Agricultural Practices & Products | Animal Husbandry |
Architecture | Art |
Beverages | Botany |
Building Materials | Burial Practices |
Clothing & Fashion | Color Schemes |
Community Planning (e.g. traditional types of streets or neighborhood) | Concepts |
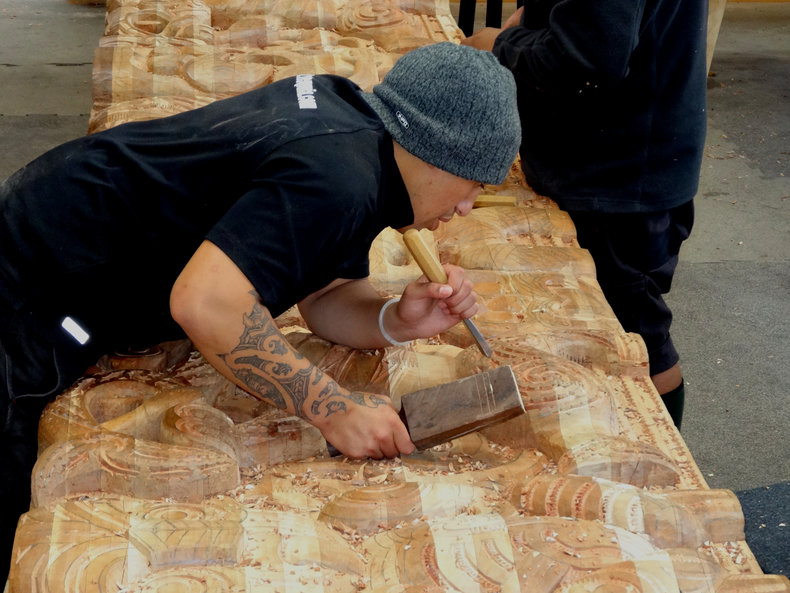
Construction Materials / Methods | Crafts |
Crops | Dances |
Economic Systems | Education & Learning |
Environmental Management | Estimates & Predictions |
Fabrics | Family Practices |
Festivals | Folklore |
Food Processing & Preservation | Foods |
Foraging | Forestry |
Furniture | Gardening |
Household Management | Housewares |
Human-Environment Relations | Hunting & Fishing |
Jewelry | Knowledge of Nature / Animals / Ecosystems |
Land Management | Landscaping |
Language | Legends |
Markets | Music |
Myths | Navigation |
Parenting Practices | Performance Art |
Philosophy | Production Methods |
Products | Repairs & Maintenance |
Resilience Practices | Reuse |
Risk Management | Rites of Passage |
Service Practices | Services |
Social Structures | Social Systems |
Spirituality | Sports & Games |
Stories | Tools |
Toys | Traditional Diets |
Traditional Medicine | Traditional Rights |
Transportation Methods | Values & Ethics |
Visual Designs | Visual Symbols |
Water Management | Writing & Communication |
Traditional Knowledge vs Traditional Cultural Practices
In the narrowest sense, traditional knowledge relates to practical concerns such as production of goods and promotion of health. According to this view, traditional knowledge related to cultural life is in a separate category known as traditional cultural practices. These are important to the identity, experience or spirituality of a culture. In practice, traditional knowledge and traditional cultural practices overlap in countless ways. For example, an art or craft may encompass much practical know-how that is important to economic production but is also clearly a cultural expression and practice.Discussion
Traditional knowledge is relevant to intellectual property whereby firms, organizations, governments or individuals may attempt to seize the rights to culture, practices and inventions that have long existed. For example, a fashion brand that attempts to trademark terms related to traditional clothing, an entertainment company that copyrights a traditional story or a biotechnology company that uses its intellectual property in ways that interfere with traditional agricultural practices.| Overview: Traditional Knowledge | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | Know-how, concepts, practices and inventions that are developed by a culture or community and passed from generation to generation. | |
Definition (2) | Knowledge and cultural practices that have been sustained by a culture or community for at least 3 generations, or about 100 years. | |
Related Concepts | ||