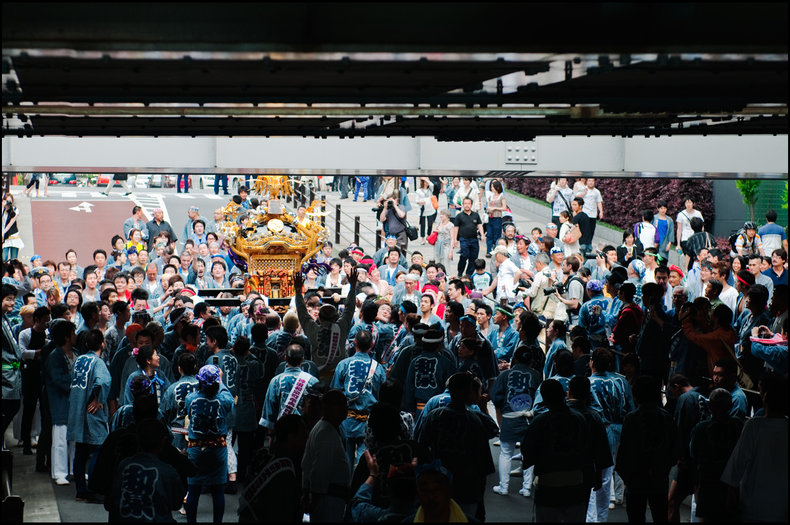
Civilization
A civilization is a group of societies that are highly interconnected such that they greatly influence each other. Historically, civilizations were regional. Now it is more accurate to say that civilization exists at the planetary level as most nations are highly connected to all others. For example, transport and communication systems connect all nations.
Nations
Nations are societies that hold territory with a formal government that enjoys sovereignty. These are primary social systems that greatly govern or influence all other social systems.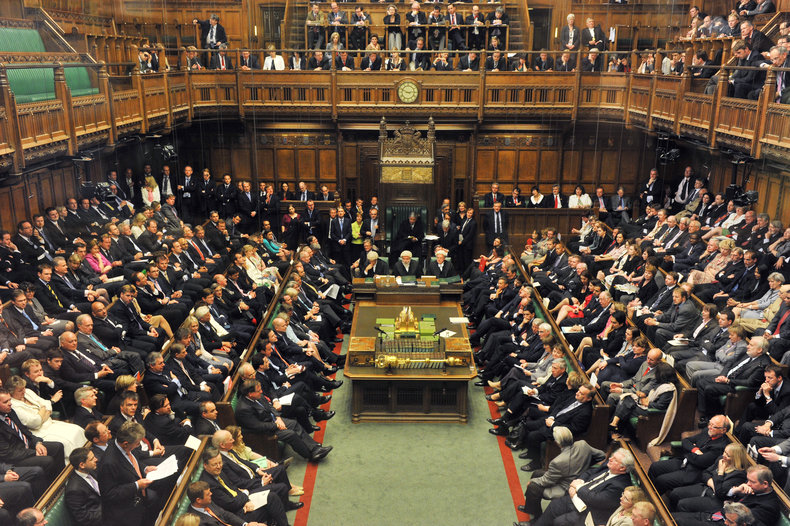
Intergovernmental Organization
An intergovernmental organization is an entity created by multiple nations. These typically implement international laws and agreements. Intergovernmental organizations may also have a global mission in areas such as human development or may act as a venue for diplomacy. In some cases, intergovernmental organizations implement political unions that resemble governments.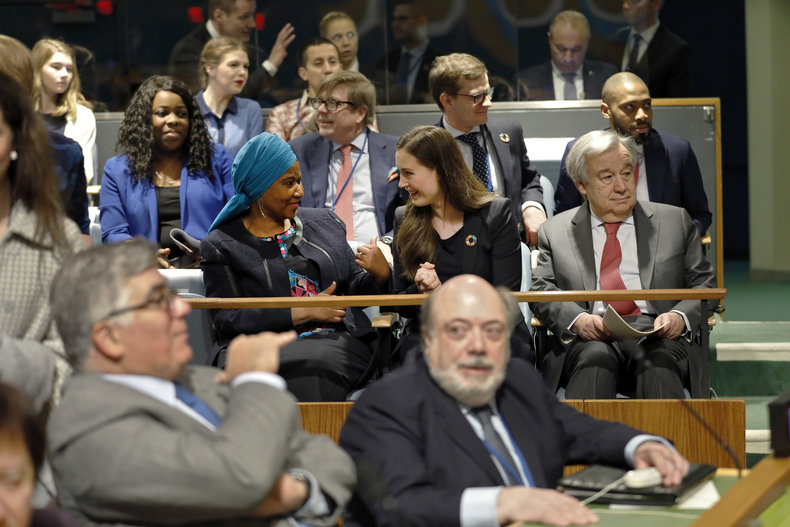
Institutions
Institutions are complex and durable elements of a society such as a university, school, religion or court system.
Family
Families are an important type of institution that provide each other with support, shared experience and belonging. Families are also economic units that may pool resources and start businesses.
Economic Systems
Systems that produce and distribute value by putting capital to work. The vast majority of economic value ever created by humans has been produced by capitalist markets driven by economic freedoms and protection of fair competition.
Organizations
Structured and organized groups that work towards some purpose such as a business or charity. In a democracy, anyone can found an organization to pursue some mission.
Cities
Cities are places where many people live. These are organized with a local government that may enjoy some degree of independence from national and regional government.
Hard Infrastructure
Infrastructure is a foundational service that is a basis for economic efficiency and quality of life. Hard infrastructure is physical infrastructure that you can reach out and touch such as a railway, road or canal.
IT Infrastructure
Foundational IT services, particularly the networks that connect to form the internet including mobile networks. Generally speaking, IT systems are the most complex systems made by humans such that they may approach the complexity of natural systems such as the human brain.
Soft Infrastructure
Soft infrastructure refers to infrastructure that produces mostly intangible value such as a hospital or school.
Media
Media is a means of communication. Historically, this was broadcast media with concentrated ownership such as television networks or newspaper empires. The internet has allowed anyone to publish information to the world using platforms such as blogs or social media.
Self-Organizing Systems
If you put any 20 people in a room together they will begin to form a social hierarchy and culture. In other words, humans spontaneously build systems to meet their needs. This can be seen in protest movements that can quickly develop to challenge dominant systems such as a government, firm or education system.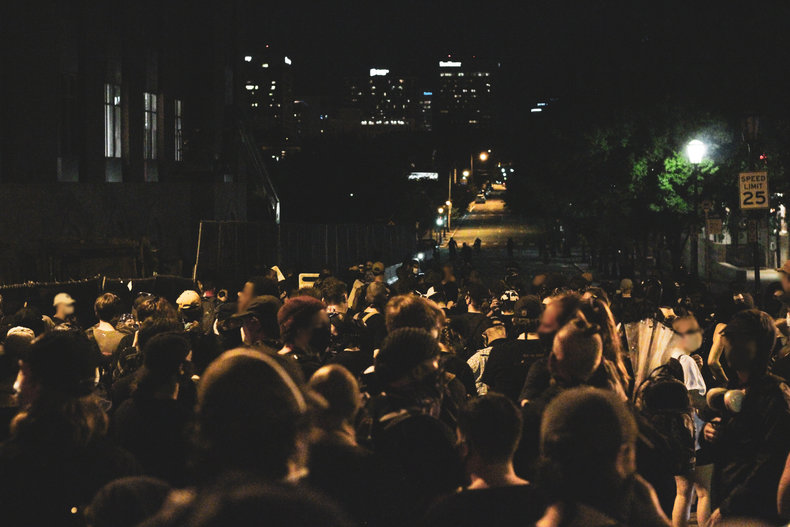
Political Systems
A system for deciding what to do as a group. This involves elements such as leadership, communication, debate and voting. Political systems often produce suboptimal strategy and decisions. However, optimal strategy isn't the only goal of politics as they must also create civility whereby people agree to work within the system to resolve differences. This can include elements of creative tension such as protests.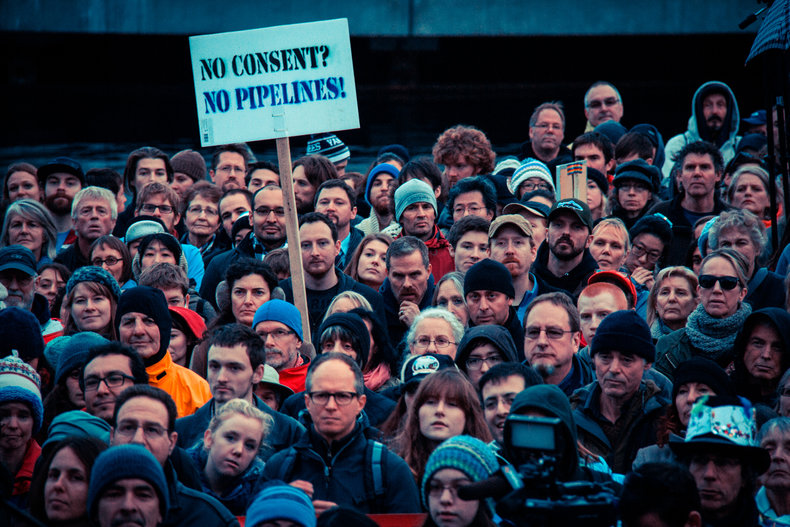
Bureaucracy
Political decision makers typically delegate policy implementation and the day-to-day operation of things to experts in appropriate areas. This is known as a bureaucracy or technocracy. For example, an urban planning department that sets building standards that don't interest politicians. Much of the detailed strategy and decision making in a society or organization is done by various bureaucracies.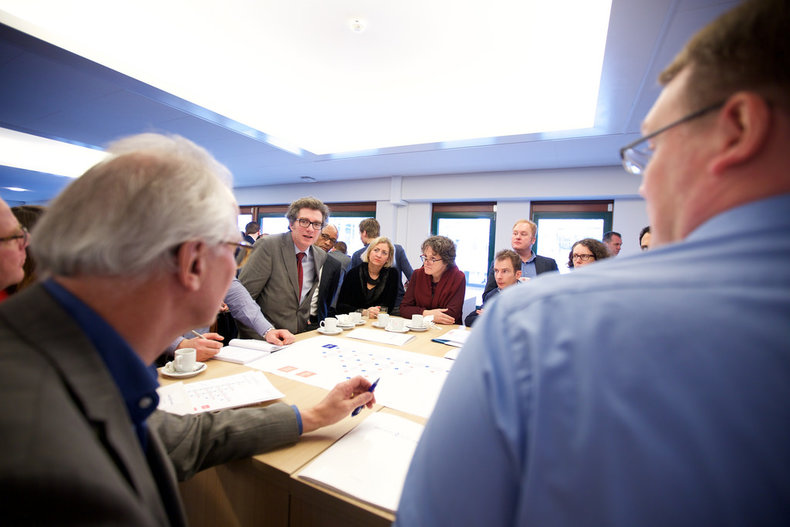
Controlled Systems
Systems can be centrally controlled, often using technology. For example, a nation that controls its airspace to make air travel safer. Other examples of controls include laws, rules, regulations, procedures, monitoring, validation, automation and the use of force such as a police or military organization.
Designed Systems
Systems can be centrally designed, often by a bureaucracy, whereby the people doing the planning are trained to do so. For example, a city plan that lays out an orderly transportation system.
Emergent Systems
Systems can emerge with the individual decisions of a large number of people such as a city with no central design that emerges each time somebody builds a house or makes an agreement with a neighbor to produce some shared infrastructure.
Culture
Culture is any social system that emerges with the shared experience of groups. This often comes into conflict with designed and controlled social systems that are implemented by political or bureaucratic processes. Generally speaking, culture represents human expression such as freedom, joy, play, art and music while controlled systems represent more basic goals such as safety, security and economic production.
| Overview: Social Systems | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Complex interconnected entities that organize the life of human populations. | |
Related Concepts | ||