Life Skills
The acquisition of life skills such as language literacy and basic mathematics. This is required for full participation in society, culture, community and the economy and is therefore a critical element of the human experience that all people deserve as a human right.
Knowledge
Humanity has built up an extremely large pool of knowledge that has immense value in enriching the lives of individuals and the future of societies. For example, learning about the past helps us to avoid repeating painful mistakes.
Know-how
Learning how to do things. For example, learning how to automate work and solve problems with computer code.
Socialization
Schools can be a place to socialize and acquire social skills. This can include the process of dealing with conflict and people you find difficult to build social resilience.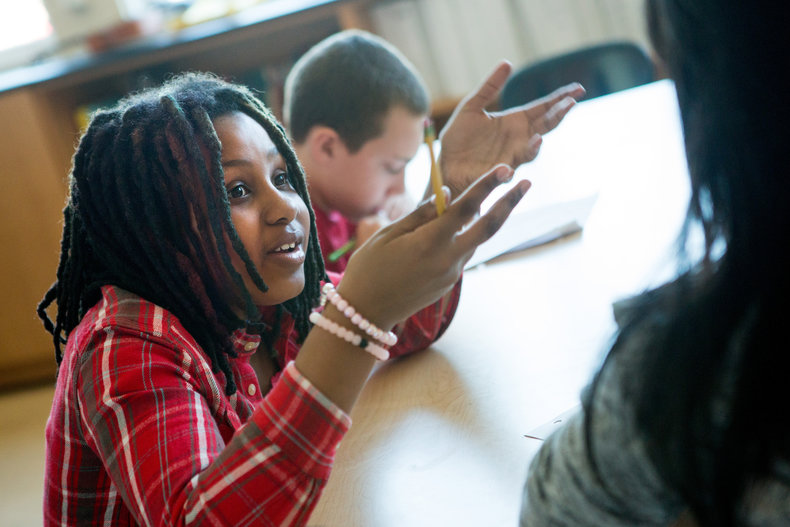
Cooperation
Schools may provide cooperative exercises that give people experience working as a team.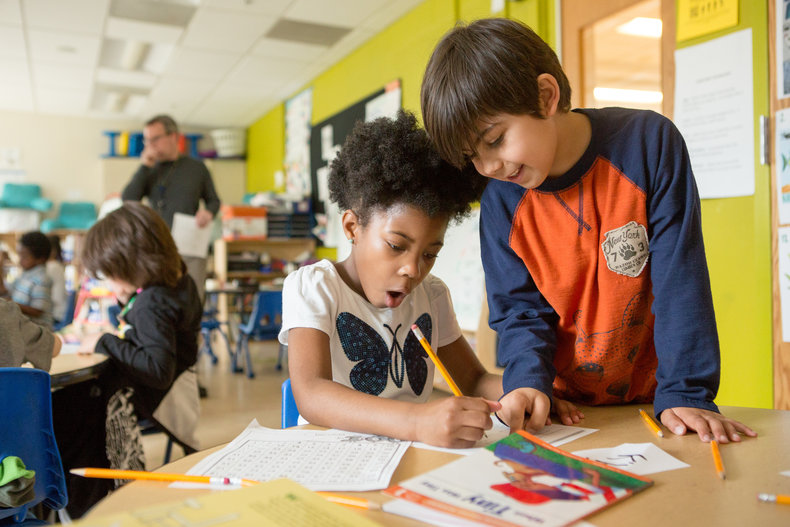
Free Expression
The experience of expressing your opinion or creativity and engaging in processes such as public speaking, debate and peer review. This is a critical process that helps us to understand different perspectives and gain experience influencing, arguing, critiquing and handling criticism.
Cultural Competence
Where schools are diverse, they provide an opportunity to interact with people from different backgrounds. This can be stimulating and allows individuals to build cultural competence.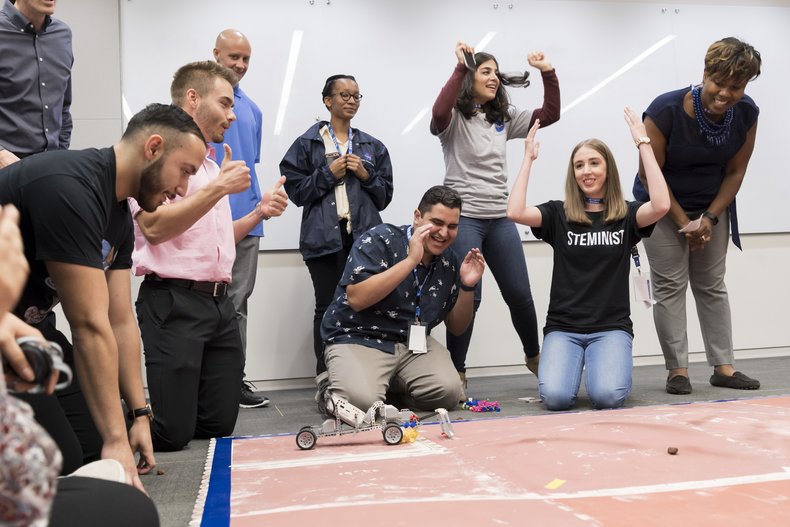
Cultural Capital
Cultural capital is the ability to thrive in a culture. This comes with experience and schools are often a social environment that can help to generate cultural capital. For example, the culture of high status universities may be heavily connected to the culture of high status institutions and firms in a society. Beyond this, schools may offer a means to engage the culture surrounding an art, science, sport, hobby, profession or place.Competition
Gaining experience with competition in areas such as grades, social processes and sports. It could be argued that life is fundamentally competitive such that immersion in competitive environments helps students to thrive in life.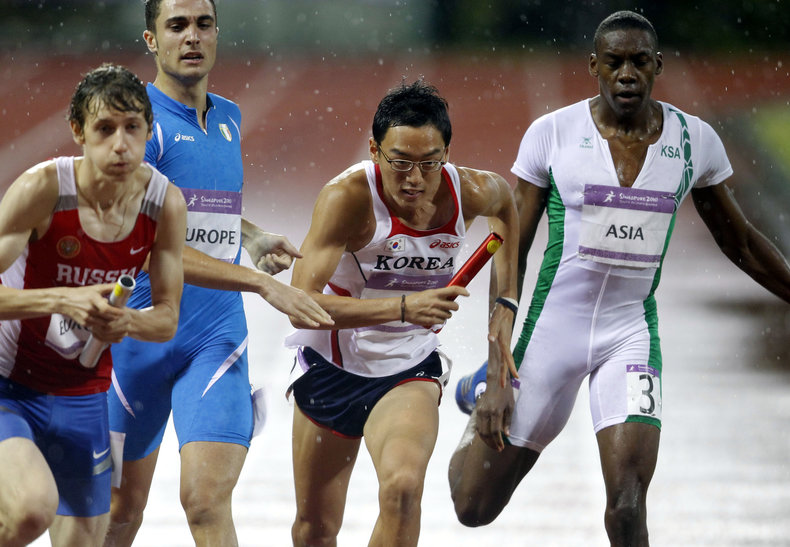
Play
Schools often provide an opportunity to play with others. It is a right of children to have time to play and this is critical to their development.
Quality of Life
In some cases, schools play an important role in the quality of life of an individual. For example, a child who receives much of their nutrition from a school meals program or a university student whose social life is centered around their school.Talent
Opportunities to identify and cultivate talents. For example, a student who discovers a passion for journalism after joining a school newspaper.Inspiration
At its best, education builds passion for learning, debate, cooperation, research, development and creative processes.Research
Learning to discover information, design research and conduct experiments to create new knowledge.
Lifelong Learning
Learning how to learn and acquiring a lifelong habit of curiosity, debate, research and discovery.Economic Opportunity
Education is a basis for professional competence, productivity and creative output. In an advanced economy, many jobs require extensive knowledge and experience. Education is a common way for individuals to increase their earnings prospects, job satisfaction and improve other aspects of their career such as working conditions.Counterarguments
The following arguments could be used to qualify or counter the position that education is important.