Hue
In nature, almost all light is mixed with different wavelengths. The human mind approximates mixed light from the visible spectrum from 380 to 740 nanometers as a color. Random wavelengths of light that contain great variation are perceived as white or as a light color. Mixtures of wavelength of similar length are often perceived as a bright color that is free of white. These are known as hues and are considered pure colors.Spectral Colors
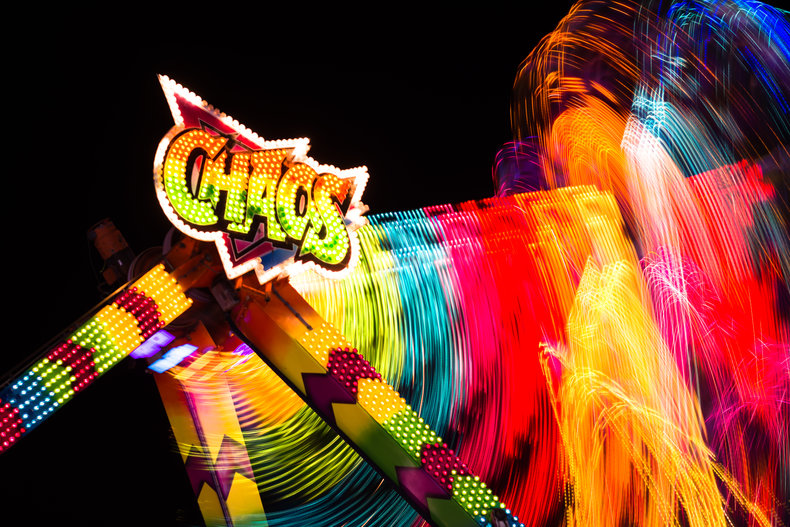
Spectral colors are hues that correspond to a single wavelength of light or narrow band of wavelengths. These exist on a continuum based on wavelength that spans from violet, blue, cyan, green, yellow, orange to red.Pigments
In painting theory, a hue is a pigment that has not been mixed. From this perspective, unmixed pigments are pure colors.Saturation
Saturation is the intensity and purity of a color. A laser light is the most saturated color because it can be based on a narrow wavelength and be extremely intense. A color that is pure and intense can be described as heavily saturated. A saturated color appears bright against both a white and black background due to its intensity and lack of grey content. For example, a neon green highlighter pen that is highly visible on both white and black paper.Shades
A shade is any hue that has been mixed with black. This is less pure than the hue itself.Tints
A tint is any hue that has been mixed with white. This is less pure than the hue itself.Tone
A tone is any hue that has been mixed with both white and black. In other words, a hue that has been mixed with grey. This is less pure than the hue itself.| Overview: Color Purity | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | The degree to which a color is free of white and black. | |
Definition (2) | The degree to which a color pigment is unmixed with anything that changes its color. | |
Related Concepts | ||