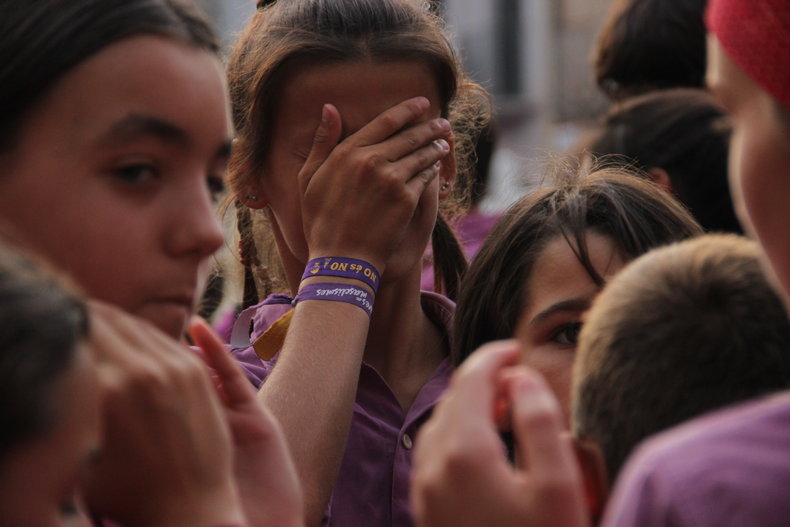
Empathy & Sympathy
Empathy is the ability to share emotions and sympathy is the ability to recognize emotions and react appropriately.Imagination
The ability to think in ways that differ from concrete reality.
Creativity
The ability to produce things from the imagination such as designs or new concepts.Art
The unconstrained pursuit of expression.Aesthetics
The ability to feel that elements of the world are beautiful or otherwise appealing.
Play
Play is the drive to find joy and fun in the world.Competition
Humans appear to be competitive and may seek to create competition with sports, games, challenges and similar pursuits.
Social Comparison
People commonly compare themselves to other people.Social Status
The desire for respect and recognition from others.Growth
The drive to grow, explore and improve.
Productivity
The drive to create and produce.Rational Thought
The ability to consider evidence in a systematic way to form opinions.Discipline
Discipline is the ability to transcend motivation to do what is required in a situation. For example, the discipline to wake early in the morning to train when your motivation is telling you to sleep late.
Introspection
Introspection is the ability to examine your own character, thinking, emotions and behavior to self-improve.Memory
An ability to remember information for a lifetime. Human memories are often fuzzy and surrounded in emotion such as nostalgia.
Intuition
Intuition are opinions and feelings that are formulated with processes that are unknown to your conscious mind. Plato and Socrates viewed this in mystical terms as a connection to an eternal force. Modern theories view intuition as unconscious knowledge and unconscious cognition although this isn't well understood.Knowledge
The ability to try to understand things and to share this information.
Language
Humans think and communicate with language.Communication
People try to communicate with each other.Concepts
Humans can think in ways that differ from concrete reality. In fact, all languages have a large number of concepts that have no direct physical equivalent.
Technology
A knack for making useful tools.Society, Culture & Tradition
Humans demonstrate complex social behavior with an ability to develop shared systems, rules, celebrations and meaning.
Experiments
People are curious and try things to discover new knowledge. This can be seen in babies who commonly perform experiments to investigate cause and effect such as intentionally knocking something over.Risk Taking
The ability to act in an environment of uncertainty and risk to pursue opportunity.
Failure
Human beings aren't infallible such that they often fail, make mistakes and misjudge things.Strengths
Humans are highly capable and well adapted to life on Planet Earth. For example, humans have a large number of social capabilities such that they can cooperate in large groups in a highly organized way.Resilience
Humans can learn from failures, stresses and risk taking to become stronger.
Weakness
Humans often lack capabilities that would be advantageous to their life. These can be physical or cognitive. For example, individuals commonly have character weaknesses. Each individual has a unique set of strengths and weaknesses.Tactics
The ability to identify actions that may achieve a short term advantage.
Strategy
An ability to think out a series of actions that will achieve a goal in the long term. Humans have significant capacity for strategic thinking.Control
People commonly seek to control their environment. They may also seek to exert control or influence over each other.Freedom
People seek freedom from control. They demonstrate reactance, meaning they may strongly react to attempts to take freedoms away.
Diplomacy
The ability for groups such as nations to use communication and understanding to resolve differences.Politics
Politics is the process of making decisions as a group through communication. Often involves intense power struggles that may nonetheless remain somewhat civil. Politics tends to emerge in any group that cooperates.Civility
Civility is the ability to organize into societies, communities and cultures and to conform to a shared set of rules in order to live in peace.
Conflict
A tendency for civility and diplomacy to breakdown resulting in conflict between individuals and groups.Fear
A dread of failure, uncertainty and risk. A type of instinct or motivation.
Angst
Angst is the fear that your life will be meaningless. A type of motivation.Epic Meaning
A desire for experiences that are deeply meaningful to an individual.
Love
The ability to demonstrate unconditional loyalty, deep affection and benevolent concern for others.
Philosophy & Spirituality
The ability to ponder foundational questions concerning the nature of the universe and the meaning of life.Morals
People commonly adopt principles of right and wrong that they use to judge thoughts and actions.
Altruism
An unselfish desire to make things better even if it means personal sacrifice.Transcendence
An ability to overcome elements of society or human nature that is inconsistent with your pursuits. For example, an individual who can transcend the common tendency to engage in social comparison to reach a state of joyful self-confidence.
Notes
The list above isn't exhaustive. All the traits above aren't necessarily universal but are common human characteristics.It is often argued that humans can act in ways that are contrary to their nature. For example, being anti-social when you are innately social.| Overview: Human Nature | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The common dispositions and characteristics of people. | |
Related Concepts | ||