Advertisements
Design Guides
Related Topics
| |
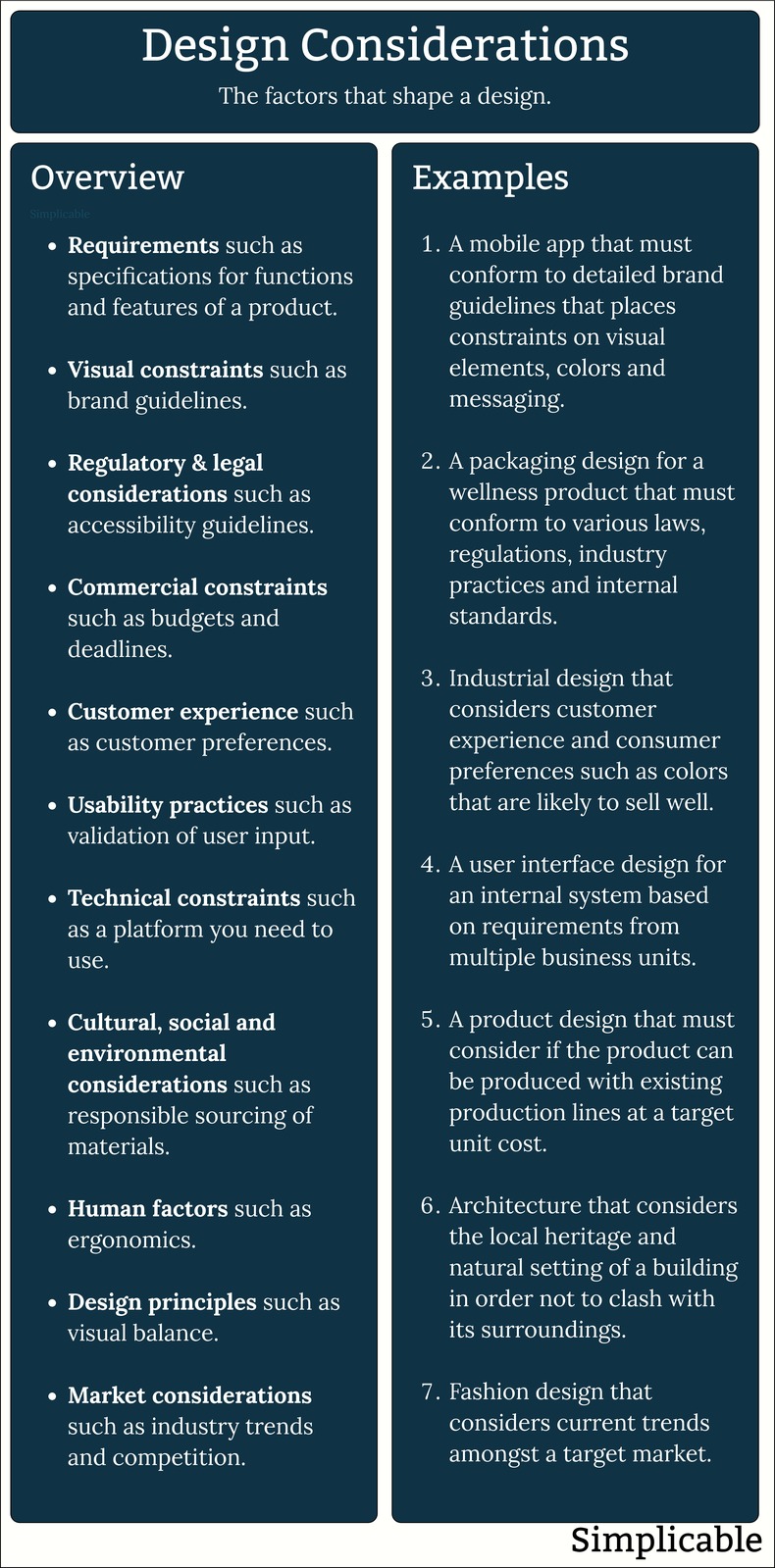
Design considerations are the factors that shape a design including requirements and other constraints such as branding, standards and user experience. Design differs from art in that it considers factors such as strategy, customers, markets, technology, regulations and competition. The following are common design considerations.
AccessibilityDesigning things so that they can be accessed by people with disabilities.ArchitectureArchitecture is a structure for design. For example, the architecture of a building provides a structure for interior design.AutomationAutomation of functionality and decisions. BrandingBrand considerations such as identity, image and positioning. These are often specified in brand guidelines that provide a comprehensive specification for the visual identity of a brand.
CohesionDesigning things to belong together such as a fashion line designed to match.ColorUse of color techniques such as color harmony and color temperature.ConvivialityThe friendliness and liveliness of a design such as an urban design with attractive public spaces.ComplianceCompliance to laws and regulations.Cost Development costs, unit costs and operational costs.CultureCulture exists at many levels such as the culture of a nation, region or city. Design such as architecture may seek to reflect local culture. Customer Preferences Customer tastes and preferences such as fashion sense.DeconstructionDesigns that are easy to take apart to fix, reuse and recycle.Design Constraints Constraints such as cost, time and politics.Design PrinciplesDesign principles are basic laws of design such as visual balance that states that designs should look balanced on both sides of middle.DurabilityDesigns built to last.Efficiency Designs that make efficient use of energy and resources.EngagementTechniques for engaging users such as gamification.ExperienceConsidering the lifetime of interactions between your design and customers.ExtensibilityDesigns that can be extended with future designs or components such as accessories.FeaturesA collection of related functionality.FunctionalityThe operations that a design provides to customers.GoalsThe goals and strategy behind a design. In other words, your motive for creating the design.Health & Safety Designs related to health & safety such as running shoes designed to be highly visible under a variety of conditions.Human FactorsDesigning things to suit human physical, physiological and social characteristics.Human ScaleThe practice of designing things at a size, speed, weight, temperature, energy level, pressure and distance that is appropriate for humans. Virtually everything small and large is built to human scale.InteroperabilityDesigning things to work with other things.LanguageDesigns that minimize the rework required to offer products and services in multiple languages.Layout & Composition The arrangement of elements of a design.LightnessElements that get out of the way so as to appear almost nonexistent.LookThe overall visual appeal of a design.MaterialsChoice of materials.Modeless vs Contextual Contextual user interfaces produce different results depending on the circumstances. Modeless designs always work the same way.Negative Space A background that plays an active role in a design. OperabilityOperational considerations such as maintenance procedures.PerformancePerformance such as speed or accuracy.PositioningThe position of a product, service or creative work in a crowded market. ProductionHow the design will be produced. For example, a design that can be produced by the equipment at a particular factory. ProximityProximity is the closeness of things. It is a common consideration in practices such as urban design that deal with large physical spaces.QualityA general term for any quality that makes a design more valuable such as ambiance, character and consistency.Requirements Requirements such as use cases and user stories.ReusabilityDesigns that can be reused as a goal of sustainability or as a feature.ScalabilityHow well a design performs as business volumes such as website traffic increase.SecurityPhysical and information security.Shape And FormShape is 2D and form is 3D.StandardsRelevant standards such as electrical safety standards or web design best practices.StyleA character that shows through in a line of products, brand or work of a designer.TechnologyTechnology considerations such as green technology for sustainable design.TouchHow something feels to the touch including techniques such as haptics.TrendsThe near future direction of technology, markets or customer preferences.Usability Ease of use.WasteDesigns that minimize production, operational or end-of-life waste.ValuesYour values as a designer or the values of your organization.OverviewDesign considerations are the requirements, standards, practices, principles, commercial and technical constraints that are considered in a design.SummaryDesign considerations include anything that shapes a design such as requirements, regulations, design principles and brand guidelines.
More about design considerations:
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
An overview of design composition with examples.
The common types of design constraint.
A list of what is included in design requirements.
The definition of form with design examples.
A list of human factors in design.
A comprehensive guide to design.
An overview of color theory.
The difference between layout and composition.
The difference between modeless and contextual user interfaces explained.
A list of common types of design.
The steps in a design process.
The common types of design quality.
A definition of universal design with examples.
A definition of sensory design with examples.
An overview of emotional design.
The definition of elegance with examples.
Definitions of color theory.
The study of color mixing and the visual effects of color.
Colors that can't be seen under normal circumstances.
Why colors match or clash.
The definition of color.
A definition of color symbolism with examples.
An overview of the colors of the rainbow including a few common myths.
A large collection of color palettes.
TrendingThe most popular articles on Simplicable in the past day.
Recent posts or updates on Simplicable.
Site Map
|