Social Norms
Perspectives and expectations that are adopted by a social group such as a society, culture or family. For example, the norm that you not wear shoes in the house in many cultures.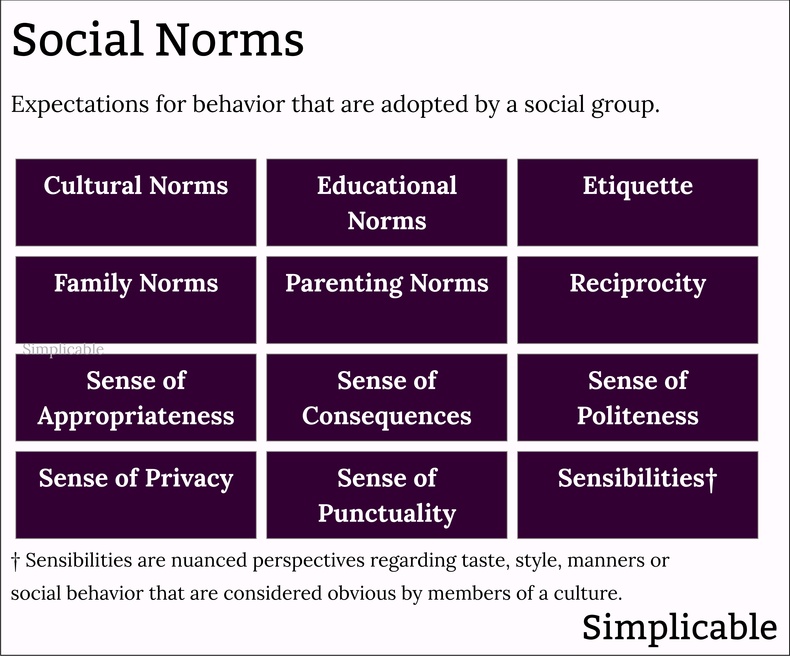
Ideologies
Ideologies are sets of ideas that offer a complete system and philosophy for organizing life. Many ideologies emerge naturally in societies while others, such as communism, have an academic origin.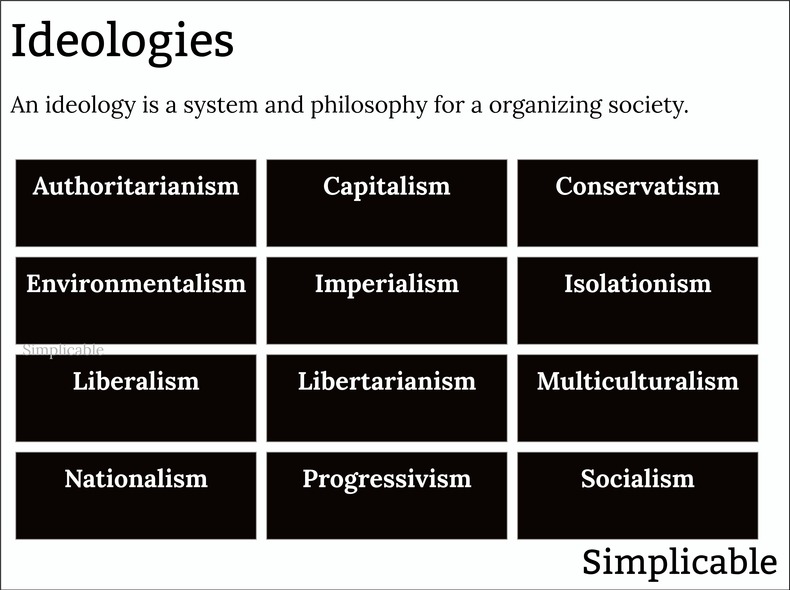
Traditional Attitudes
Attitudes that have been transmitted over generations to be sustained over time. These provide stability and a sense of continuation with the past.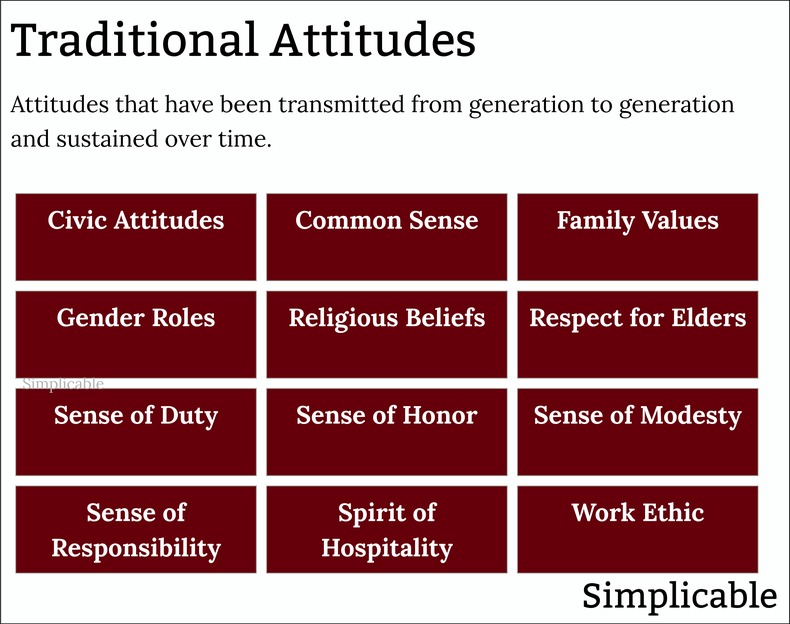
Modern Attitudes
Attitudes that originate or have grown into prominence in the modern-age. Technically speaking, the modern era begins as early as 1789 with the start of the French Revolution. However, when people discuss modern attitudes they are typically referring to post-WWII society and culture.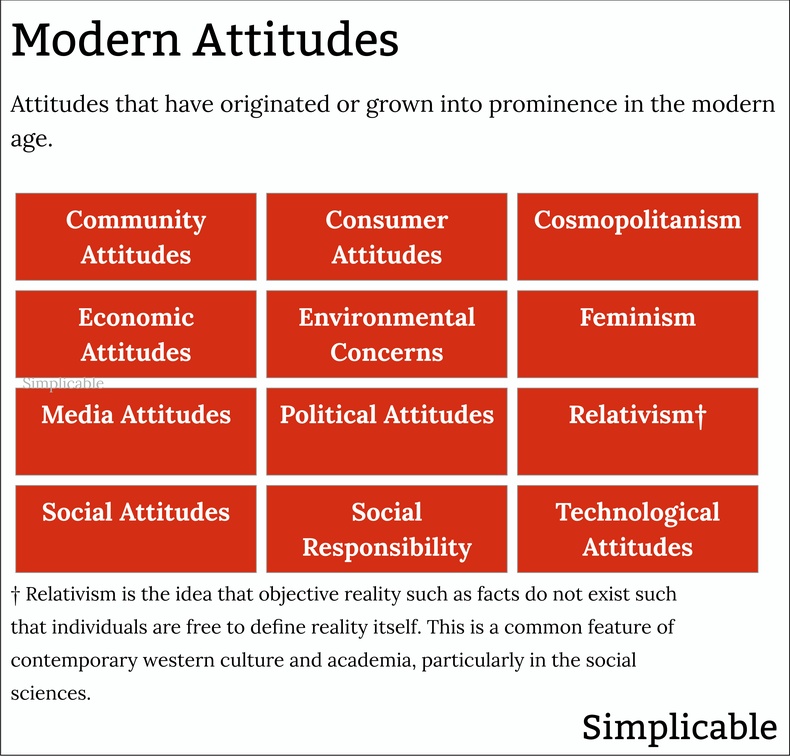
Worldview
Foundational ideas that answer questions such as what is the world and how should one live life. This includes fundamental views of society such as collectivism and individualism that are transmitted to individuals via institutions such as families and schools.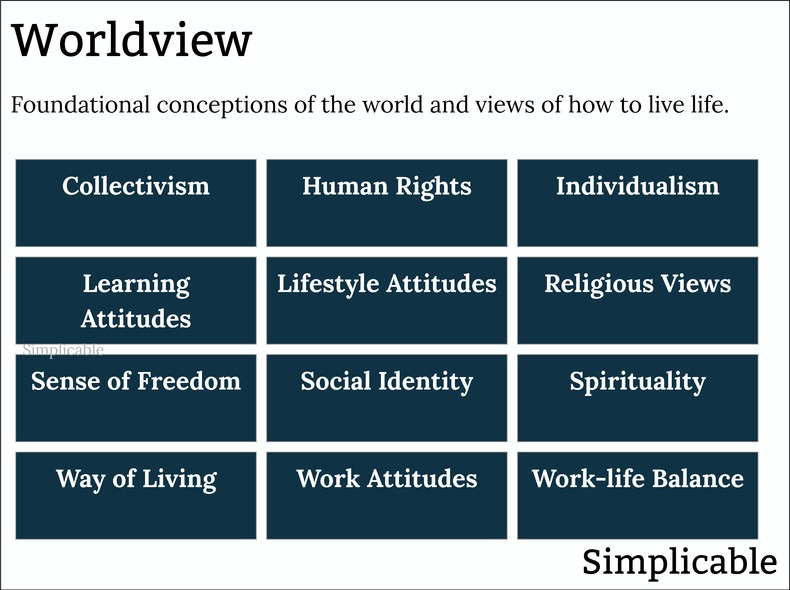
Values & Beliefs
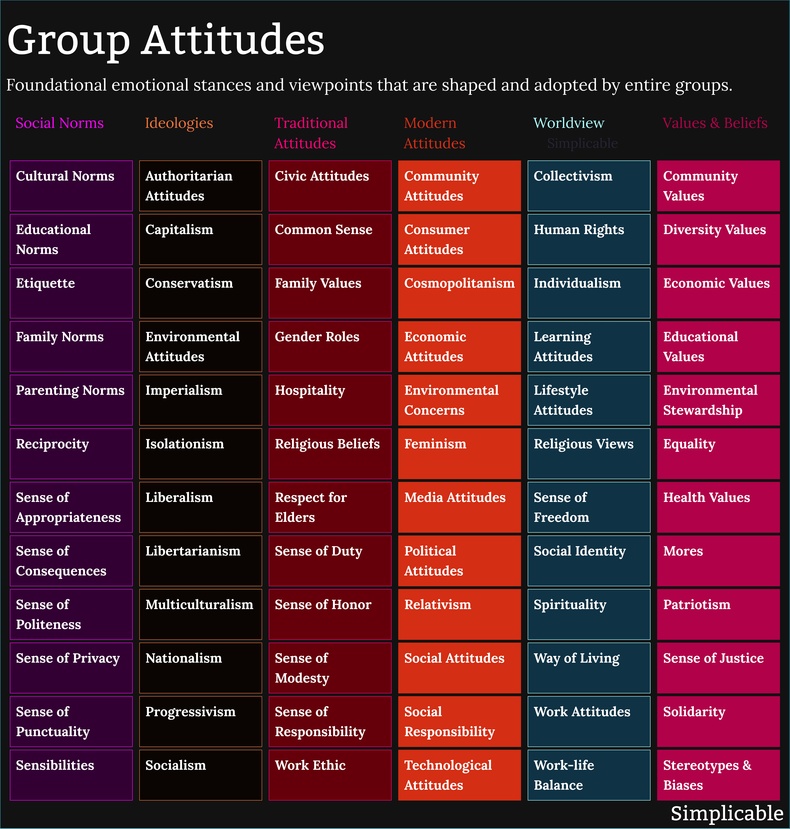
Group attitudes can include values and beliefs such as a sense of justice or environmental stewardship.
Influences on Group Attitudes
Group attitudes emerge in groups through a process of communication and shared experience. This can be influenced by ideas such as academic theories, change such as social change, pressures such as an economic crisis and group dynamics including the composition of the group and leaders that emerge in the group.Academic Theories | Communication Processes |
Conformity | Crisis Situations |
Cultural Change | Demographics |
Economic Change | Education Levels |
Emotional Bonds | Group Assumptions |
Group Cohesion | Group Dynamics |
Group Goals | Group Polarization |
Groupthink | Interpersonal Relationships |
Leaders | Media |
Peer Pressure | Physical Environment |
Political Climate | Political Processes |
Problems | Risks |
Role Models | Social Environment |
Social Identity | Social Pressure |
Socioeconomic Status | Technological Change |