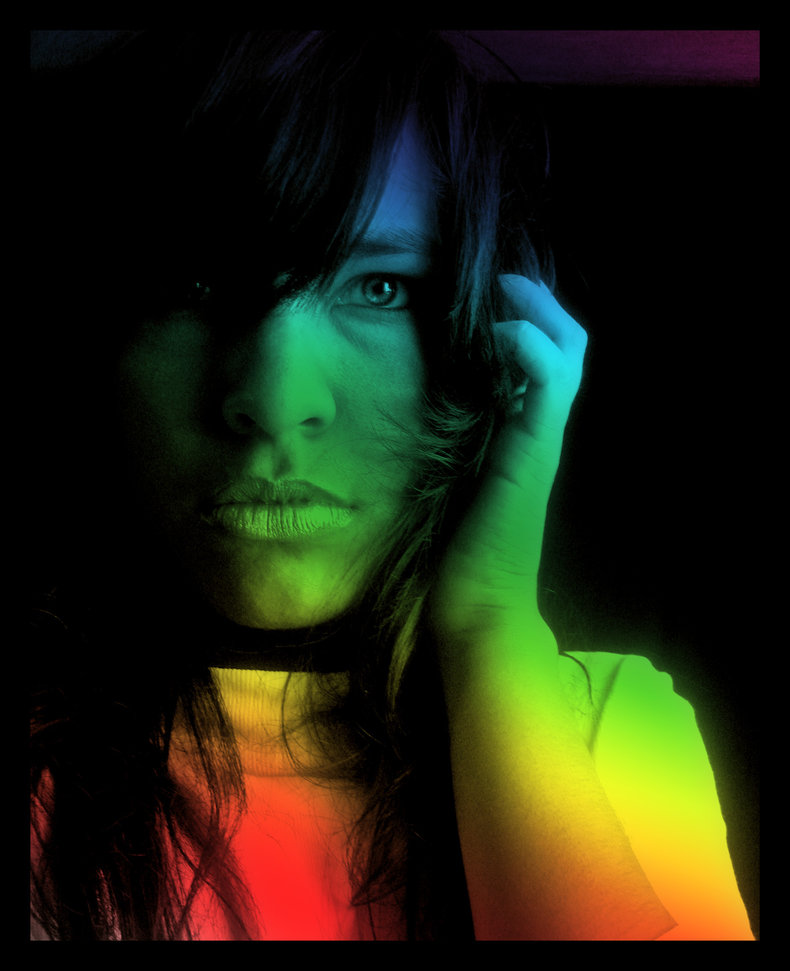
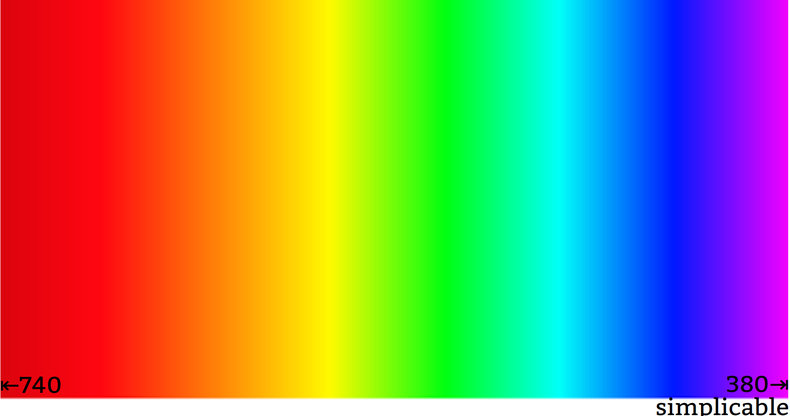
| Color | Wavelength (nm) |
| Violet | 380 - 430 |
| Indigo | 430 - 460 |
| Blue | 460 - 500 |
| Cyan | 500 - 520 |
| Green | 520 - 565 |
| Yellow | 565 - 590 |
| Orange | 590 - 625 |
| Red | 625 - 740 |

Spectral Color vs Primary Color
Spectral colors are based on the science of light perception such that they map to the physics of light that can be perceived by humans. Primary colors are a set of colors defined by a color system that can be used to simulate all other colors. The following chart illustrates the difference between these concepts.Spectral Color | Primary Color | |
Based On | Science | Art & Technology |
Represents | The physics of light that can be perceived with the eyes. | A system for simulating all colors with a small set of colors. |
Can reproduce all colors? | Yes | No, some colors are only simulated with primary colors such as red, green and blue (RGB). You need all spectral colors to truly reproduce all colors. |
Usefulness | Understanding color | Implementing a technology or painting method that simulates a wide range of colors. |
Notes | There is only one set of spectral colors. | There are many different sets of primary colors corresponding to different technologies and painting methods. |
Notes
Although spectral colors are the root of all colors, other factors impact color. For example, light intensity can be used to make colors light or dark.Visible light is a tiny part of the electromagnetic spectrum that includes extremely shortwave lengths such as a 1 picometre gamma ray all the way up to a extremely low frequency radio wave that is 100,000 kilometers long. White light is what your brain perceives when hit with all spectral colors at the same time as in sunlight.Pure spectral colors are relatively rare as most colors are some mix of color. Rainbows are a good example of spectral colors in nature.| Overview: Spectral Color | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A color that corresponds to a pure wavelength of visible light. | |
Related Concepts | ||