Herd Behavior
The tendency for people to follow groups without thinking much. For example, a group that rush for the same exit in an emergency without realizing that other exits exist.Swarming
Swarming is the ability of groups to act in coordination without any apparent communication. In humans this is greatly influenced by culture. For example, crowds in Japan typically self-organize to walk on the left because people drive on the left in Japan such that it feels intuitive.Imitation
A tendency to look to others when you don't know what to do. For example, students in an art class who begin to copy each other after they fail to understand the directions provided by the instructor.Mirroring
Unintentionally mimicking the behavior of someone else. For example, subconsciously beginning to copy the accent of someone in conversation.Empathy
The ability to feel what you imagine someone else is feeling. For example, an audience that breaks into tears in a film.Moral Panic
An fear of a perceived moral decline that can drive excessive behavior by groups. For example, in the 1950s there was a moral panic in the United States about the influence of comic books on youth that sparked comic book burning events and a series of Senate hearings. This forced the comic book industry to form what was essentially a censorship board to avoid government regulation.Mass Hysteria
Outbreaks of mass illness that have no apparent cause such that they are assumed to be psychogenic (a product of the mind). For example, outbreaks of involuntary dancing known as Choreomania in Europe between the 14th and 17th century whereby groups of people would spontaneously dance until exhausted or injured.Madness of Crowds
The theory that people are willing to drop their values, principles and logic to follow a crowd resulting in terrible behavior by large groups.Groupthink
The spontaneous ability of groups to establish and enforce an ideology using social penalties for "wrong" thinking. This behavior can spread rapidly over a group whereby people become self-appointed enforcers of the groupthink.Collective Effervescence
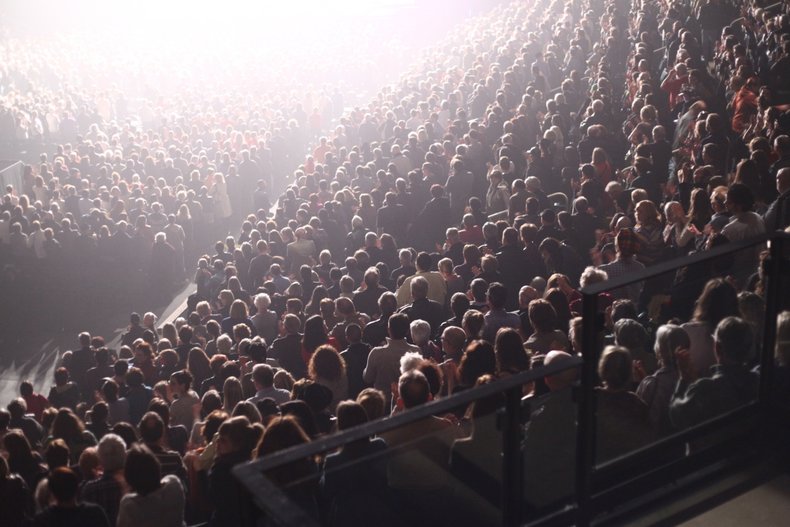
A feeling of elation and connectedness that can occur as a result of participating in group activities such as a concert. Groups are described as having a shared mood whereby an emotion spreads and is shared by a large number of individuals based on shared experience.| Overview: Social Contagion | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | The spontaneous spread of emotions, moods and behaviors through groups. | |
Definition (2) | The spontaneous spread of emotions, behaviors and ideas through groups. | |
Related Concepts | ||