|
| |
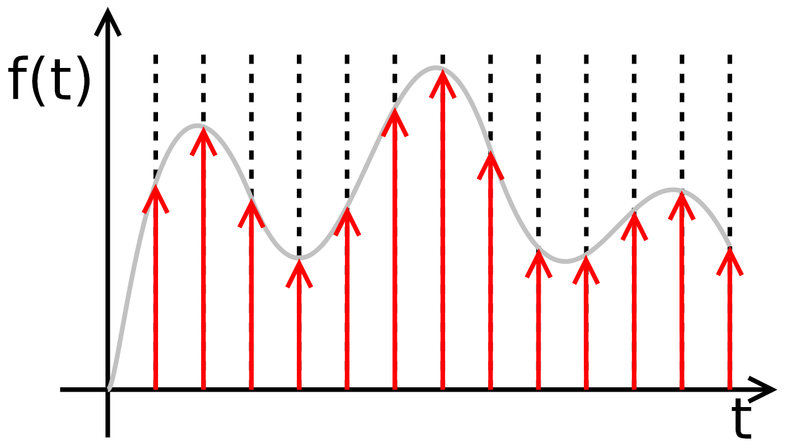
Analog is continuous information of very high precision that is often incorrectly described as "infinite." The universe is inherently analog. For example, sound waves and light waves are analog streams of information that can be measured at greater and greater precision that feels almost infinite. This can be contrasted with digital information used by machines that consists of sequences of 0s and 1s that have a finite and well-defined precision. The following are common examples of analog things.
Analog Amplifier | Analog Computer | Analog Data | Analog Electronic Circuit | Analog Synthesizer | Analog Television | Cameras (Film) | Cassette Tape | Clocks (with hands) | Dial (e.g. volume dial on a stereo) | Electromagnetic Waves | Headphones | Human Mind | Human Voice | Light & Color | Microphones | Musical Instruments | Natural Sounds | Photocopiers | Pinball Machine | Radio | Record Players | Sensors (e.g. gyroscope) | Sound | Speakers | Speedometer | Sundials | Thermometer | VCRs | Weight Scale |
Analog
This is the complete list of articles we have written about analog.
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|