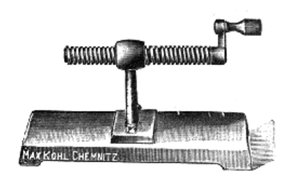
Simple Machine
A simple machine is one of six basic mechanical mechanisms that were identified by Renaissance scientists as being the basis for all machines. These are the lever, wheel & axle, pulley, inclined plane, wedge and screw. With the industrial revolution, machines evolved that used hundreds of new mechanisms.Tools
Devices that people use to perform work such as a hammer, saw or ruler.Vehicles
Machines that transport people or cargo including trains, ships, aircraft, cars, trucks and bicycles.Elevators
Equipment that provides vertical transport within a structure such as a building.Building Technology
Machines that are used to improve buildings such as an escalator or smart window. In many cases, building technology is passive such that it's not considered a machine. For example, sunlight transport systems that bring sunlight deep into the interior of a building without using any power.Home Automation
Machines for home automation such as an automated well pump or a self-cleaning swimming pool.Appliances
Machines that are used in the home for common household tasks such as cooking and cleaning.HVAC
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning, or HVAC, is a category of machines that provide a suitable temperature and air quality for homes and buildings.Construction Equipment
Equipment that is used to construct buildings and other built environments such as an bulldozer, crane, dump truck or excavator.Heavy Machines
Machines that are literally heavy. This includes machines for mining, manufacturing, construction, agriculture, forestry, energy production, waste management, transportation infrastructure and heavy industry. For example, a trash compactor or tunnel boring machine.Computers
Machines that process data.Memory & Storage
Machines that store data. Memory provides fast access to data for computers. Other data storage devices such as solid-state drives provide large, non-volatile storage that is slower than memory.Sensors
Sensors are devices that record the state of the physical world such as a digital camera or an altimeter on an aircraft.Instruments
An intricate tool or data display device. For example, instruments that are used for science, engineering, process control in a factory or by pilots in the cockpit of an aircraft.Clock
Instruments used to measure, keep and indicate time. Essential to a wide variety of machines, including all computers.Robots
Robots are a class of machines that can respond to their environment in a semi-autonomous or autonomous fashion. For example, a vacuum cleaner that stops when it encounters people, pets and obstacles and figures out what to do.Microbotics
Small robots with dimensions less than 1 millimeter or 0.04 inches. These have potential to be used as swarms that may be capable of both intricate and large scale work. As such, microbots could transform the global economy. They may represent a threat to the environment and quality of life but may also be able to clean up large problems such as microplastics.Nanorobotics
Small robots around the size of a nanometer or 0.00000004 inches. These are small enough to do extremely intricate work such as repairing small parts inside a computer or targeting drug delivery to cancer cells.Self-Replicating Machine
A machine that can build itself. This may have applications whereby robots build many copies of themselves and then construct large scale things such as solar energy infrastructure in space.Factory Automation
A class of tools that can fully automate steps in a production process. For example, an industrial robot that can assemble components from parts.Machine Tools
Machine tools are machines for making other machines. For example, tools for cutting, boring, grinding and deforming various materials such as metal.Farm Machinery
Machines that improve the productivity of farmers such as tractors, combine harvesters and plows.Energy Infrastructure
Energy infrastructure such as a wind turbines, solar panels or transformers in an electrical grid.Space Infrastructure
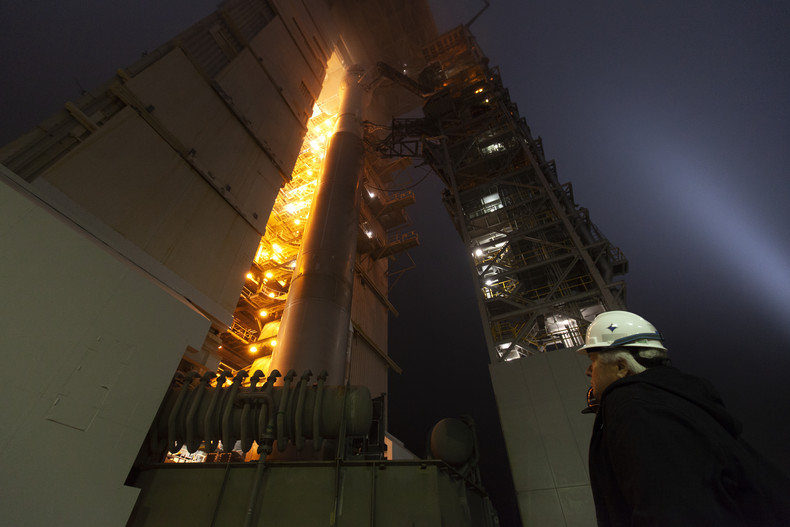
Spacecraft and machines in space such as satellites.Science Infrastructure
Large scale scientific equipment such as a particle collider.Communication Infrastructure
Communication infrastructure such as the optical transmitters and receivers that are used in fiber optic networks.Fixtures
Equipment that is installed in a fixed position in a building. For example, toilets and lighting.Media
Machines that capture, transmit or reproduce media such as a microphone, camera, audio speakers or television.Printers
Devices that produce a physical representation of digital information such a digital photograph printed on paper or a 3d model printed with a plastic or metal material.Medical
Medical equipment and devices such as a defibrillator or pacemaker.Entertainment
Machines for entertainment such as a roller coaster.Types
The following are common types of machines.
Summary
Machines are an assemblage of parts and components that work together to perform a function.
| Overview: Machines | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A physical device that actively performs work by using power. | |
Related Concepts | ||