Economic Goods
Goods are anything that have value to society. Free riding can decrease incentives to create goods. This essentially represents a missed opportunity to improve things. For example, if a company invests in research to develop a new medicine and then that medicine is instantly copied by a free riding competitor that decreases incentives for other firms to develop new medicines. Economic systems are typically designed to prevent free riding of this type to give healthy incentives to firms and individuals to create value. For example, patent rights that give a firm exclusive rights to a novel invention for a period of time.Economic Bads
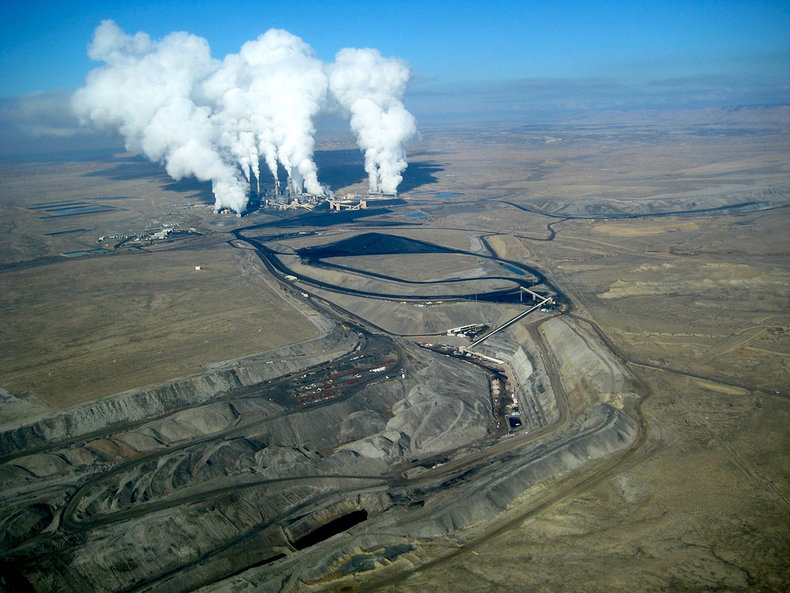
An economic bad is a product of economic activity that makes life worse instead of better. In many cases, a firm or individual pays zero cost for creating economic bads such as pollution and are therefore free riding at the cost of everyone else.Public Goods
Public goods are high capacity resources that everyone can freely use such as the atmosphere, an ocean or a beach. These suffer from massive free riding as firms and individuals have incentive to use them aggressively but have little individual incentive not to destroy them. For example, going to the beach benefits you and leaving your garbage there doesn't hurt you very much absent of regulations, social pressure or personal values.Society
Individuals benefit from a democratic system with voting but may not have incentive to personally vote themselves as they are unlikely to affect results.Organizations
A member of a prestigious institution may benefit from the organization's reputation but may have little incentive to contribute to that reputation in a positive way.Principle-Agent
An agent is someone who acts on behalf of others, known as principles. Examples of principle-agent combinations include citizen-politician, citizen-bureaucrat and shareholder-employee. In many cases, spending by an organization benefits agents but principles pay the bills. For example, a politician who gives lucrative government contracts to friends that are paid for by the taxpayer. If principles have no tools to govern the spending of agents, this can create a great deal of waste. This cost is known as an agency cost.Government
Government is the primary way to solve free riding problems. They create systems that give incentives for creating economic goods and disincentives for creating economic bads. Governments can also pool resources to create public goods such as infrastructure, schools, hospitals and green spaces that benefit an entire society.Notes
The main problem with free riding is not that it is "unfair" but that it leads to a breakdown in rational economic decision making and efficiency such that everyone is worse off.| Overview: Free Riding | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | A situation where an individual or organization benefits from something without incurring any cost. | |
Definition (2) | A situation where everyone benefits from something but no single firm or individual has sufficient incentives to make it happen. | |
Not To Be Confused With | Freeriding (investing) | |
Related Concepts | ||